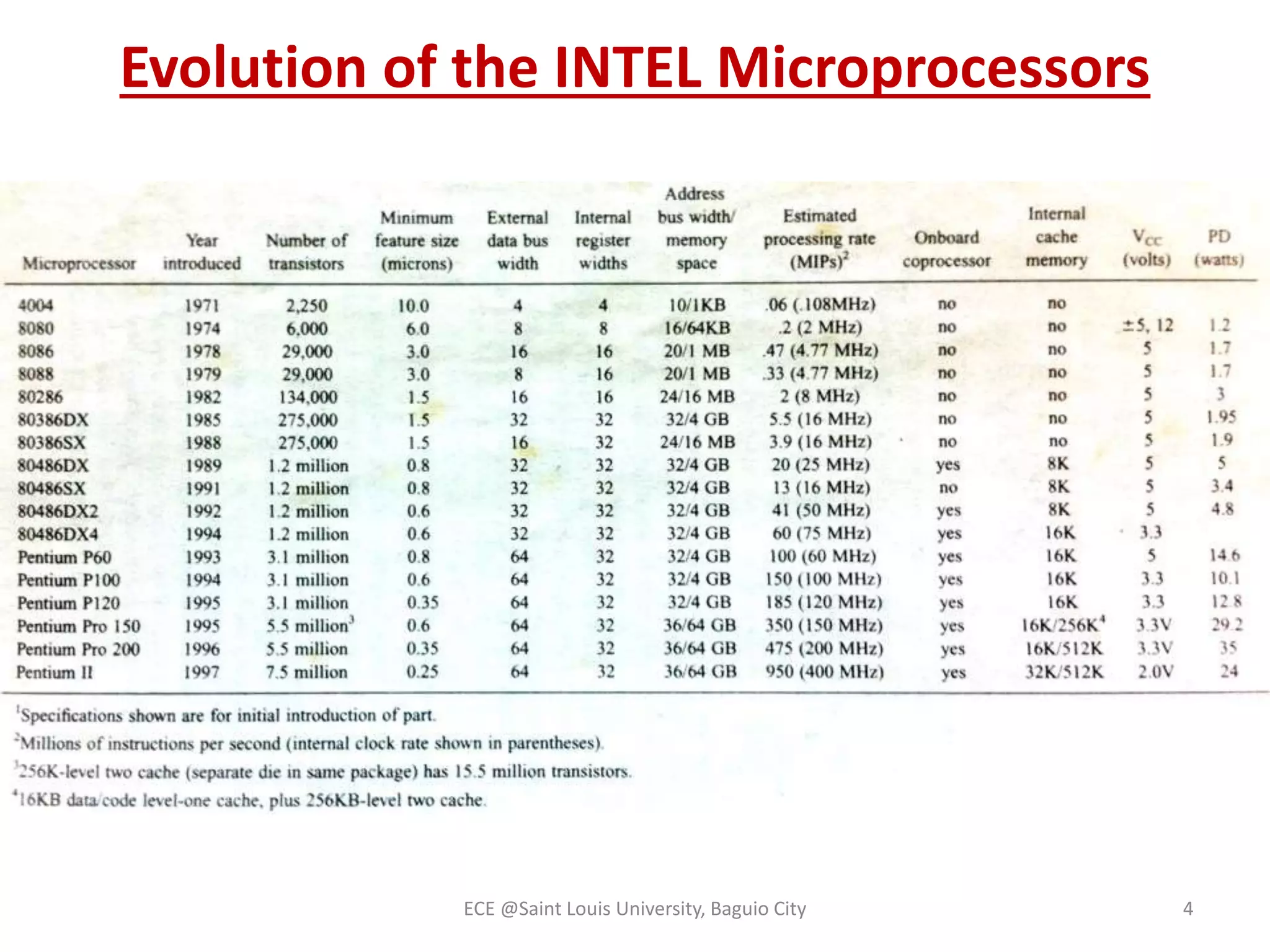
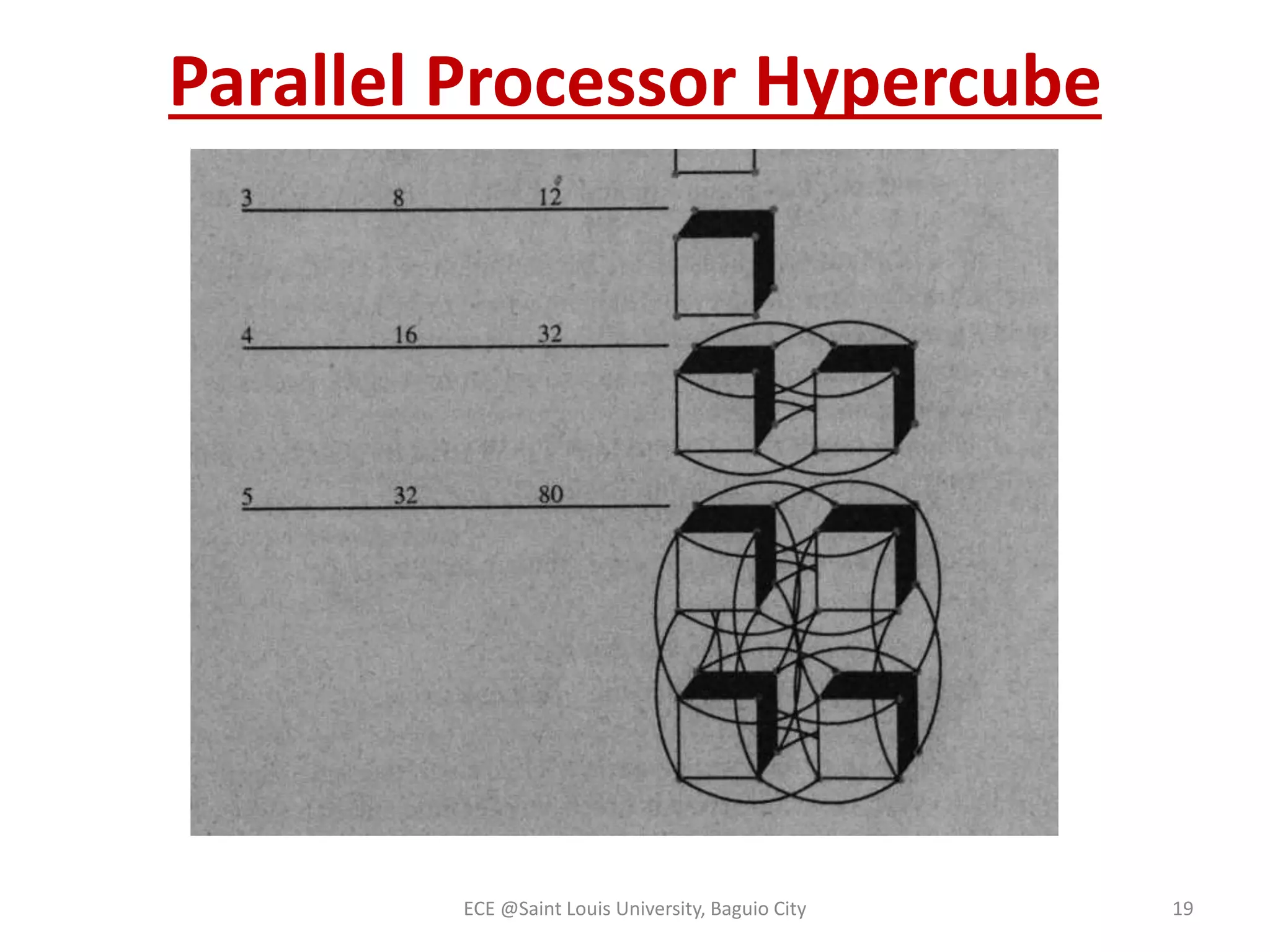
The document provides an overview of microprocessors and microcontrollers, detailing their evolution from the early vacuum tube computers to modern personal and supercomputers. It highlights the development of the Intel microprocessor family, the distinction between microprocessors and microcontrollers, and the emergence of various computer generations. Additionally, it discusses advancements in processing architectures, including parallel processing, RISC and CISC processors, and digital signal processors.