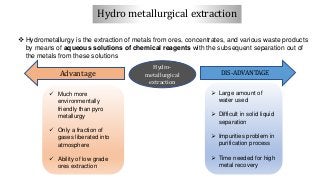
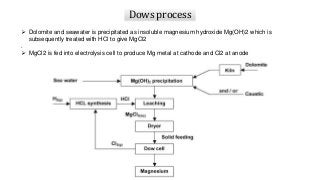
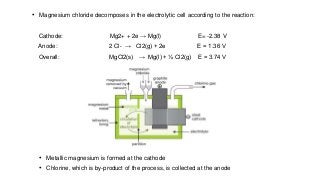
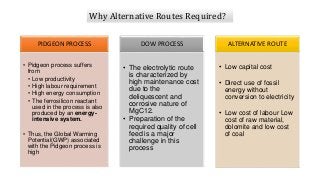
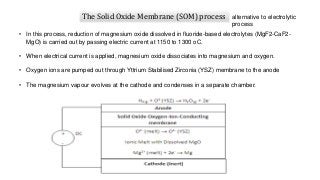
Magnesium can be extracted through pyrometallurgical or hydrometallurgical processes. Pyrometallurgical extraction involves high temperature reduction processes like the Pidgeon, Bolzano, and Magnetherm processes. However, these processes have high energy usage. Hydrometallurgical processes like the Dows process use aqueous solutions but require large water usage. Alternative processes under development include the Mintek, SOM, and carbothermic routes which aim to provide more sustainable magnesium production. Overall, new technologies are needed to lower the energy consumption of magnesium extraction from its oxides.