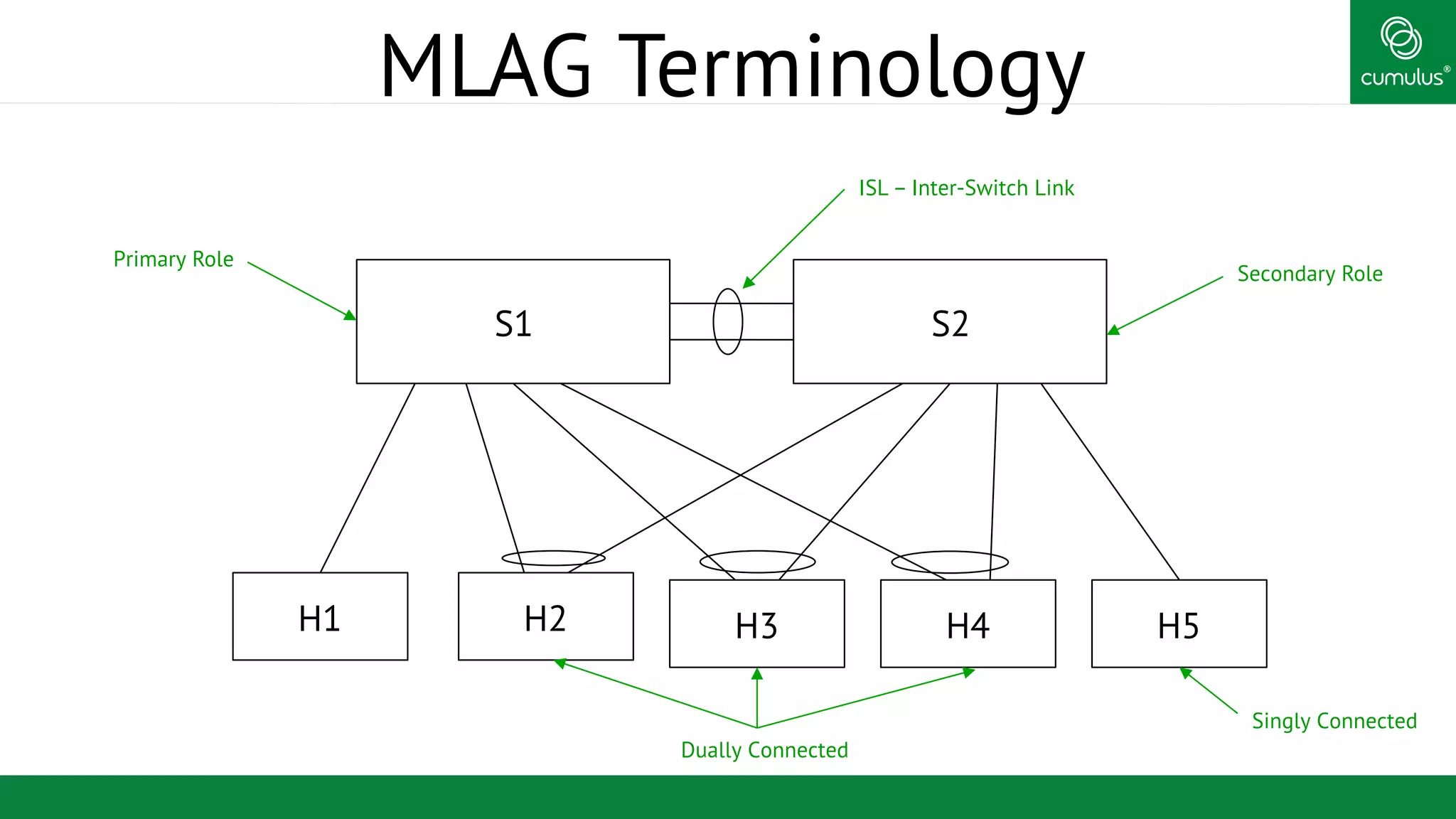
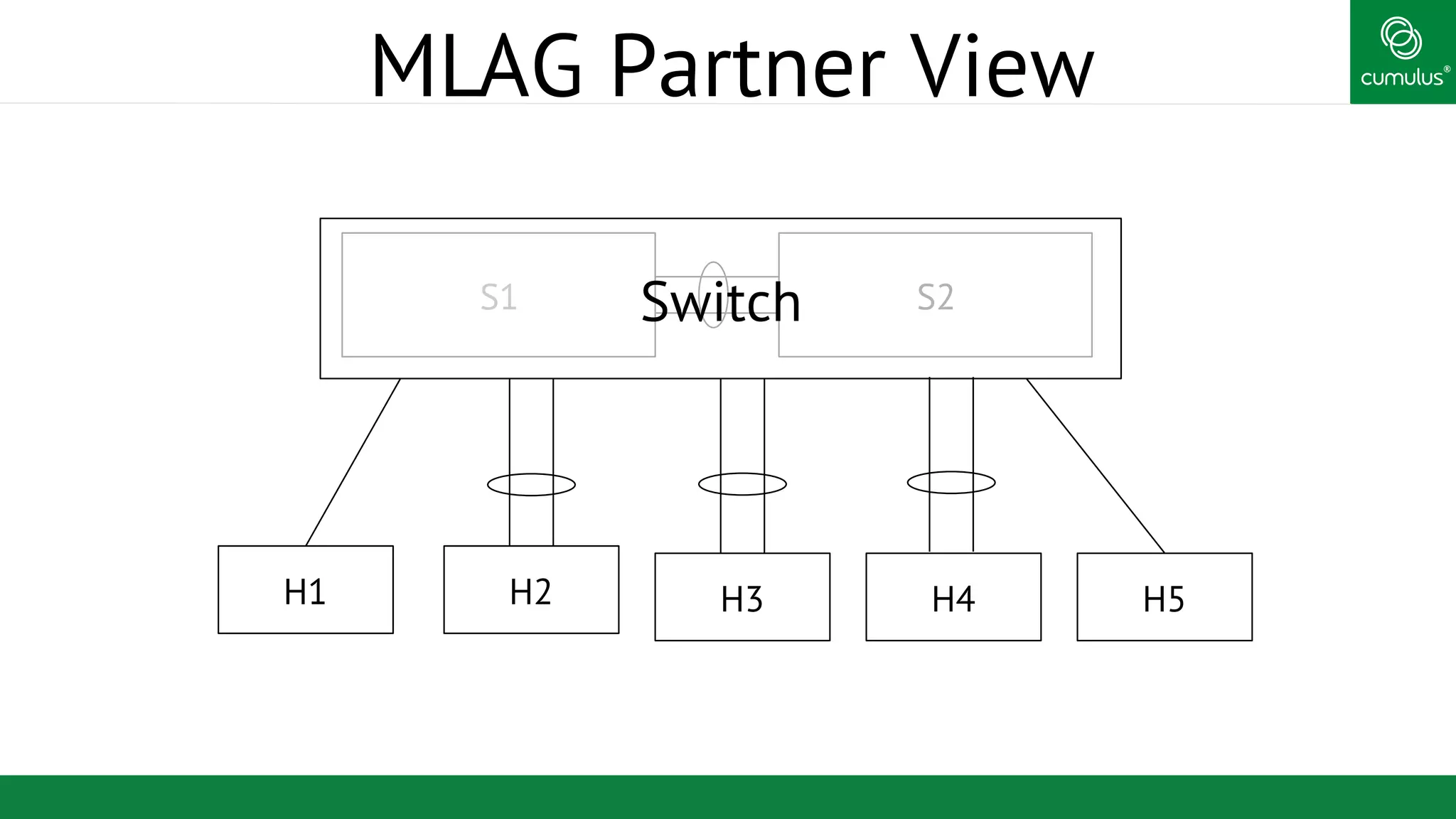
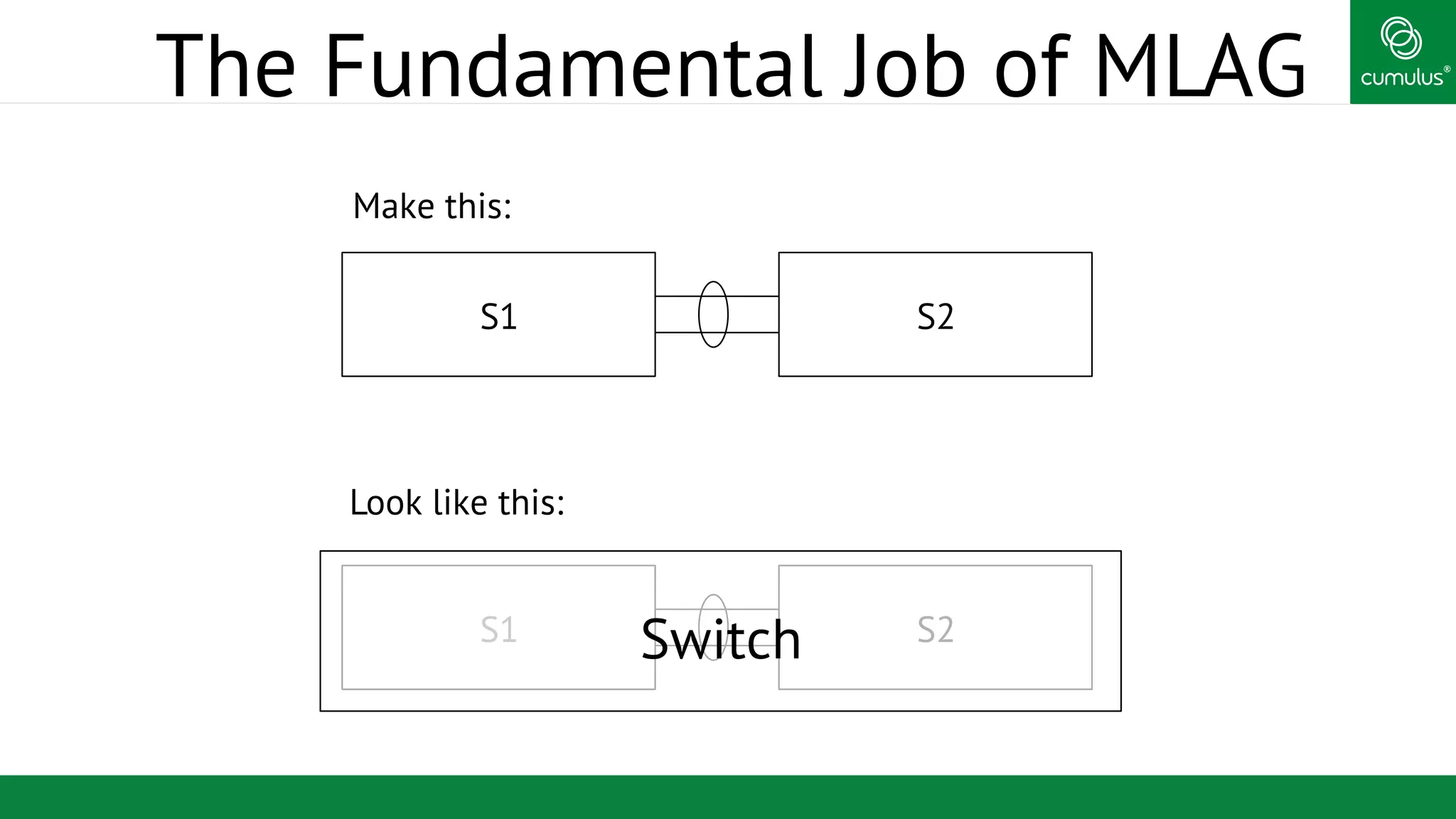
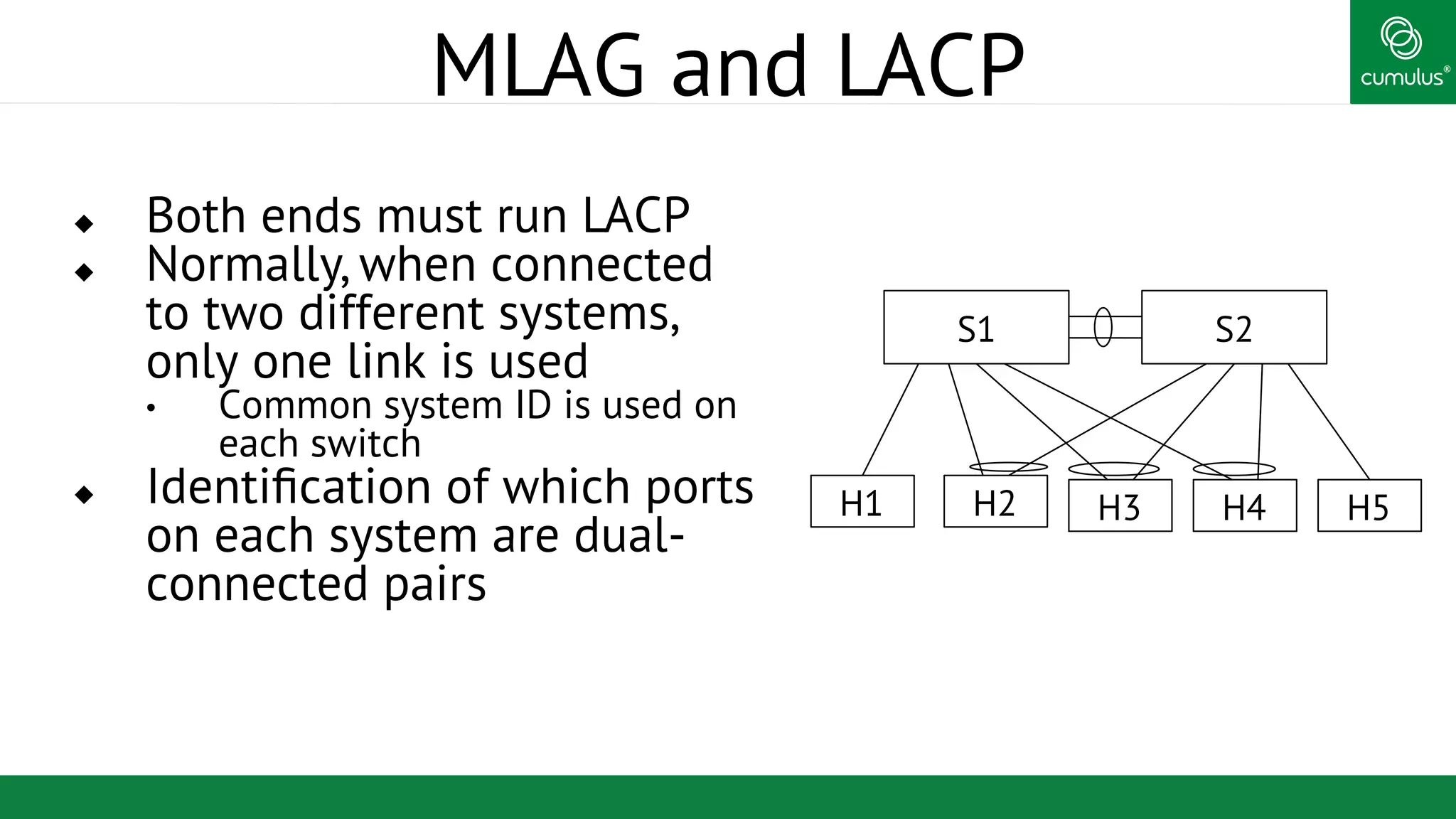
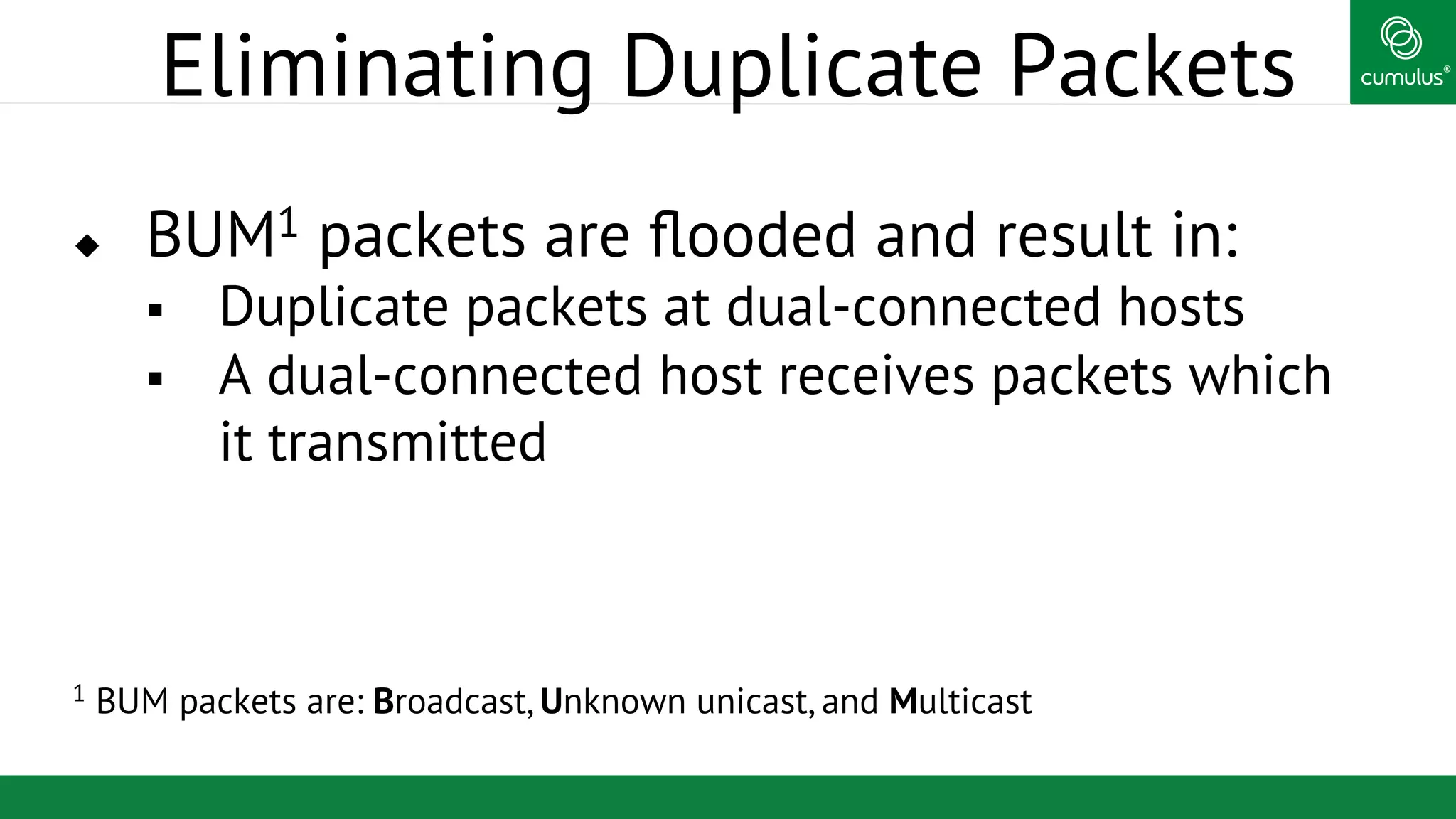
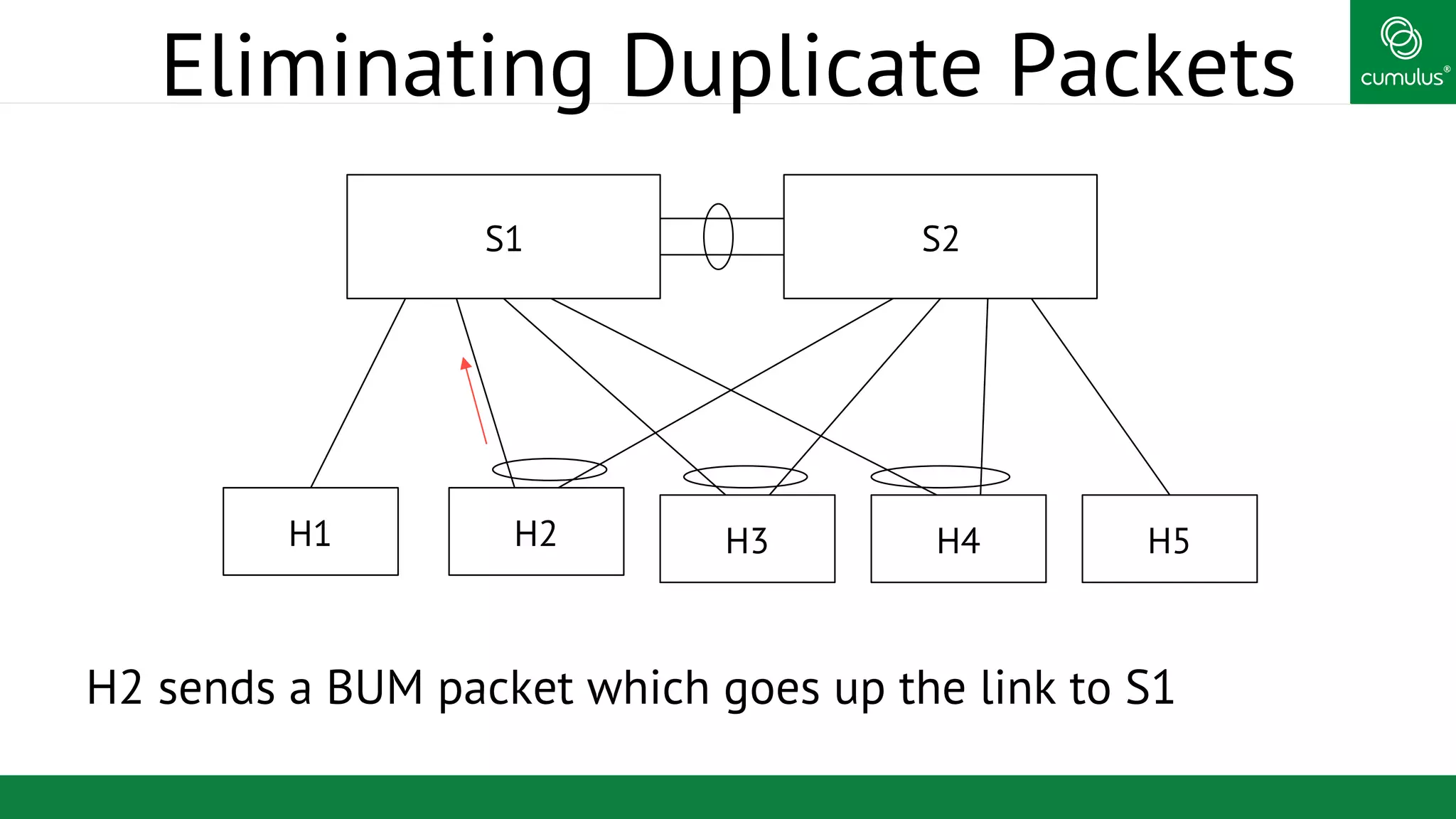
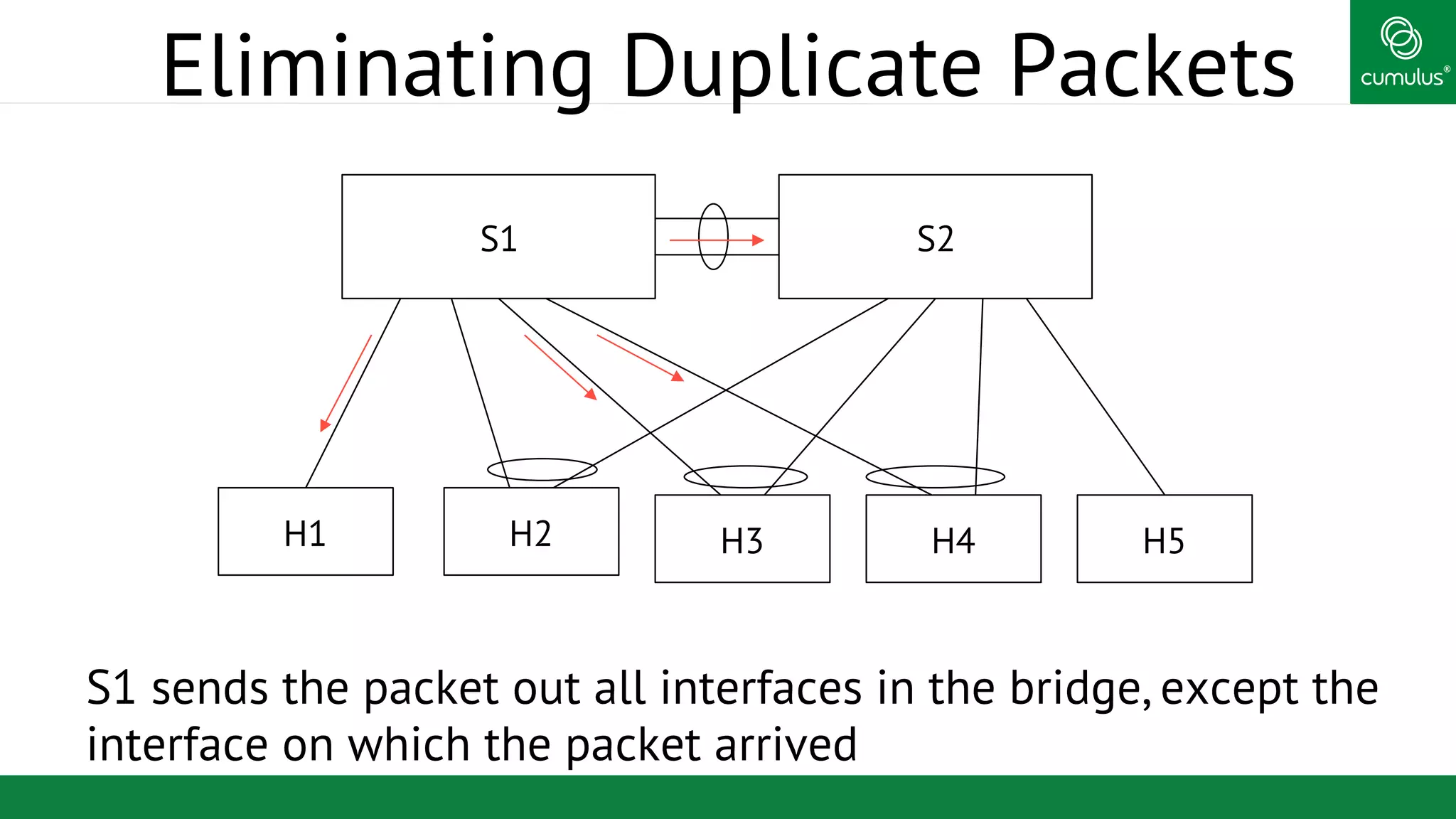
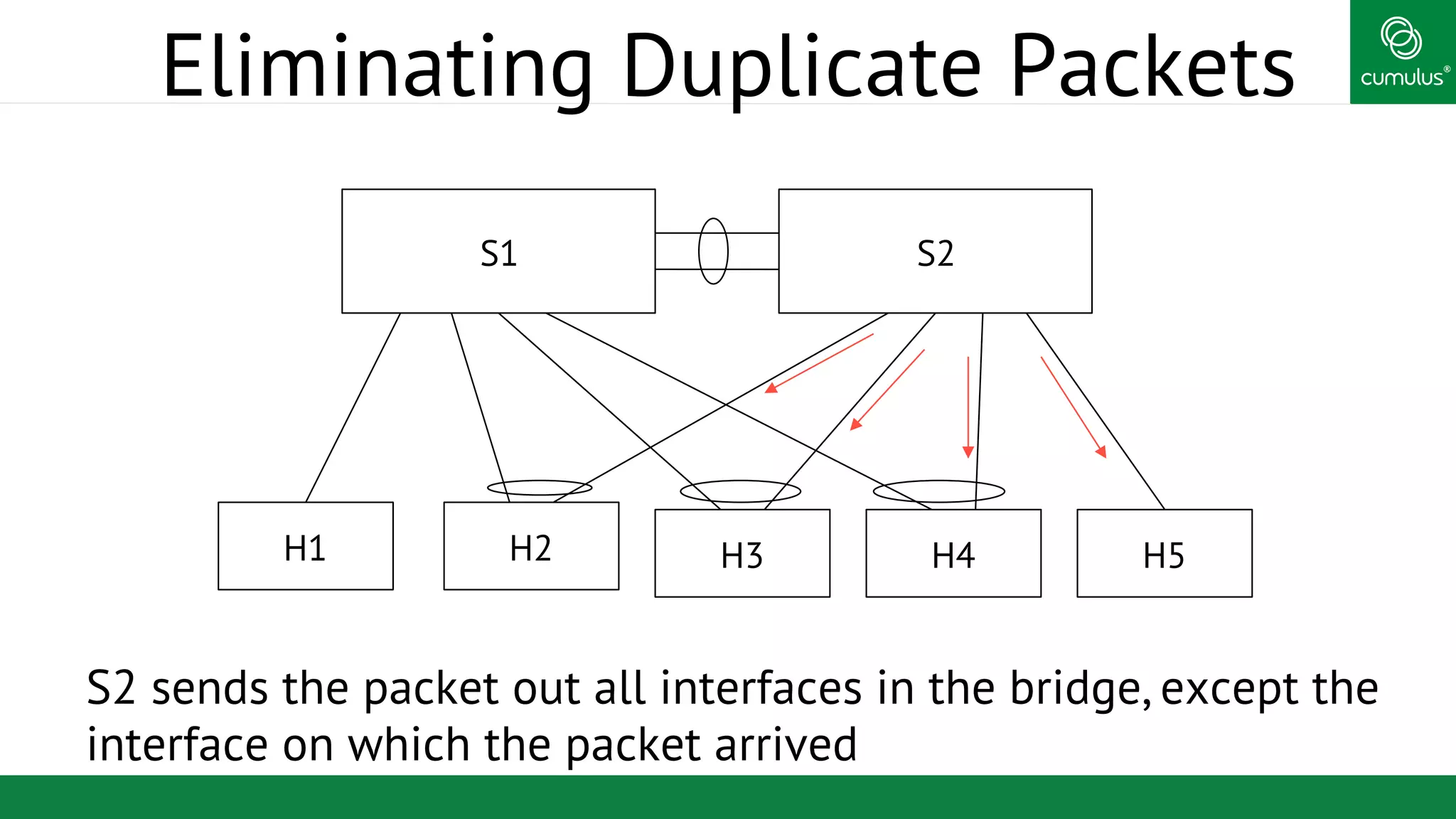
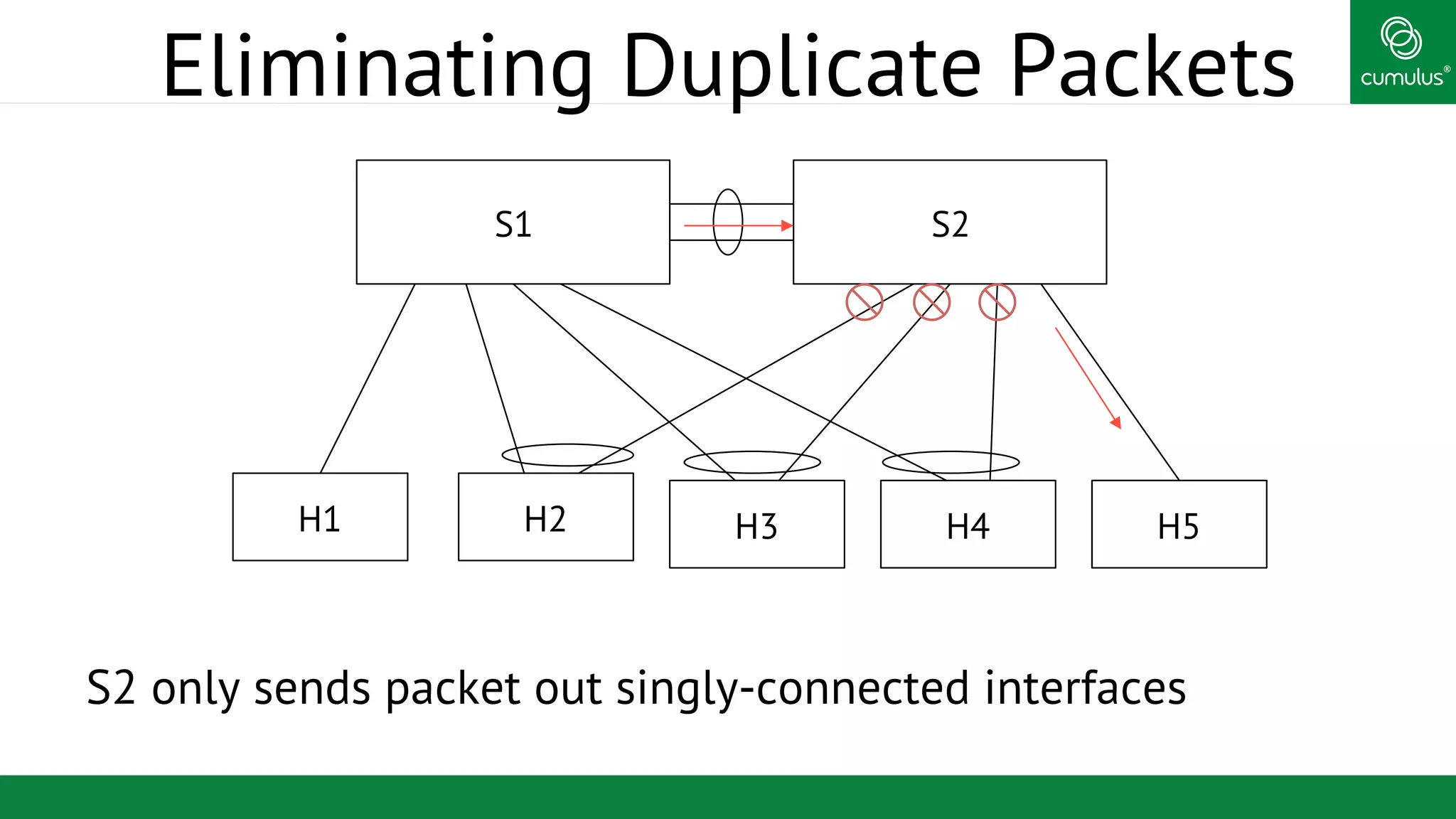
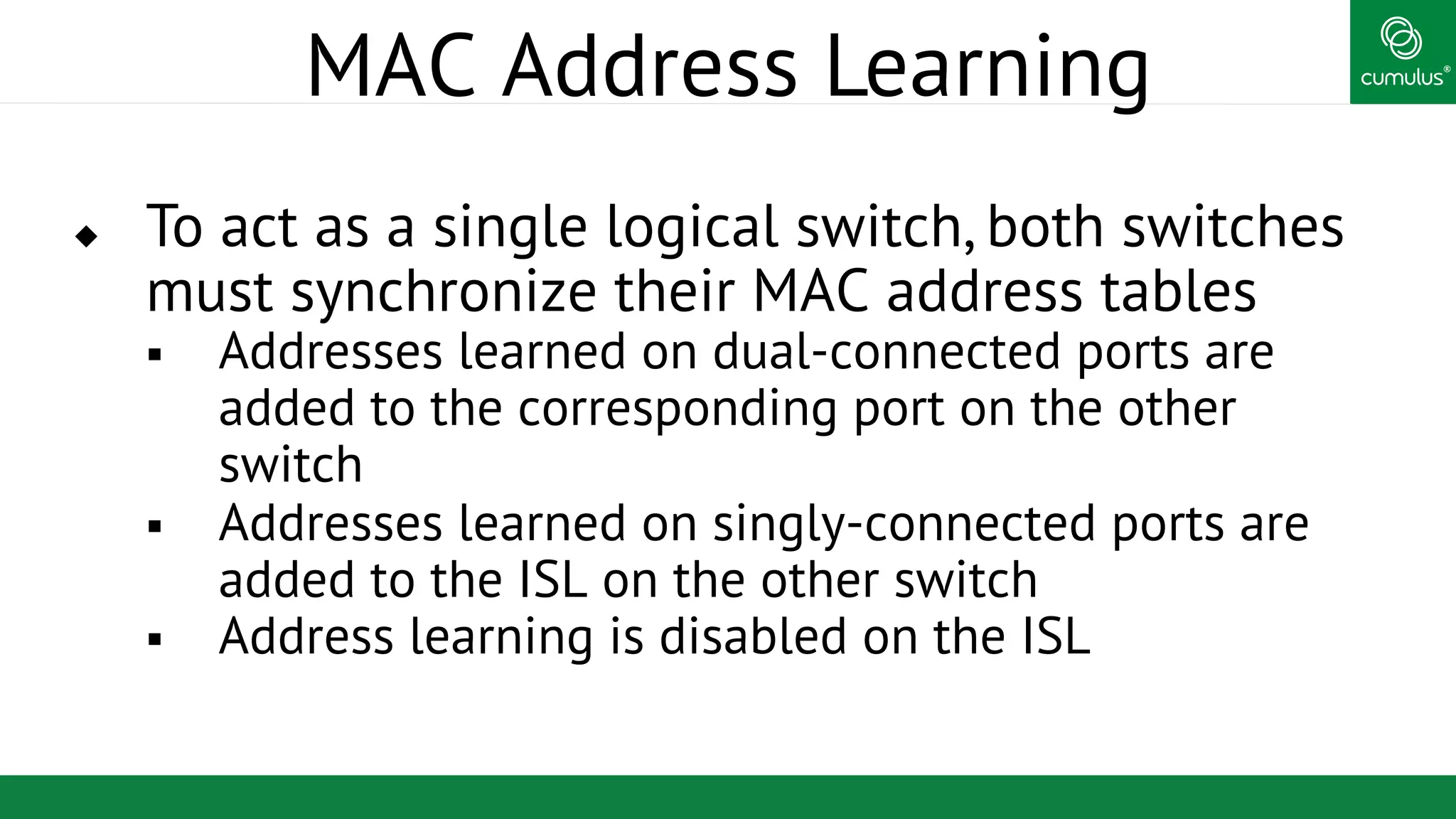
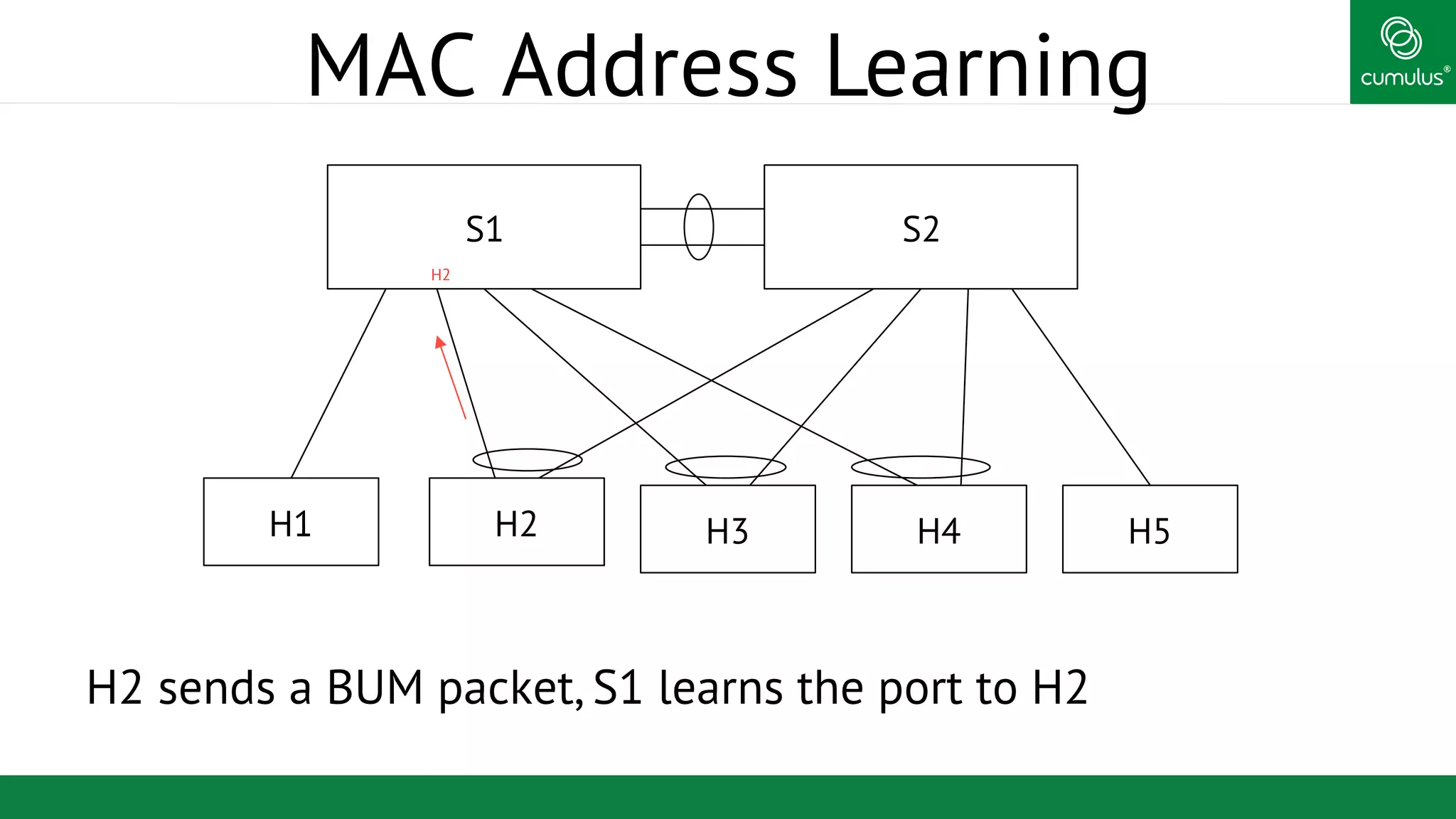
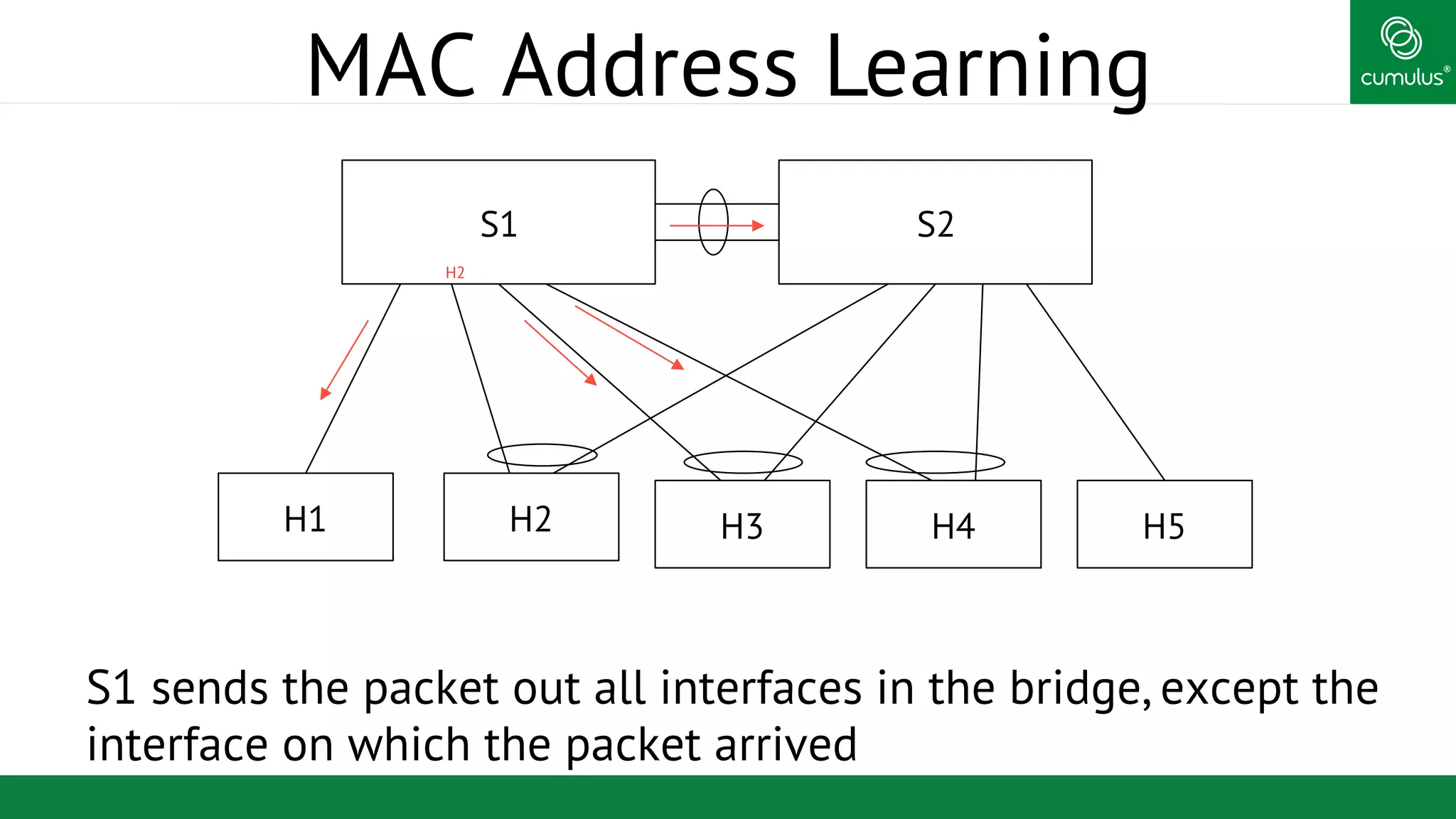
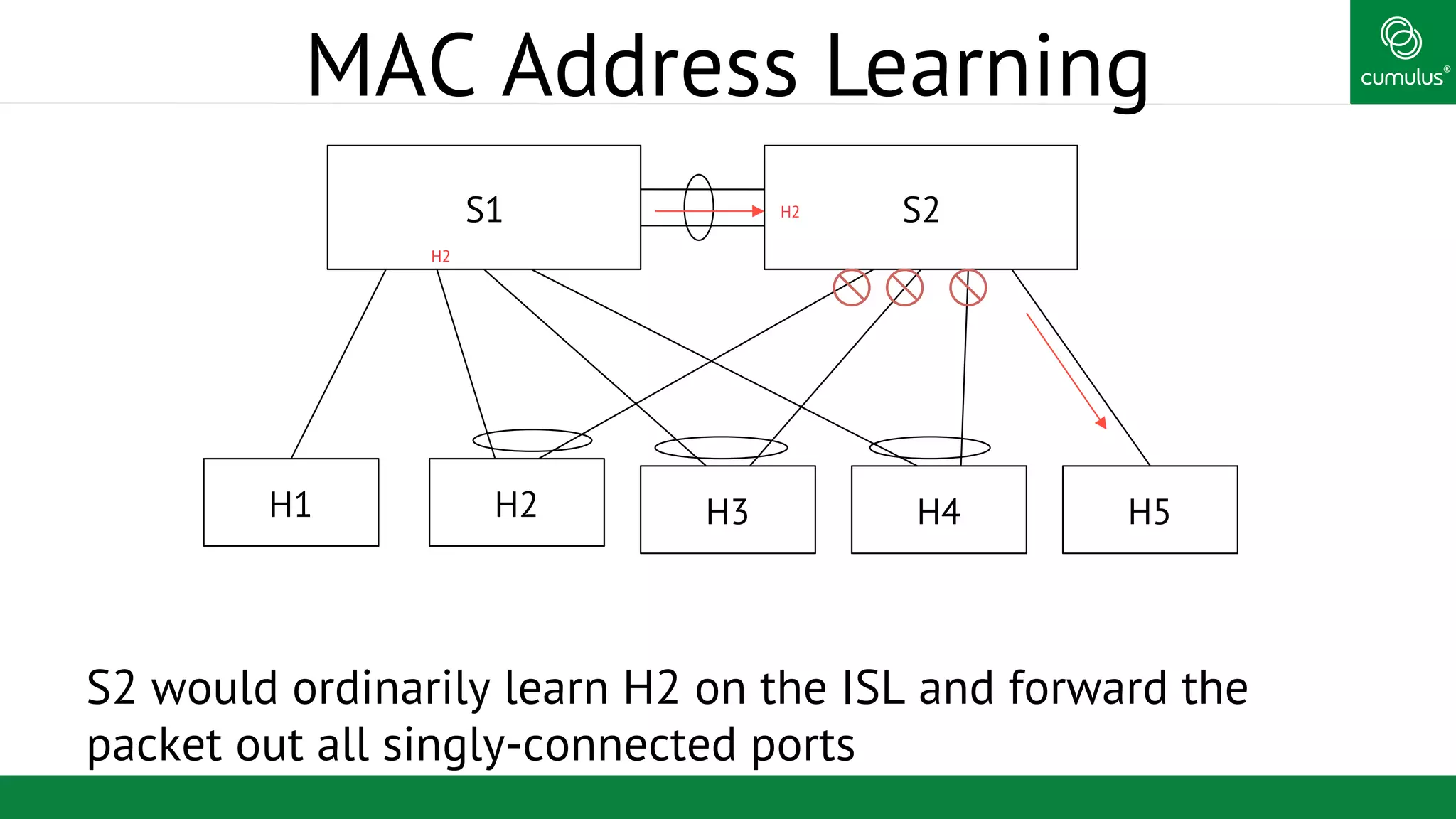
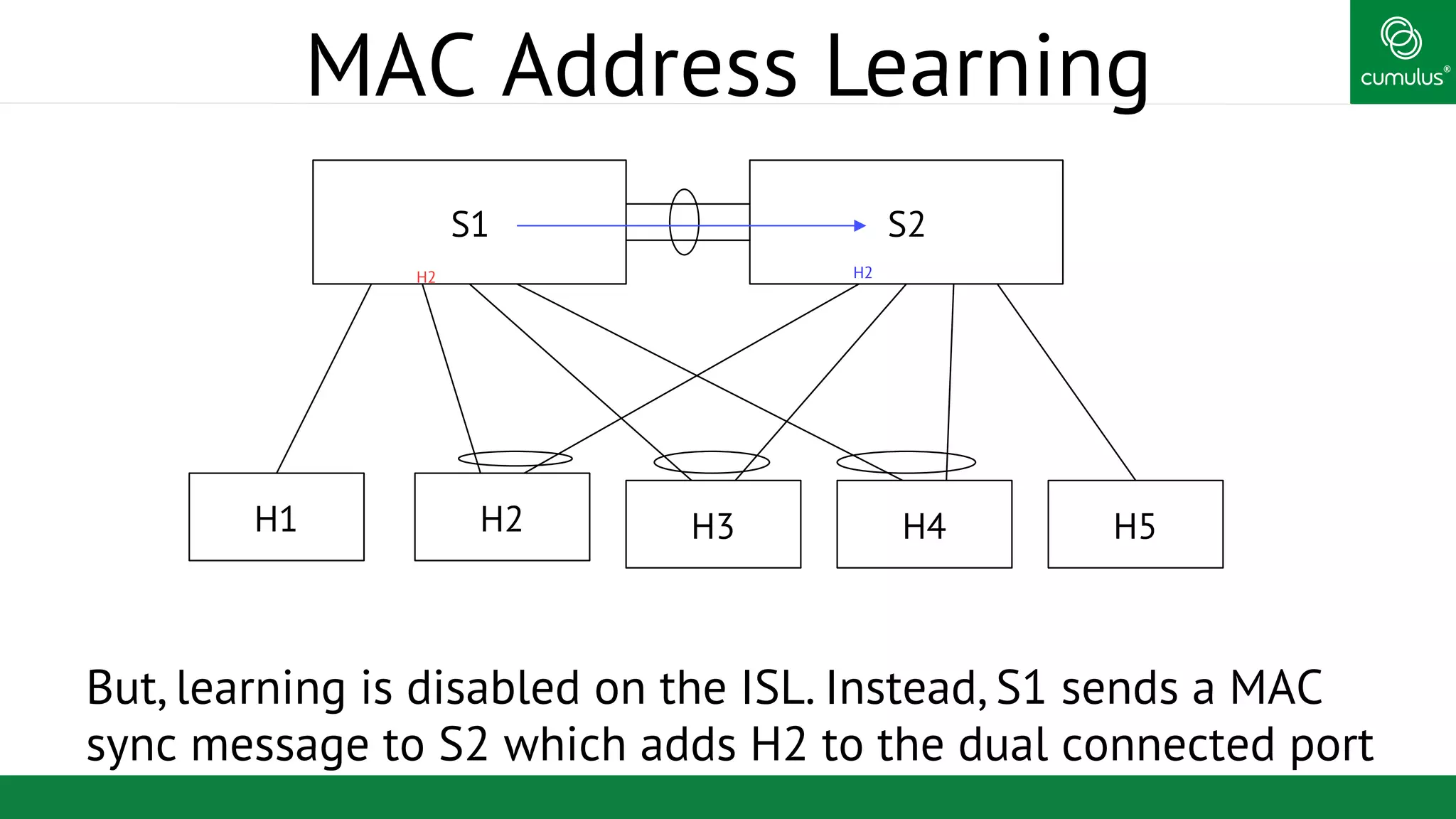
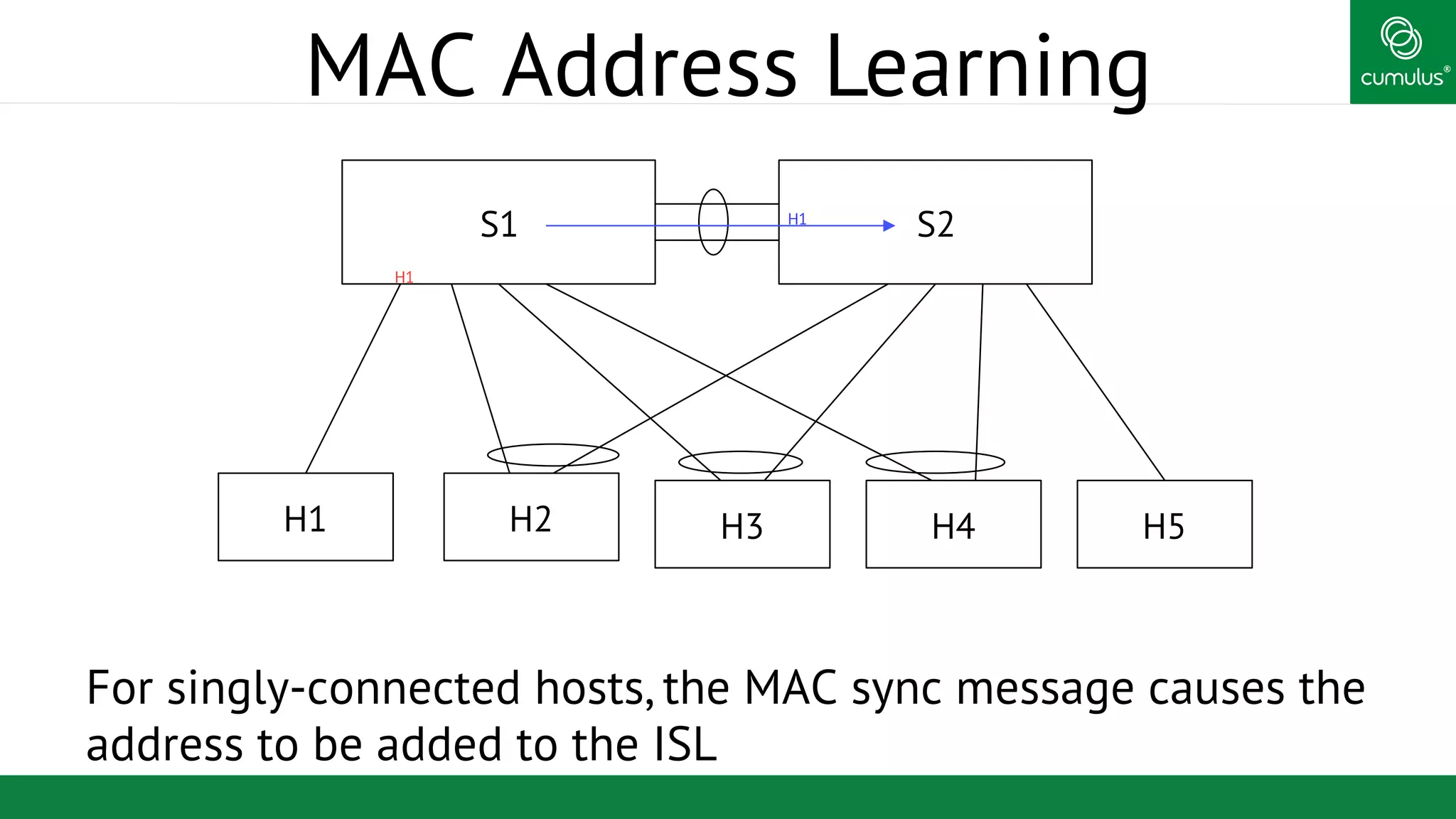
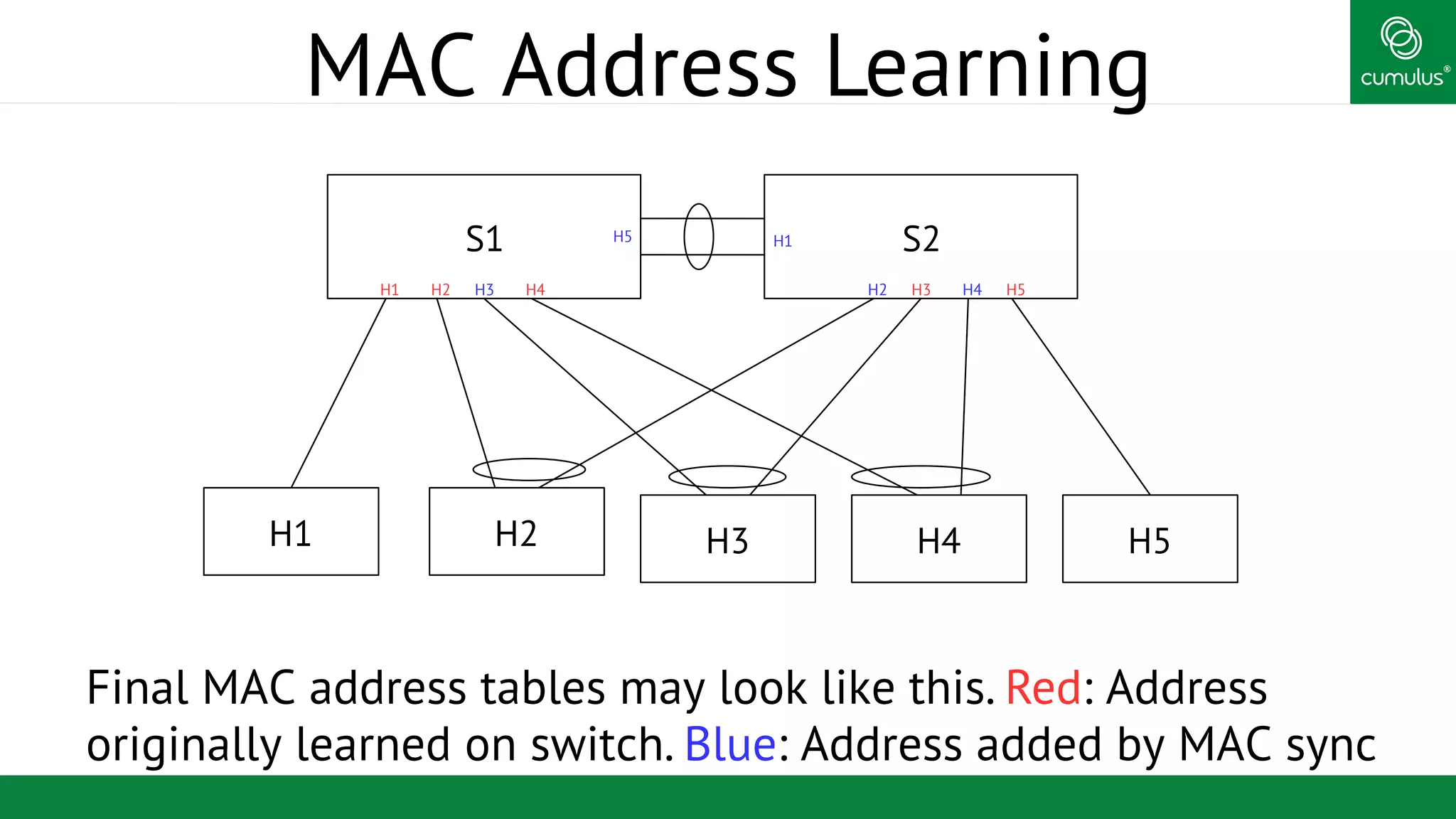
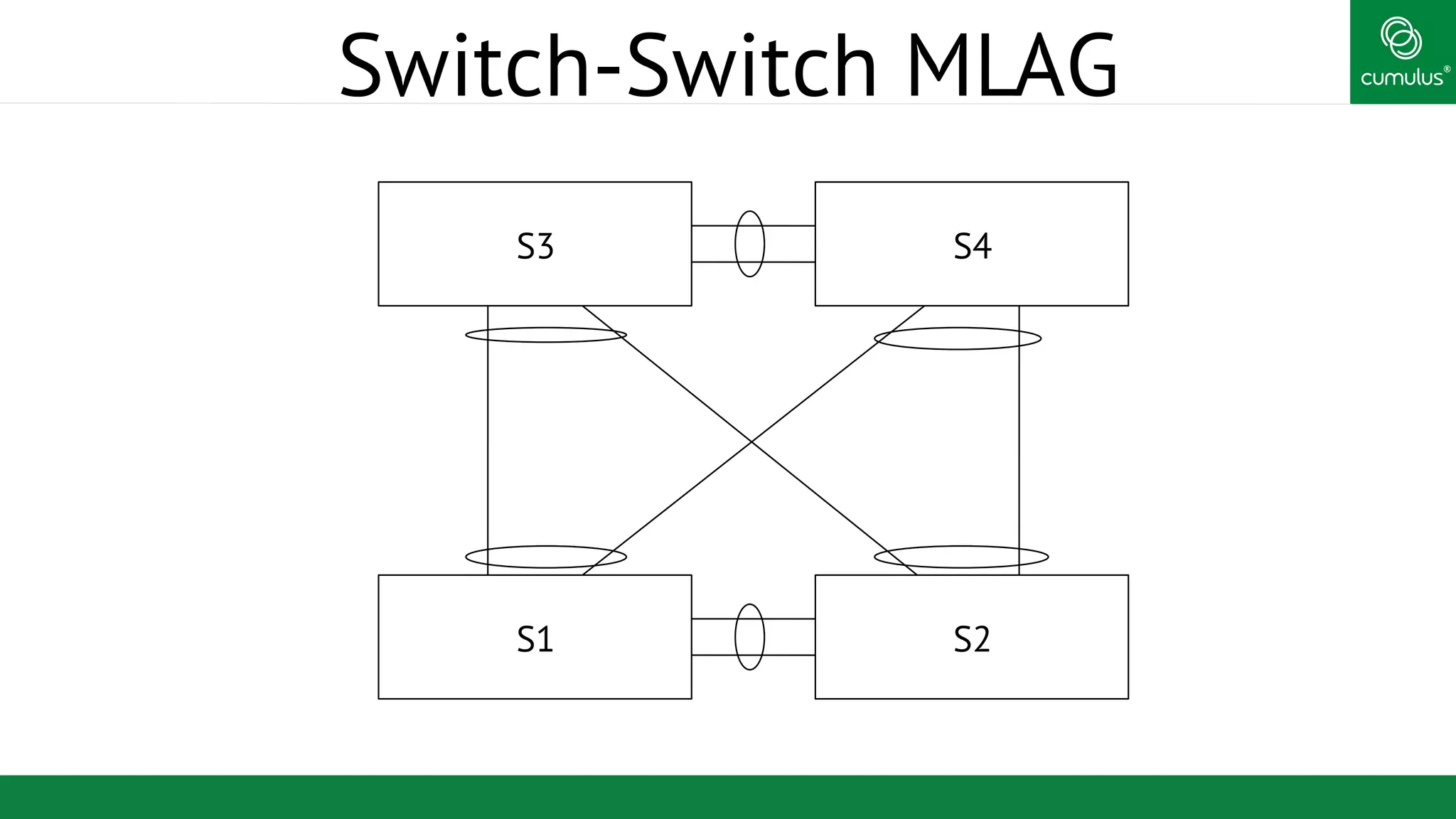
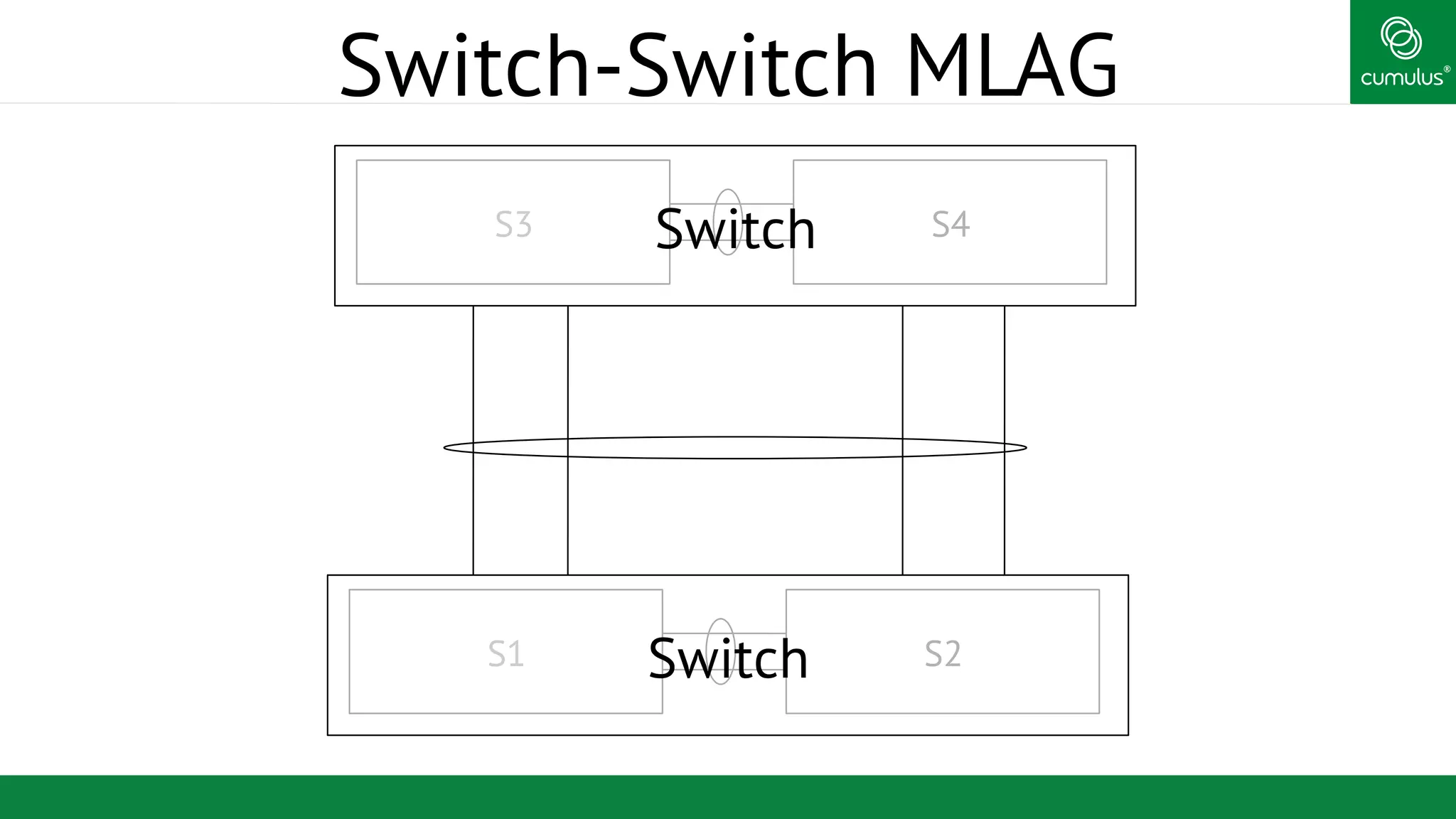
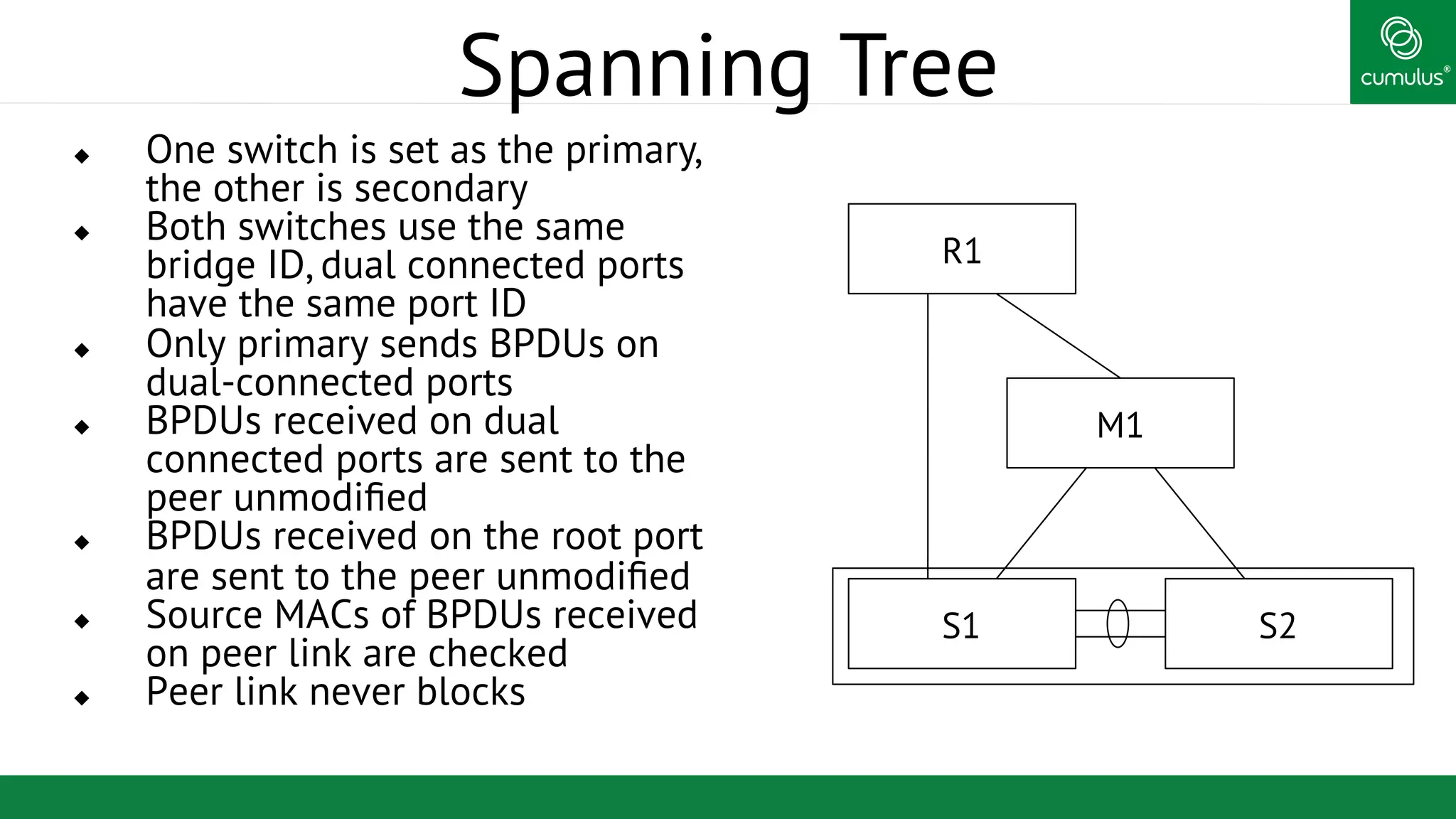
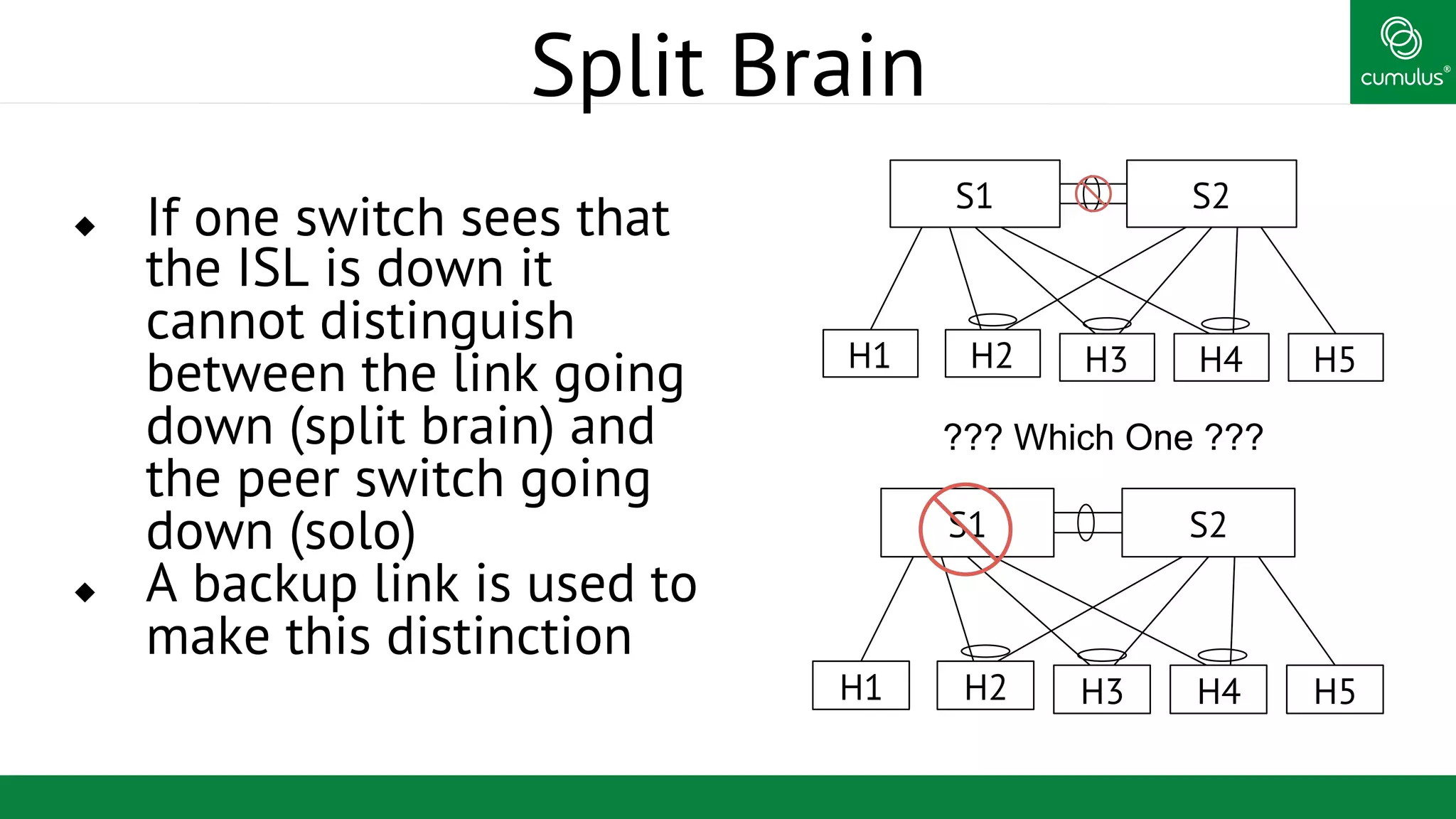
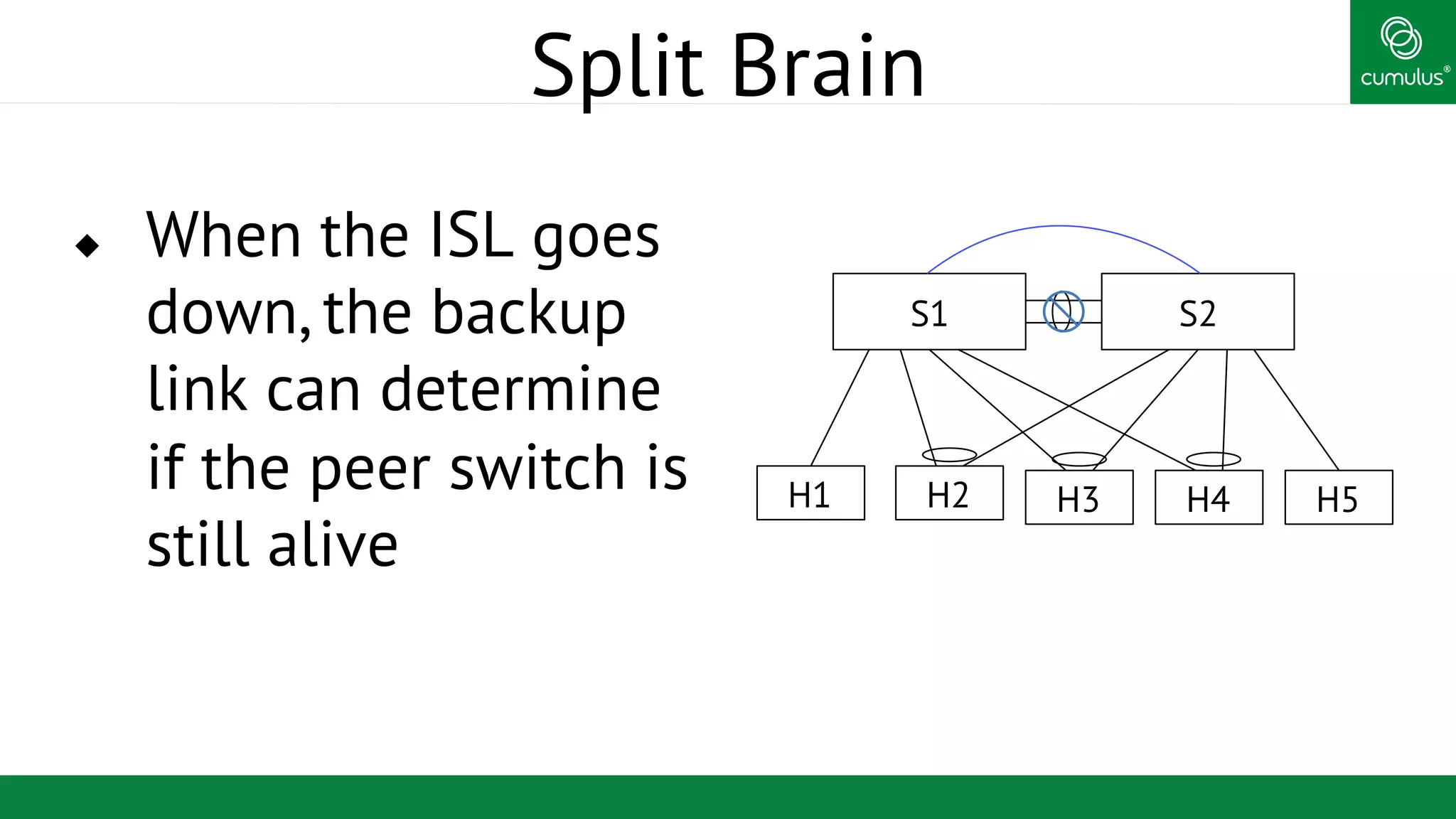
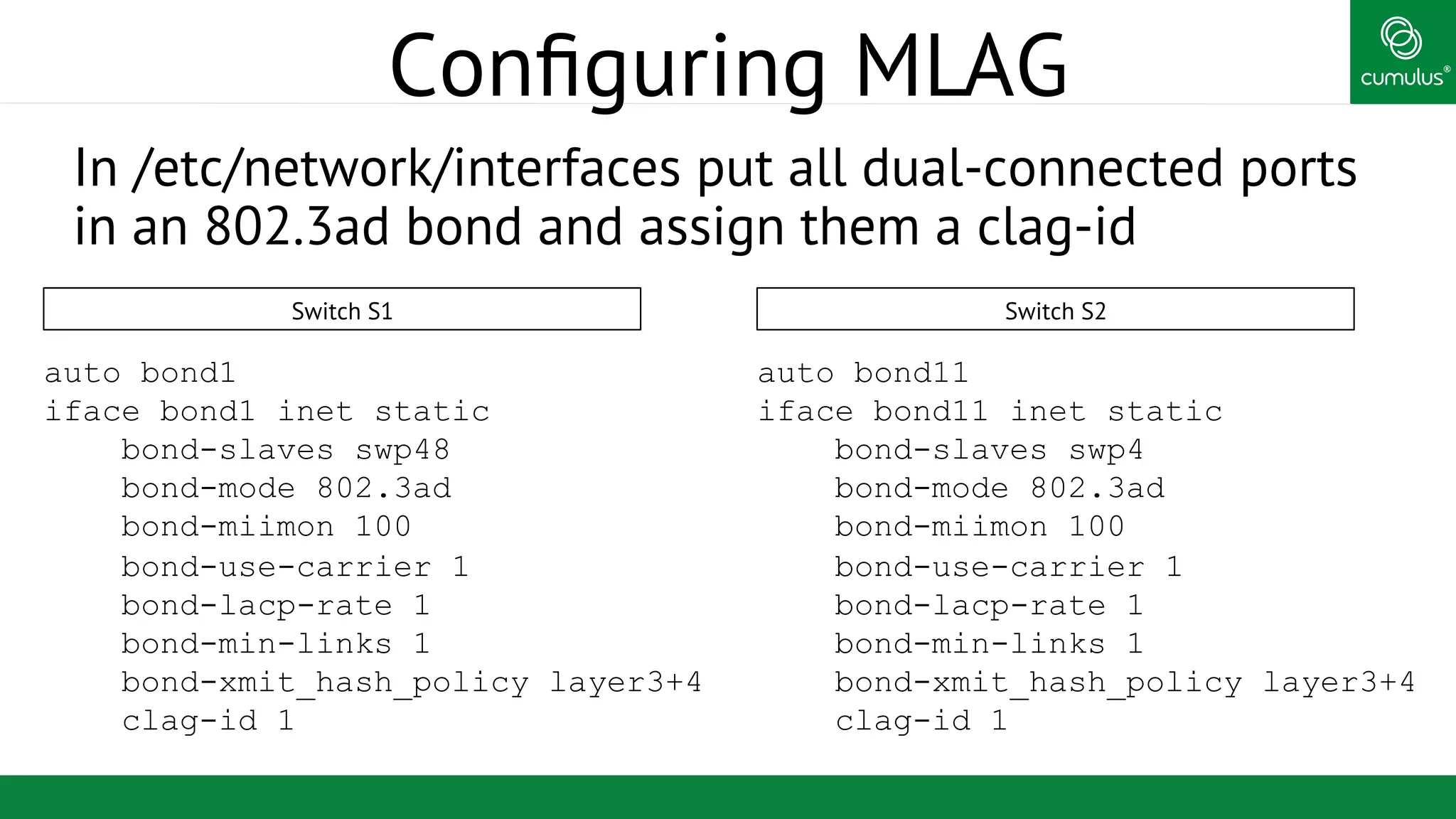
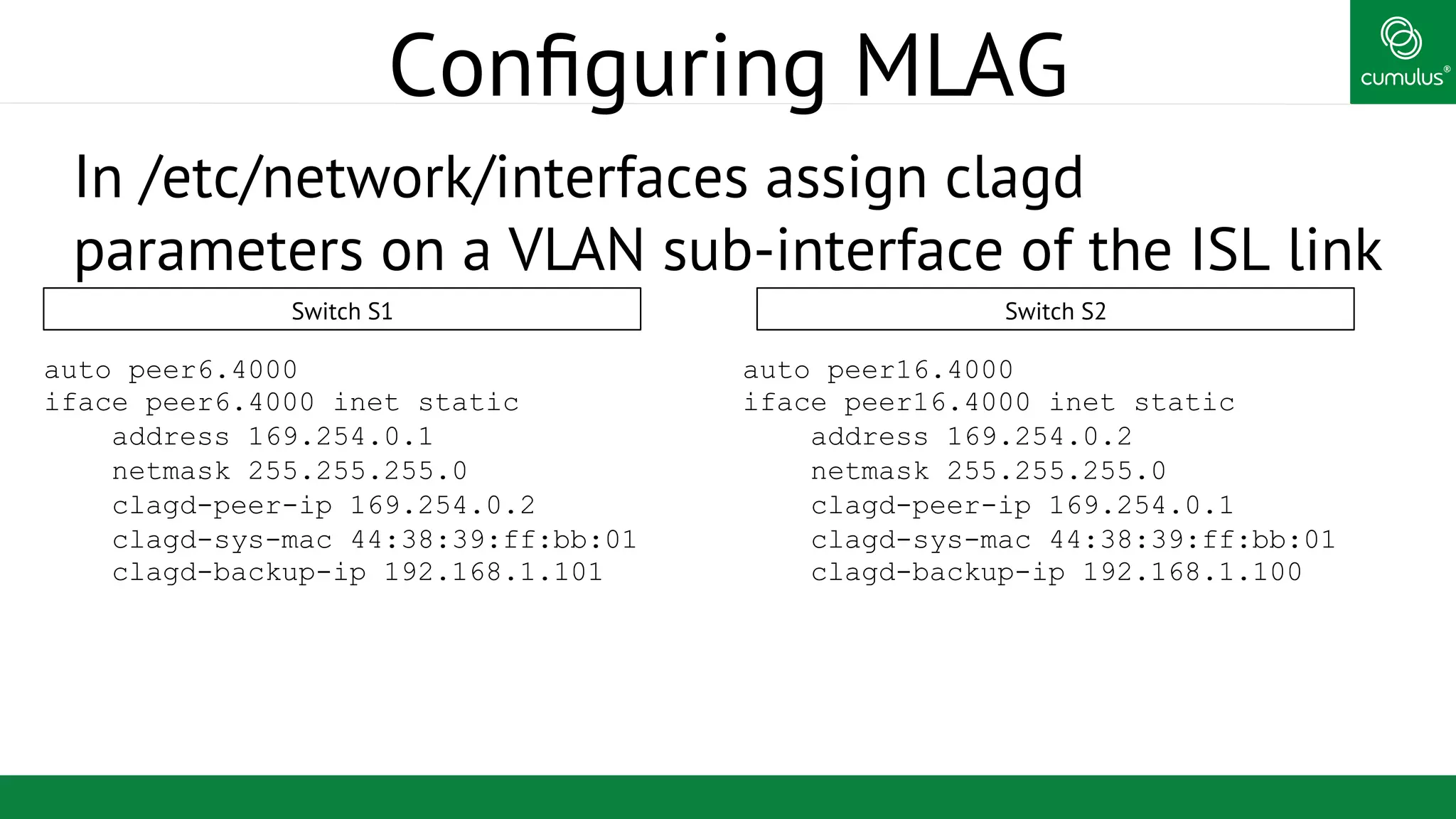
MLAG provides invisible Layer 2 redundancy across switches by making them appear as a single logical switch. It establishes dual-connected ports across switches and synchronizes MAC address tables and BPDUs to eliminate duplicate packets and prevent spanning tree loops. MLAG configuration involves bonding dual-connected ports with a common CLAG ID and running the CLAGD protocol over a peer link to synchronize state.






![®
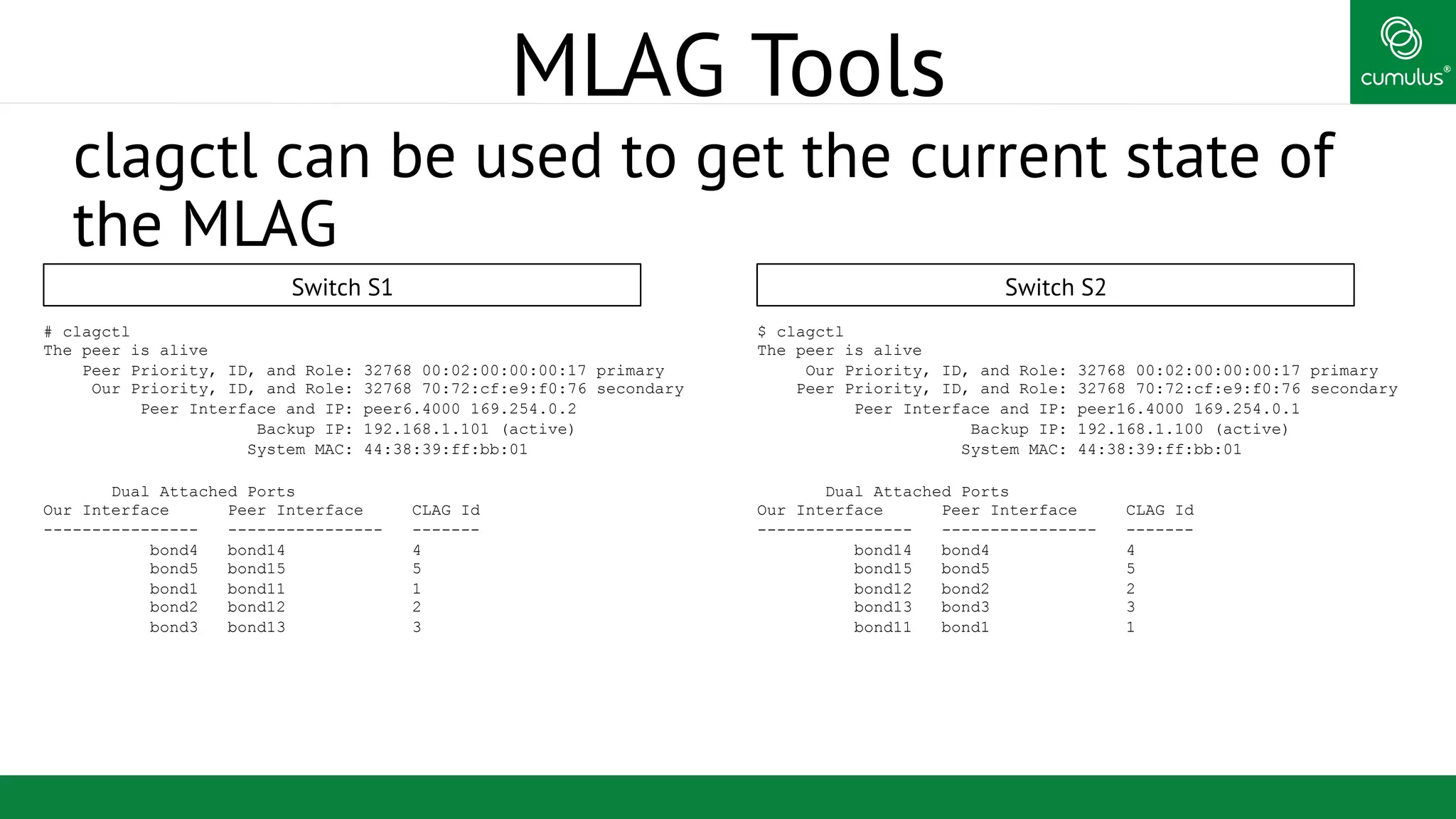
MLAG Tools
/var/log/syslog contains MLAG status changes
# grep clagd /var/log/syslog
May 19 16:25:31 act-5712-08 clagd[7253]: Beginning execution of clagd version 1.1.0
May 19 16:25:31 act-5712-08 clagd[7253]: Invoked with: /usr/sbin/clagd --daemon 169.254.0.2
peer6.4000 44:38:39:ff:bb:01
May 19 16:25:31 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: Role is now secondary
May 19 16:25:32 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: Initial config loaded
May 19 16:25:33 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: The peer switch is active.
May 19 16:25:33 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: Initial data sync from peer done.
May 19 16:25:33 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: Initial handshake done.
May 19 16:25:33 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: Initial data sync to peer done.
May 19 16:25:37 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: bond2 is now dual connected.
May 19 16:25:37 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: bond3 is now dual connected.
May 19 16:25:37 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: bond1 is now dual connected.
May 19 16:25:37 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: bond5 is now dual connected.
May 19 16:25:37 act-5712-08 clagd[7258]: bond4 is now dual connected.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlag-invisibilelayer2redundancy-150528222048-lva1-app6891/75/Mlag-invisibile-layer-2-redundancy-31-2048.jpg)
