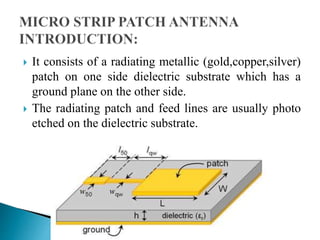
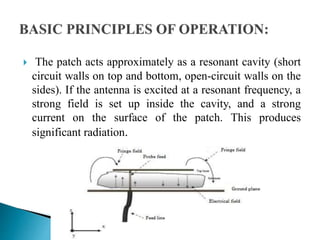
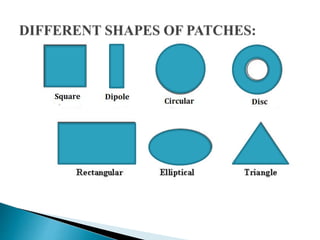
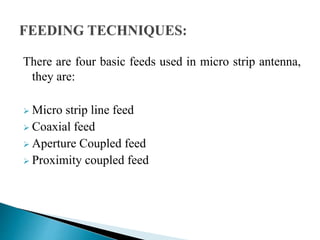
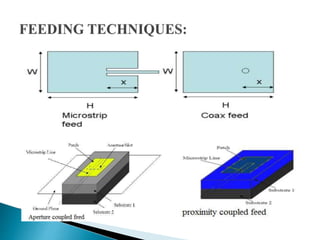
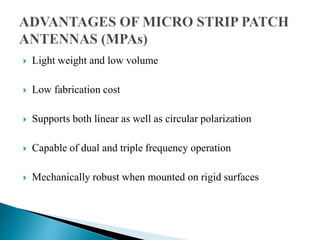
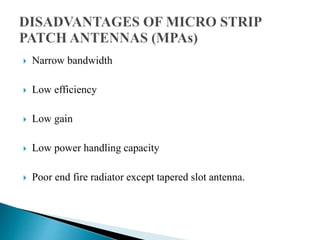
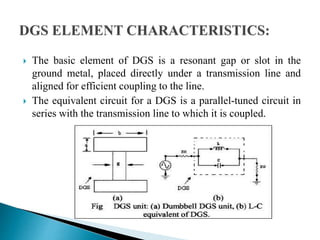
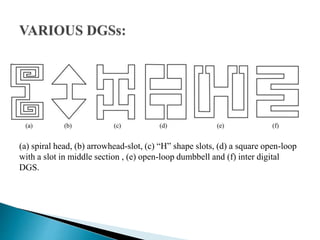
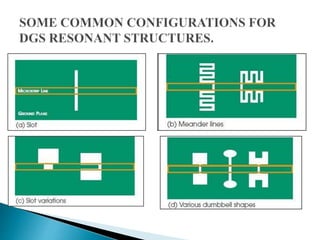
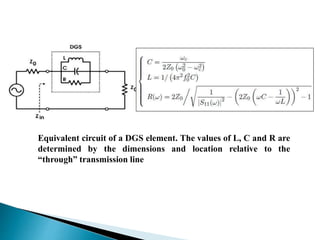
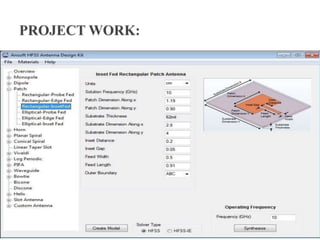
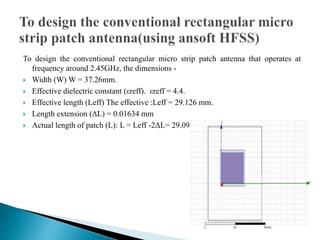
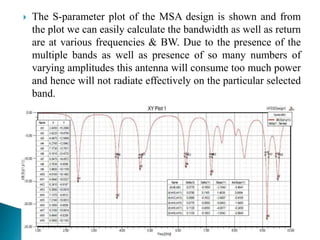
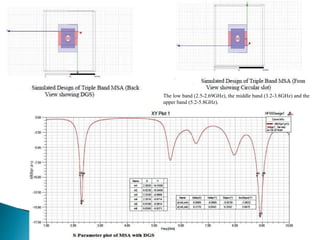
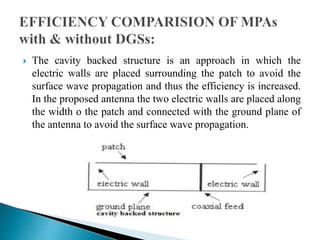
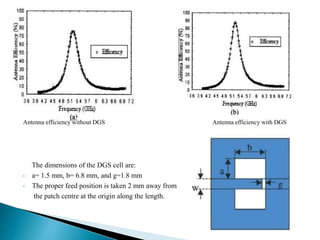
The document discusses microstrip patch antennas and defected ground structures (DGS). It provides an overview of microstrip antenna design including patch geometries and feeding techniques. It also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of microstrip antennas. Next, it introduces DGS, describing various DGS unit cell shapes and their applications in delay lines and antennas. The document concludes by presenting the design and performance analysis of a rectangular microstrip patch antenna with a dumbbell-shaped DGS cell for size reduction and efficiency improvement.