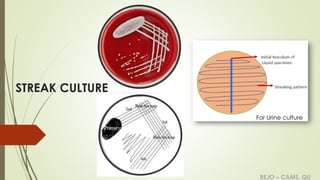
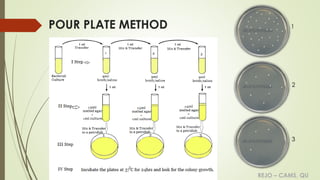
The document discusses various culture methods used in microbiology for growing and isolating micro-organisms, including streak culture, lawn culture, stroke culture, stab culture, liquid culture, and pour plate method. It emphasizes the importance of aseptic techniques during inoculation, proper labeling of culture media, and specific uses for each method, such as antibiotic sensitivity testing or maintaining stock cultures. Additionally, the document explains anaerobic culture methods necessary for growing obligate anaerobes, highlighting techniques like the McIntosh & Fildes anaerobic jar and gas pack system.