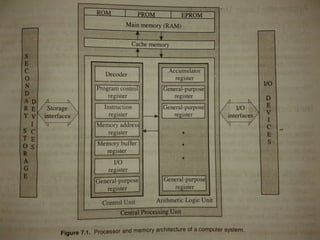
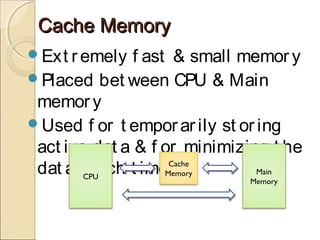
The CPU acts as the computer's brain and carries out instructions from programs. It has two main components: the control unit, which selects and coordinates instruction execution, and the arithmetic logic unit, which performs calculations. Registers temporarily store data during instruction processing, including special purpose registers like the program counter, accumulator, and input/output registers. The CPU communicates with main memory, usually RAM, and cache memory for faster access to active data. It fetches instructions from memory and decodes and executes them in a multi-step process controlled by the control unit.