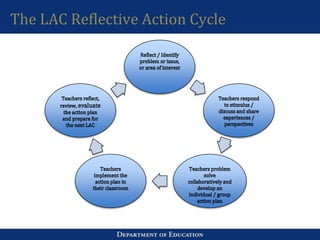
1. The workshop reviewed LAC principles and facilitation skills. Participants shared experiences from exemplary LAC sessions and discussed skills like active listening, managing participation, and keeping groups focused.
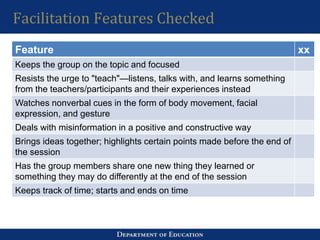
2. In an activity, participants observed role plays of LAC sessions and provided feedback. Key facilitation skills identified included ensuring materials were ready, modeling behaviors, and focusing on both content and group process.
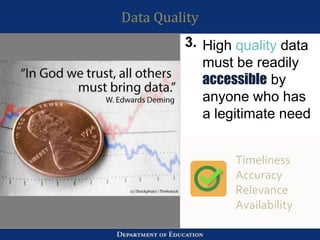
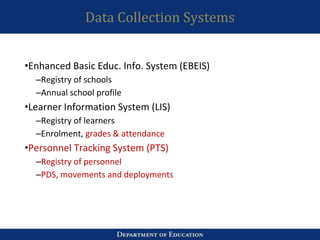
3. The importance of skills like active listening, linking ideas, and being concerned with both content and process were discussed. Creating ICT-focused LACs to support teacher training was also presented. Data