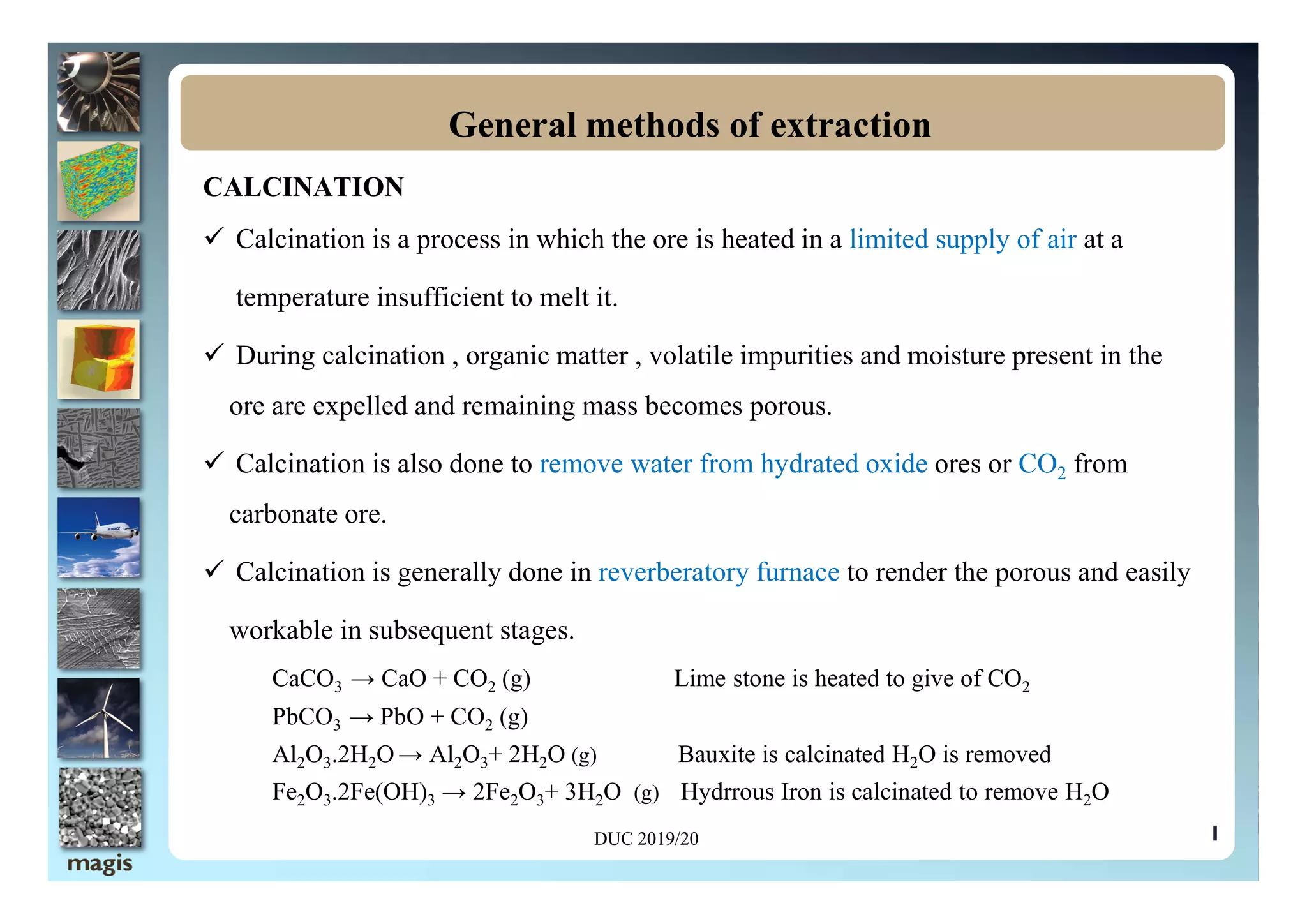
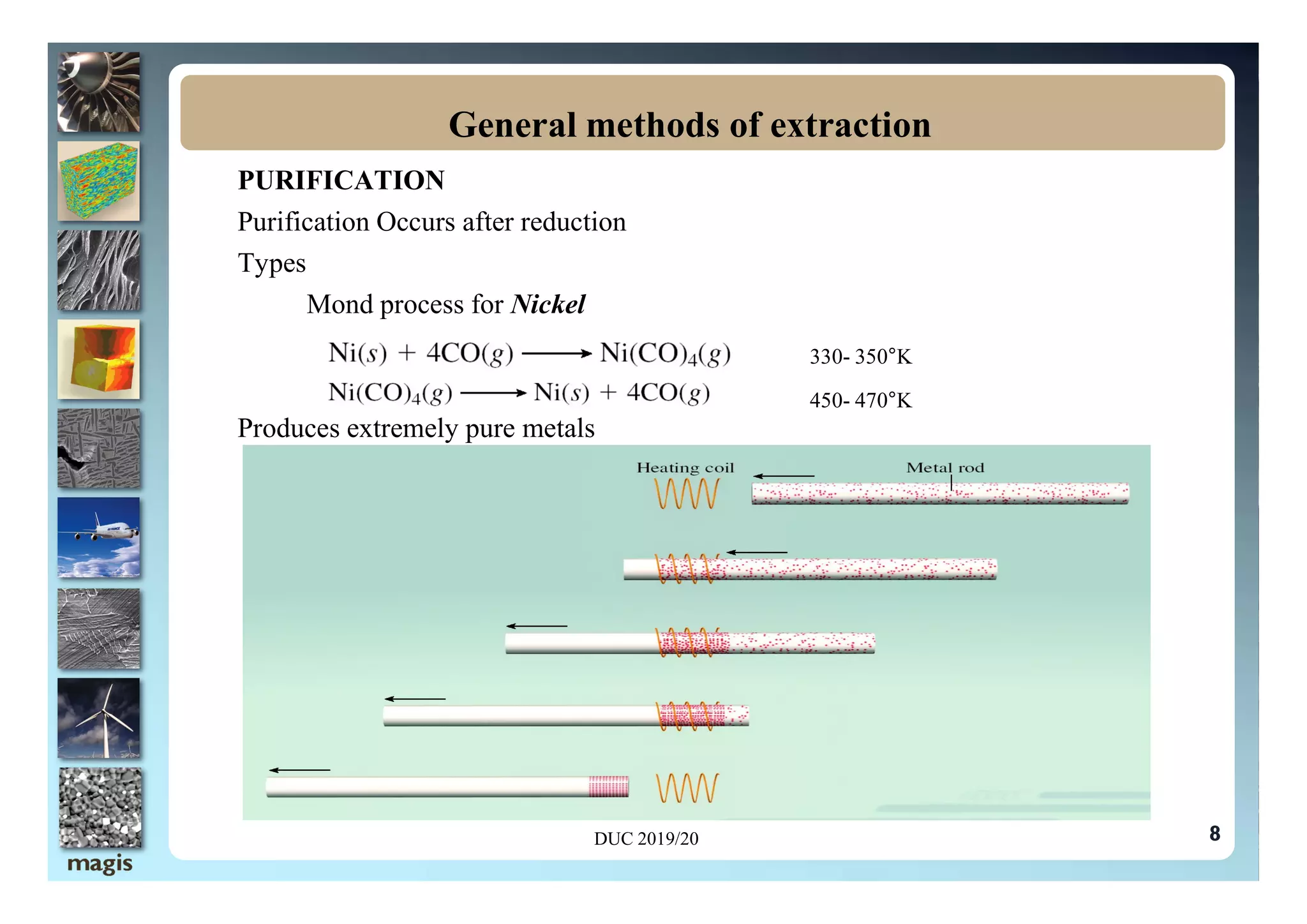
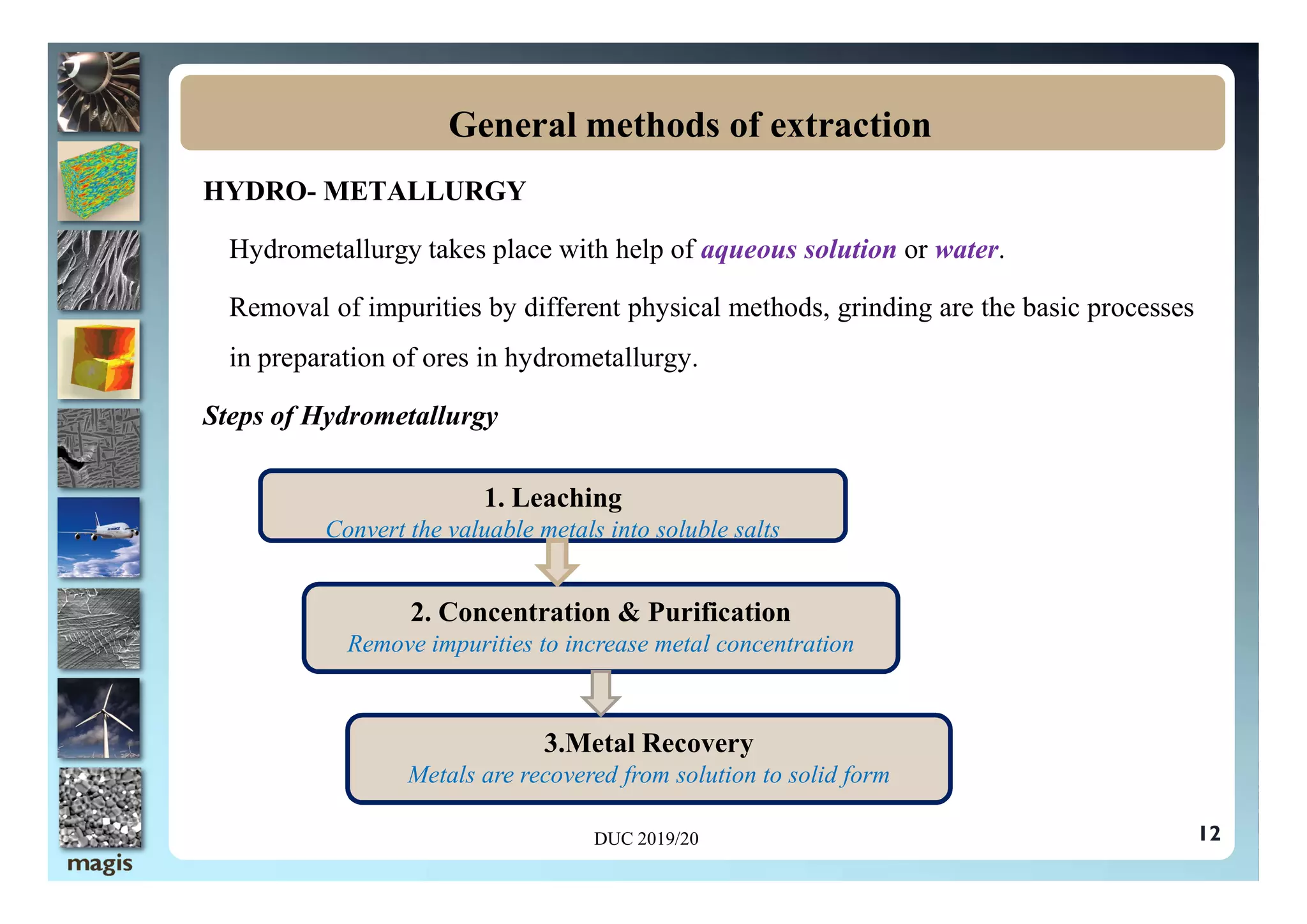
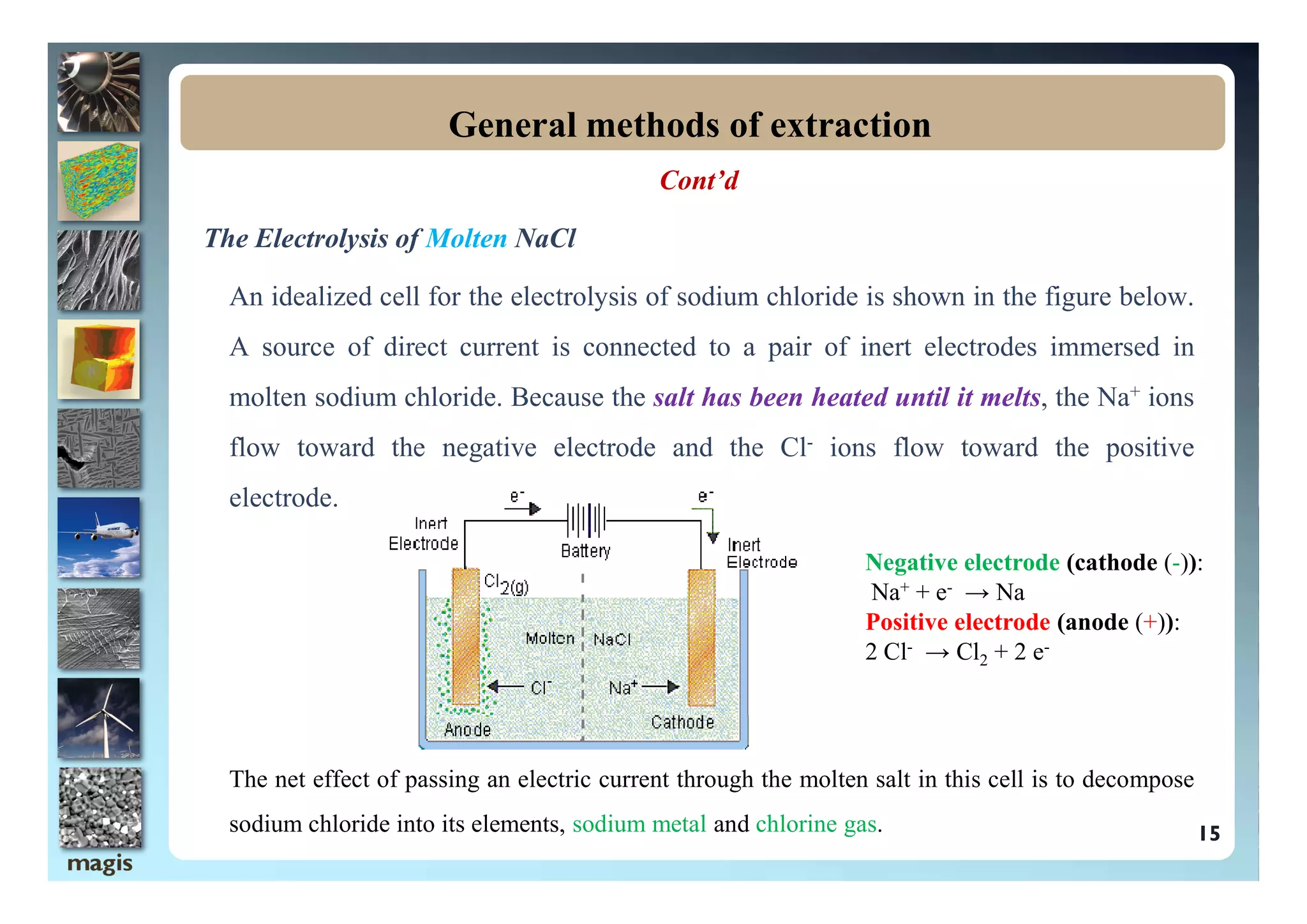
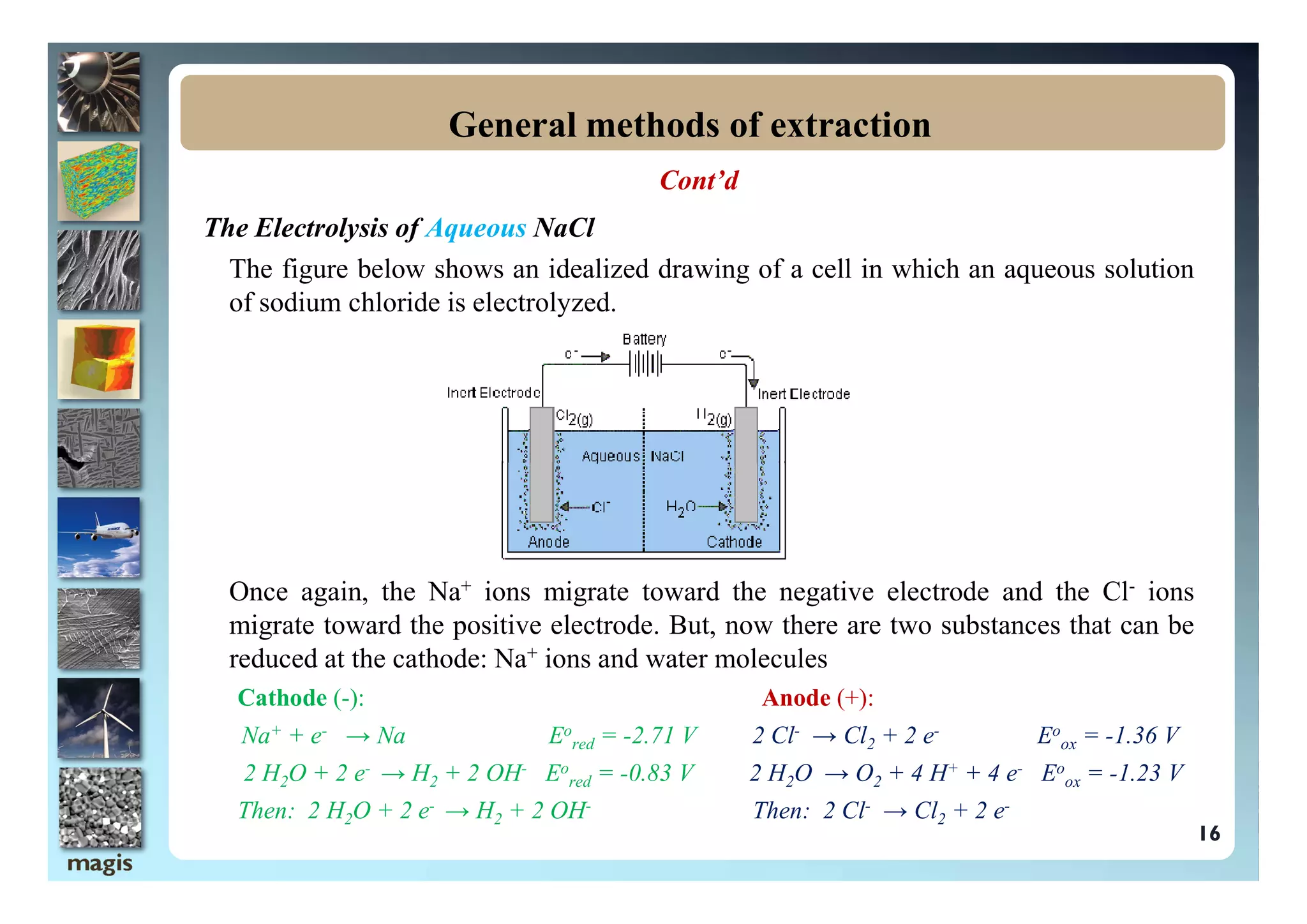
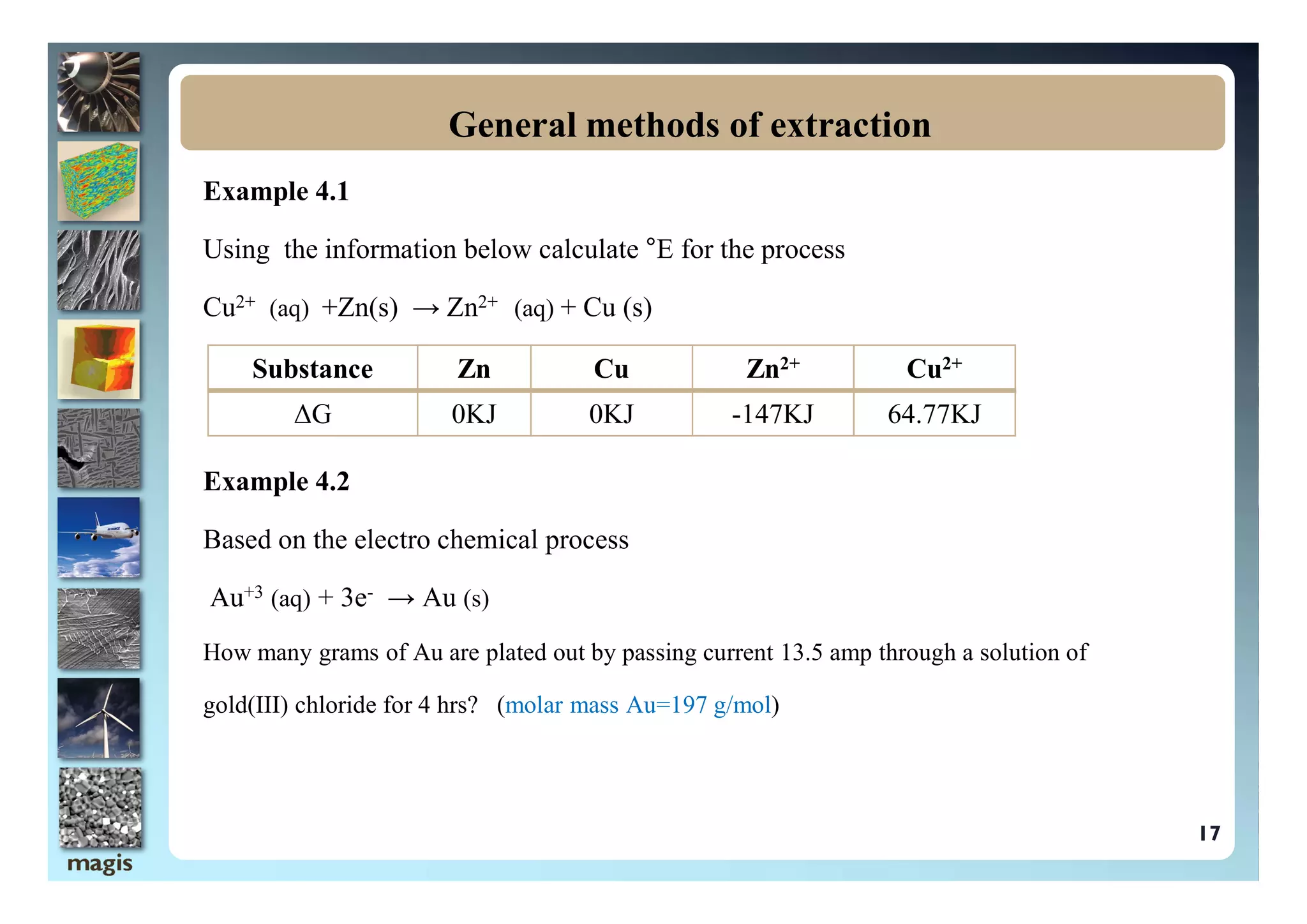
The document outlines methods of metal extraction focusing on pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy, and electrometallurgy, detailing processes such as calcination, roasting, smelting, leaching, and electrolysis. Each method is analyzed for its energy requirements, advantages, and disadvantages, particularly emphasizing the role of various chemical reactions and compounds. It also discusses the environmental impact and economic considerations associated with these metallurgical processes.