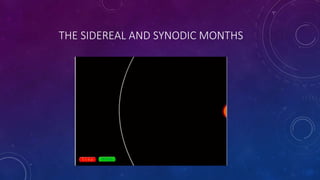
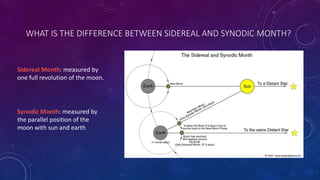
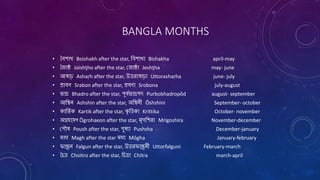
The document provides an extensive overview of the concept of months, including their definitions, types, historical origins, and cultural variations, particularly focusing on the Gregorian and Bengali calendars. It explains different types of months such as sidereal, synodic, tropical, anomalistic, and draconic months, along with their respective durations. Additionally, it discusses the relationship between months and seasons, emphasizing the significance of months in organizing time and marking seasonal changes.