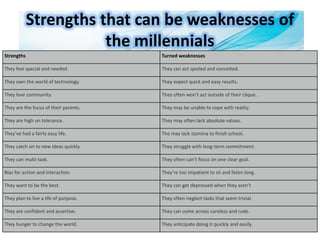
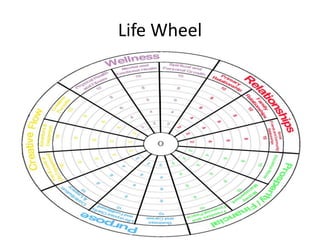
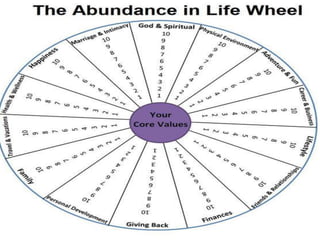
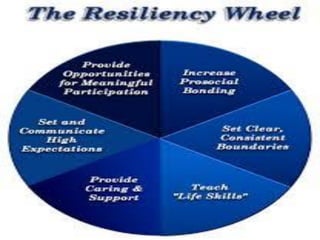
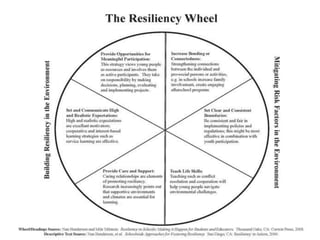
This document discusses millennial trends and behaviors. It begins with an introduction about understanding the characteristics of millennials in order to manage and counsel them. It then discusses several common characteristics of millennials such as being special, sheltered, confident, team-oriented, and pressured. The document also examines strengths of millennials that can become weaknesses. Next, it explores parenting challenges in the 21st century and positive discipline approaches. Finally, there are sections on counseling versus psychotherapy and leadership strategies for millennials.

















































![Counseling Psychology & Clinical
Psychology (The Greystone Conference)
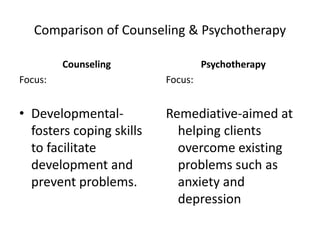
1.The Counseling Psychologist works with normal, convalescent
or recovered clients who do not require long-term treatment
because their problems are neither severe nor deep-seated.
2. The emphasis is on more typical (more normal) needs and
problems that can be dealt with monthly on a cognitive level.
3. The focus is not on reconstructuring personalities [as it is with
Clinical Psychology] but on drawing out and developing what
is already there and on helping clients use their own
resources.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/millenials101-170625031632/85/Millennials-101-56-320.jpg)



















![F00-F09 Organic, including symptomatic, mental disorders
F10-F19 Mental and behavioral disorders due to
psychoactive substance use
F20-F29 Schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders
F30-F39 Mood [affective] disorders
F40-F48 Neurotic, stress-related and somatoform disorders
F50-F59 Behavioral syndromes associated with
physiological disturbances and physical factors
F60-F69 Disorders of adult personality and behavior
F70-F79 Mental retardation
F80-F89 Disorders of psychological development
F90-F98 Behavioral and emotional disorders with onset
usually occurring in childhood and adolescence
F99 Unspecified mental disorder](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/millenials101-170625031632/85/Millennials-101-83-320.jpg)