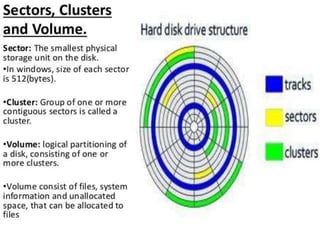
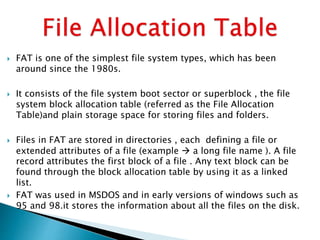
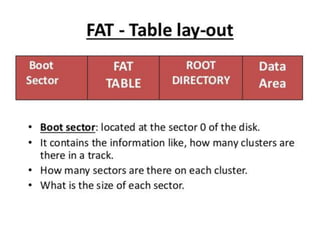
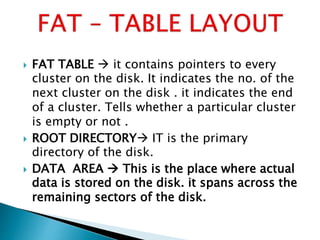
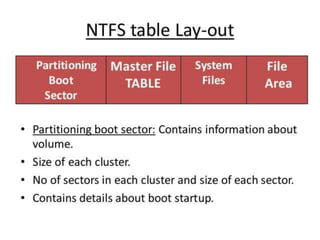
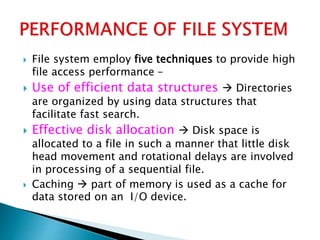
The document discusses various disk file systems used in Microsoft Windows, primarily focusing on NTFS, FAT, and ReFS. NTFS, developed to address limitations of the older FAT system, offers advanced features such as security, encryption, and better data management, making it suitable for modern storage requirements. In contrast, FAT's simplicity and early reliability have been outpaced by NTFS's capabilities in handling larger disks and ensuring data recoverability.