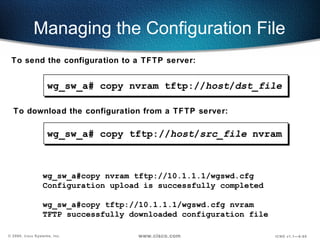
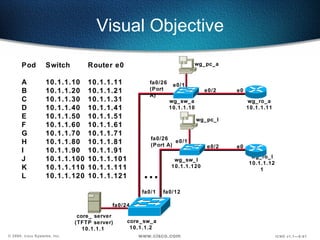
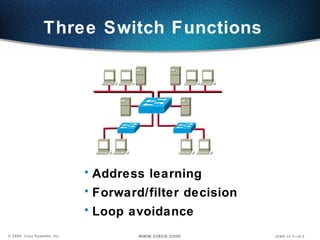
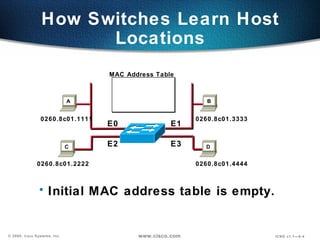
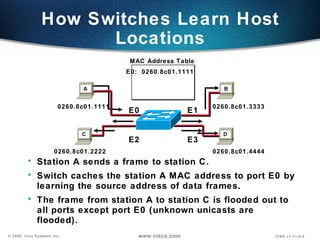
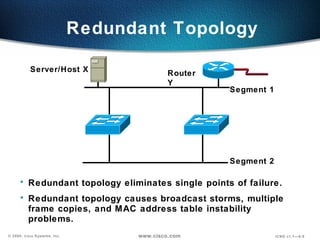
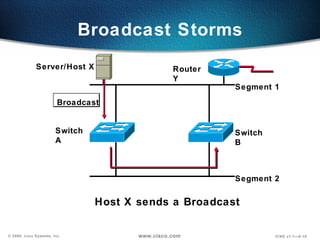
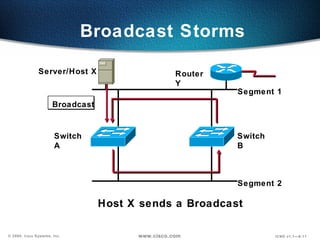
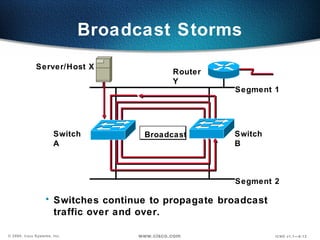
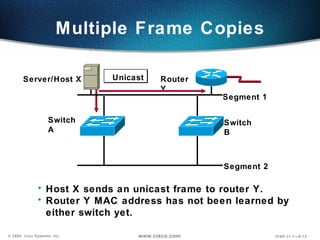
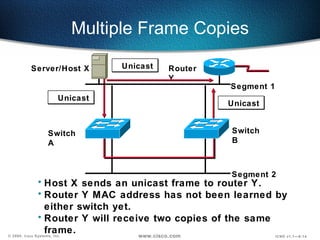
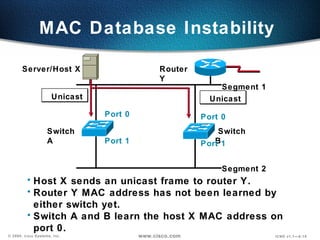
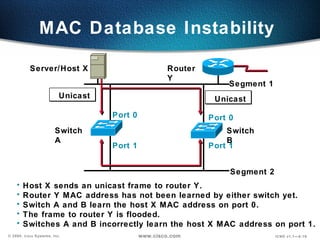
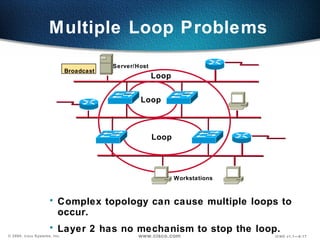
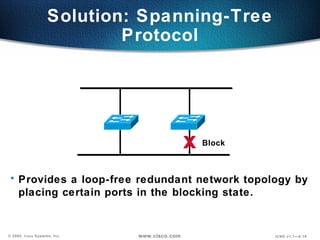
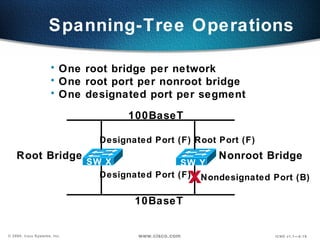
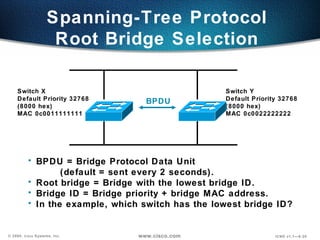
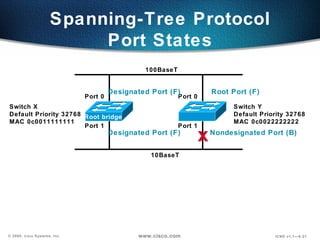
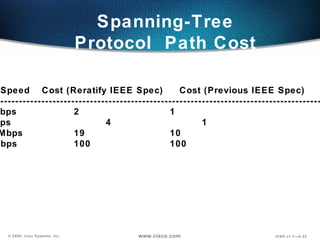
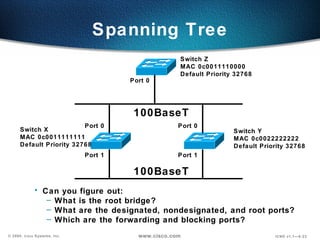
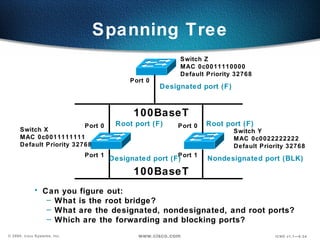
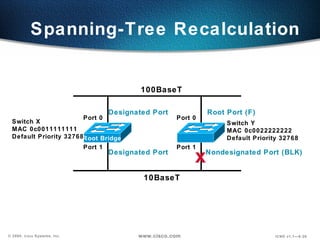
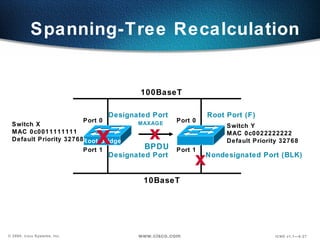
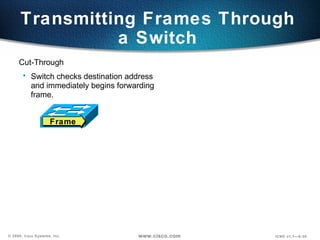
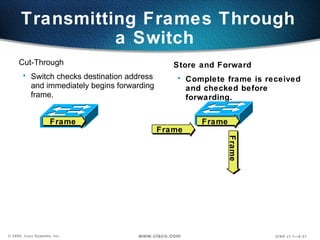
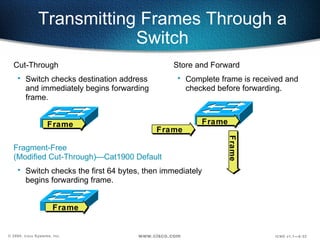
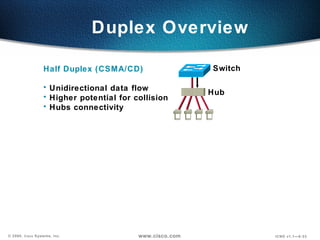
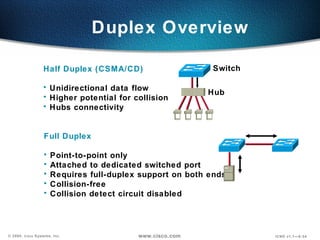
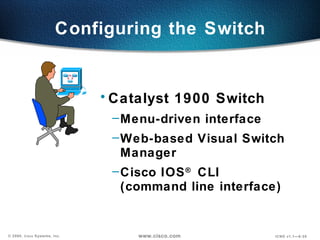
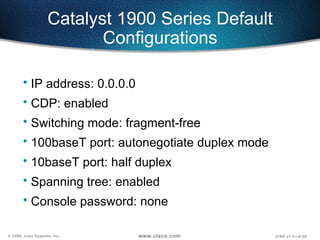
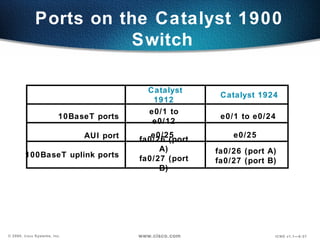
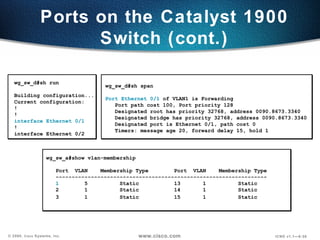
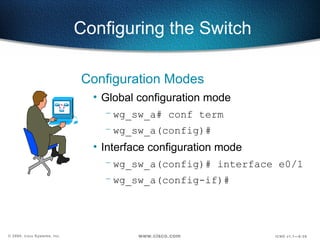
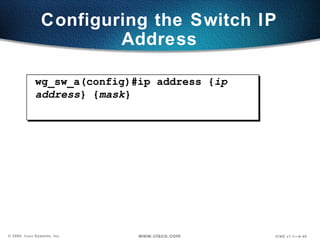
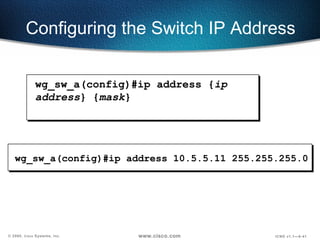
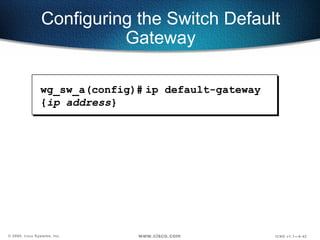
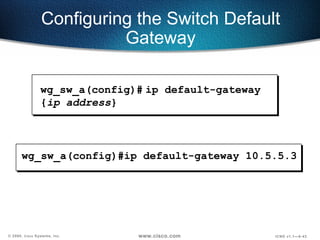
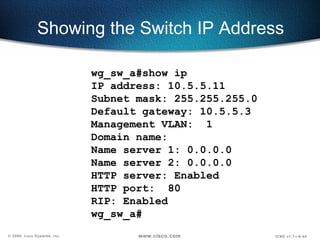
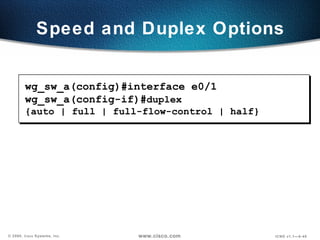
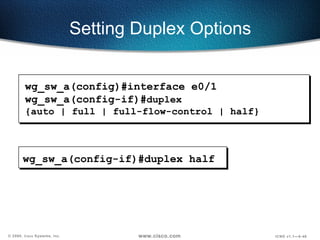
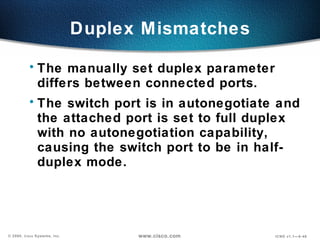
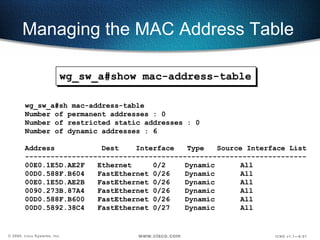
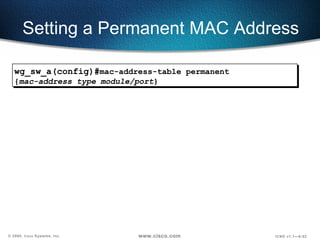
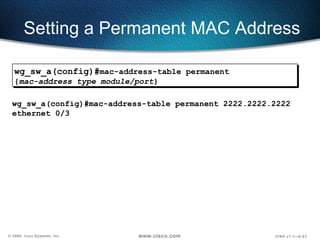
The document describes Layer 2 switching operations on a Catalyst 1900 switch. It covers how switches learn MAC addresses, forward and filter frames, handle broadcasts, and avoid loops using the Spanning Tree Protocol. Configuration topics include setting the IP address, default gateway, interface speed/duplex, and managing the MAC address table.











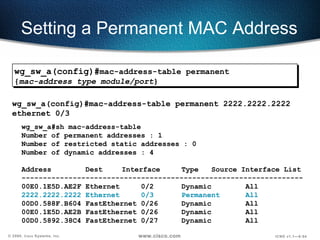


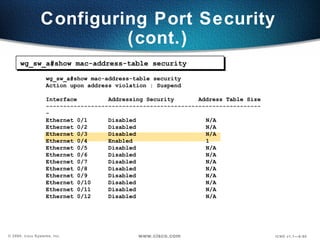
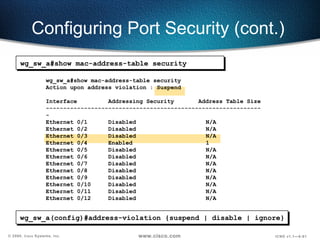
![Configuring Port Security Configures an interface to be a secured port. Defines a maximum number of MAC addresses allowed in the address table for this port. Allows counts from 1 to 132. (default 132) wg_sw_a(config-if)# port secure [max-mac-count count ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-090311180855-phpapp01/85/catalyst-switch-Operation-58-320.jpg)
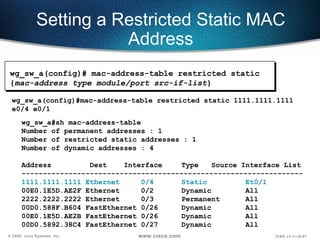
![Configuring Port Security Configures an interface to be a secured port. Defines a maximum number of MAC addresses allowed in the address table for this port. Allows counts from 1 to 132. (default 132) wg_sw_a(config)#interface e0/4 wg_sw_a(config-if)#port secure wg_sw_a(config-if)#port secure max-mac-count 1 wg_sw_a(config-if)# port secure [max-mac-count count ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-090311180855-phpapp01/85/catalyst-switch-Operation-59-320.jpg)