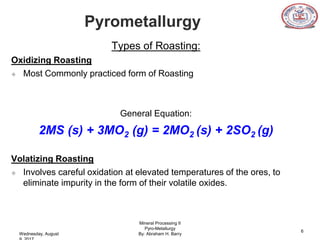
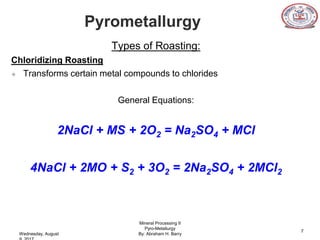
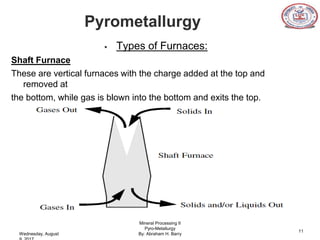
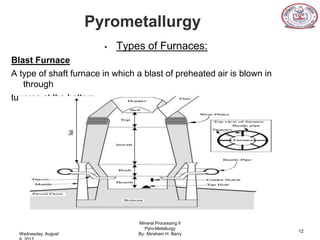
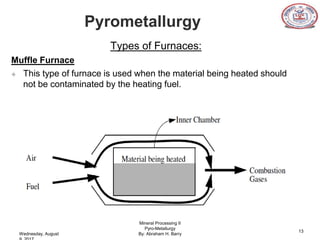
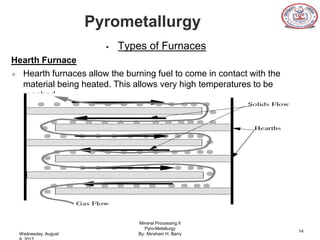
The document is a presentation on pyrometallurgy given by Abraham Barry to Nathaniel Johnson. Pyrometallurgy uses thermal energy to extract and purify metals through processes like calcination, roasting, smelting, and refining. It discusses the key processes used in pyrometallurgy like calcination, which thermally decomposes materials below melting points, and roasting, which heats sulfide ores in air. It also covers the furnace types used like shaft, blast, muffle, and hearth furnaces.