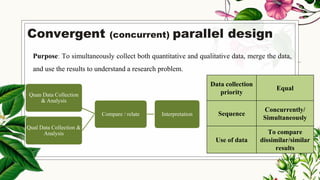
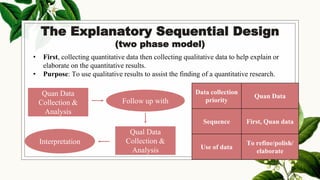
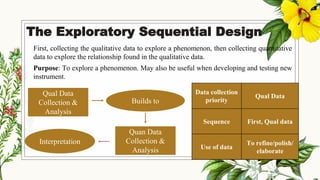
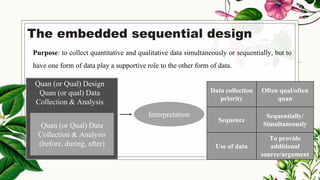
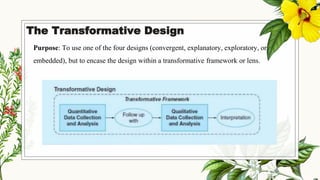
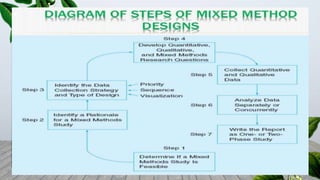
This document discusses mixed methods research, which involves collecting and analyzing both quantitative and qualitative data within a single study. It provides an overview of the main mixed methods research designs, including convergent parallel, explanatory sequential, exploratory sequential, embedded, and transformative designs. For each design, it outlines the purpose, priority of quantitative and qualitative data collection and analysis, and how the different data sources are integrated. The document also discusses evaluating mixed methods studies and some potential ethical issues to consider in mixed methods research designs.