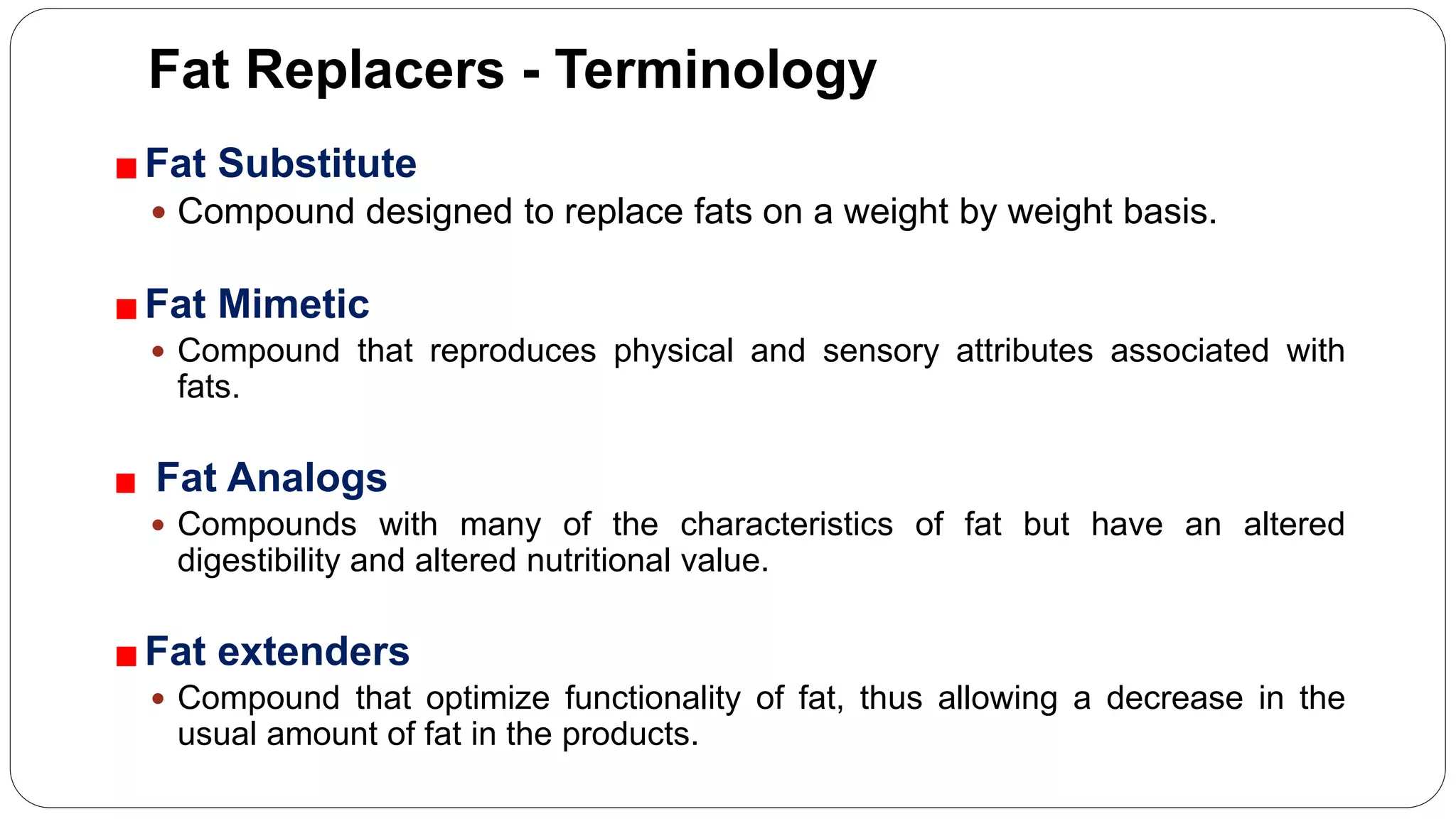
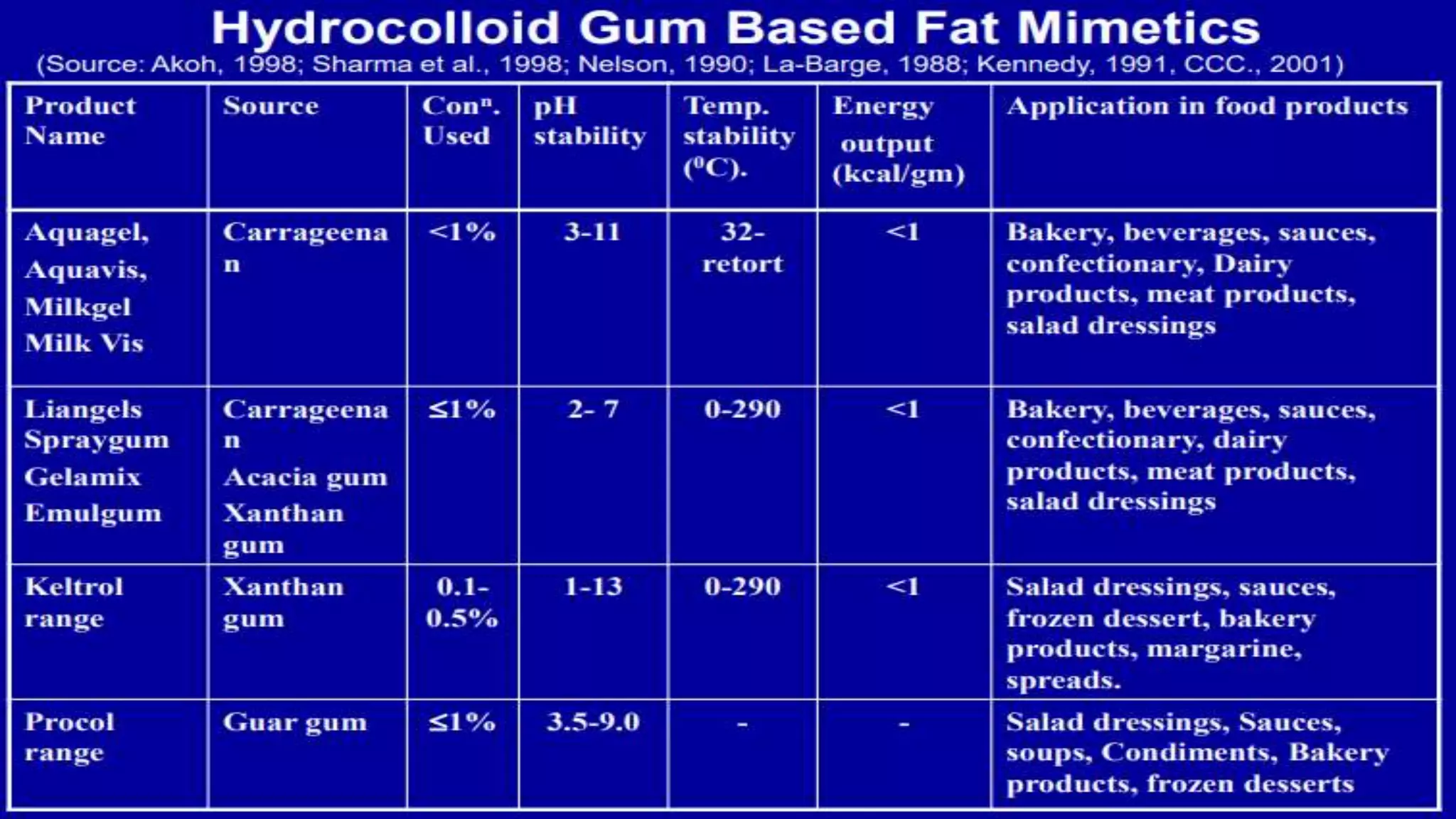
The document provides an overview of fat replacers, emphasizing their role in reducing dietary fat to lower the risk of chronic diseases. It details various types of carbohydrate-based fat replacers, their applications, and nutritional aspects, highlighting ingredients like maltodextrins, oatrim, and microcrystalline cellulose. The conclusion notes that while carbohydrate fat replacers are effective in enhancing food texture and reducing calories, no single ingredient can replace fat in all food products.