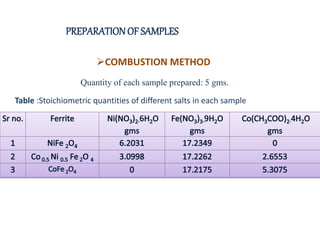
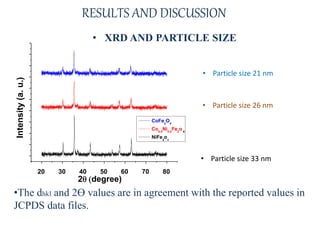
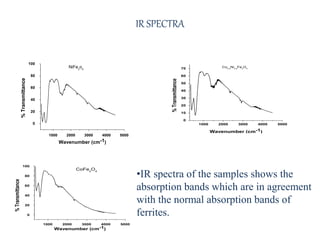
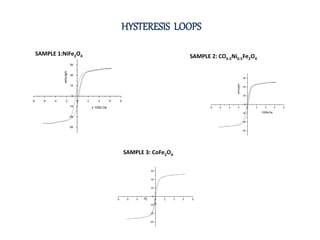
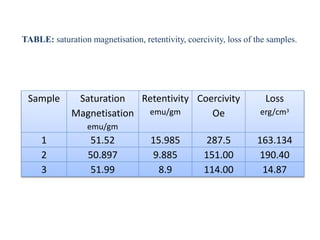
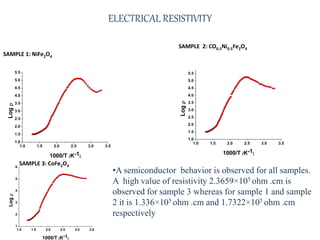
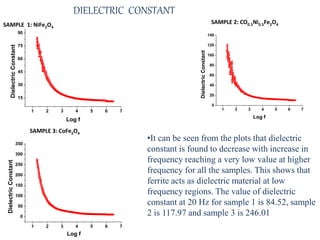
The document examines the properties and applications of mixed metal oxides, particularly focusing on ferrospinel ferrites with the general formula mefe2o4, where me is a divalent metal ion. It describes the preparation and characterization methods, including X-ray diffraction and infrared spectroscopy, as well as the magnetic and electrical properties of various samples made using the combustion method. The findings indicate that the ferrites exhibit semiconductor behavior and demonstrate significant magnetic properties dependent on particle size.