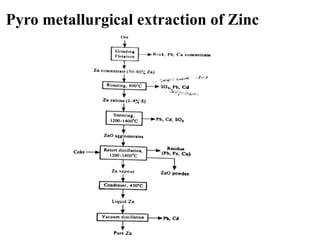
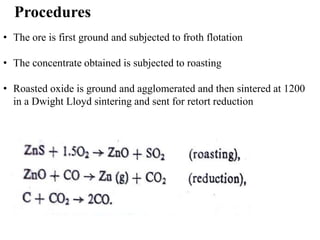
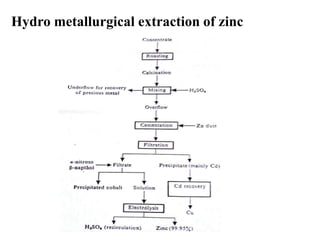
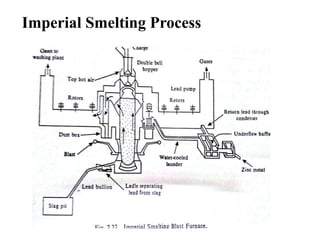
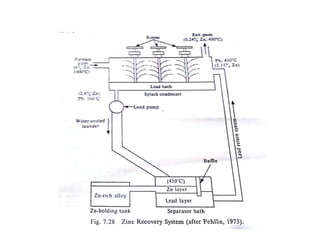
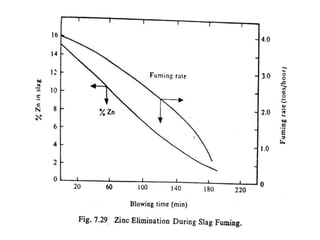
The document discusses the extraction of zinc from its ores. Zinc is extracted through either pyrometallurgical or hydrometallurgical extraction processes. Pyrometallurgical extraction involves grinding the zinc ore, concentrating it through flotation, roasting the concentrate to produce zinc oxide, and then reducing the zinc oxide with carbon to produce zinc vapor which is then condensed. Hydrometallurgical extraction involves leaching the zinc calcine with sulfuric acid, precipitating out impurities, and then electrolyzing the filtered solution to recover zinc. The Imperial Smelting Process is also discussed, which allows simultaneous smelting of zinc and lead from complex mixed ores.