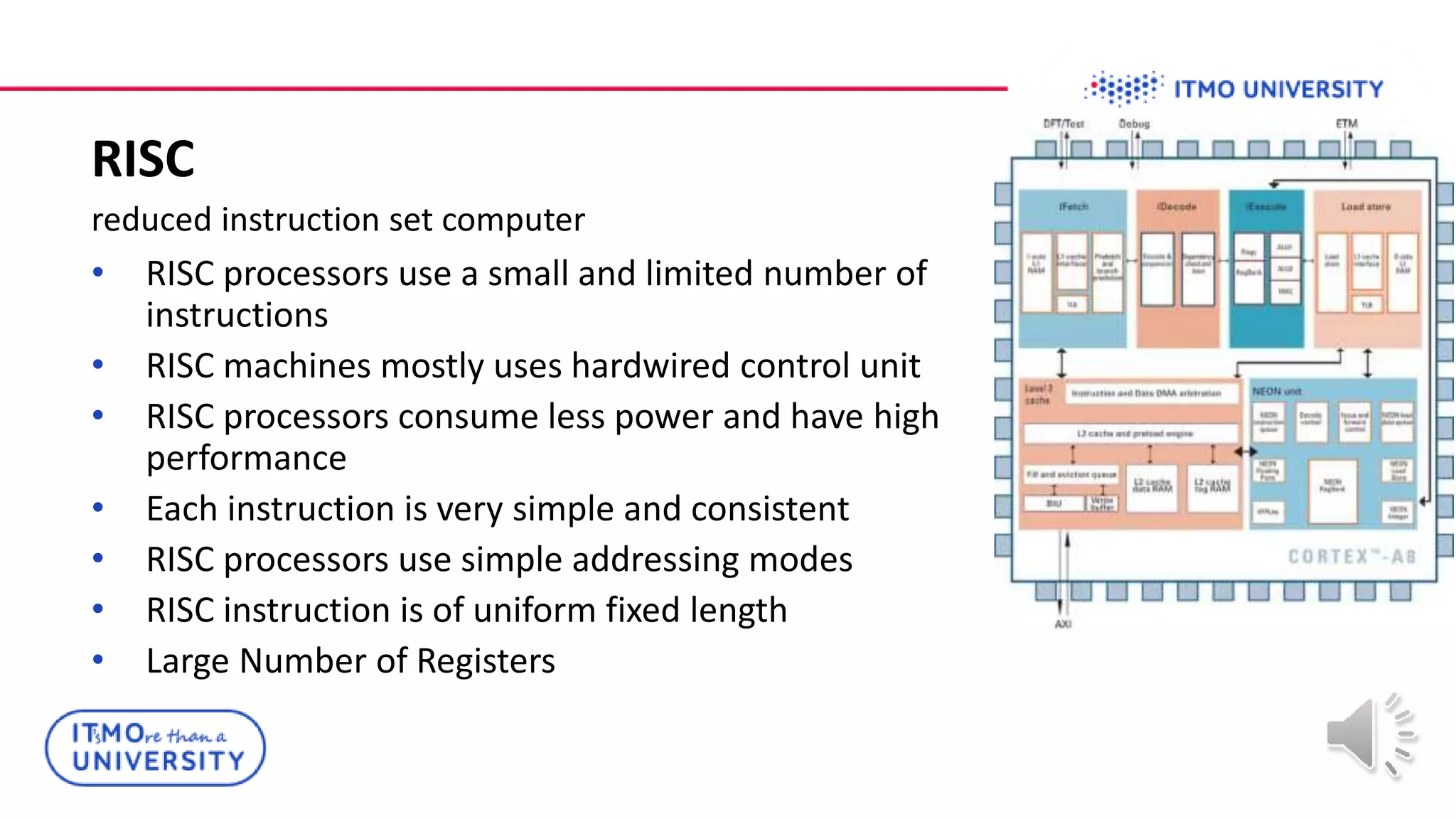
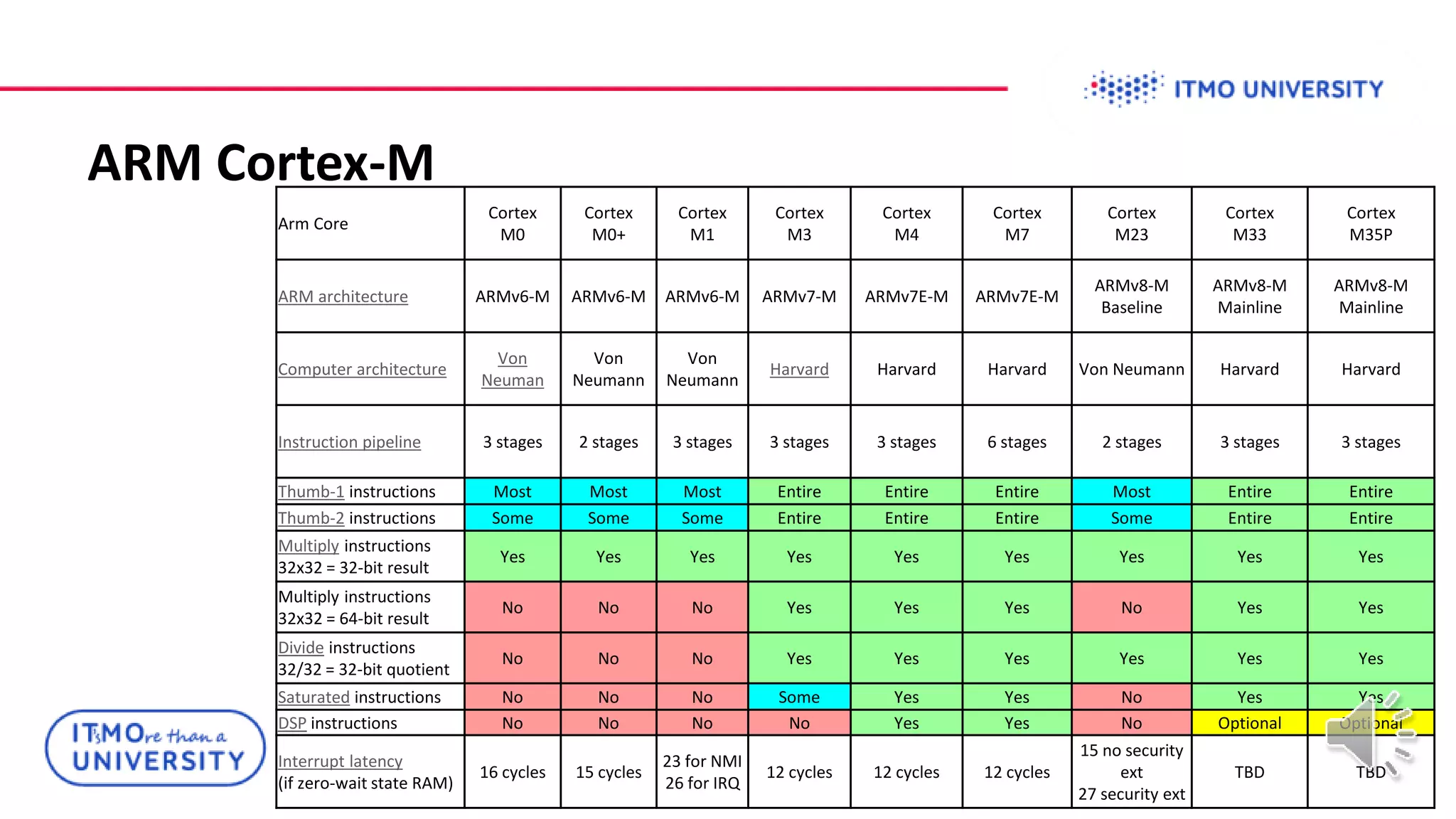
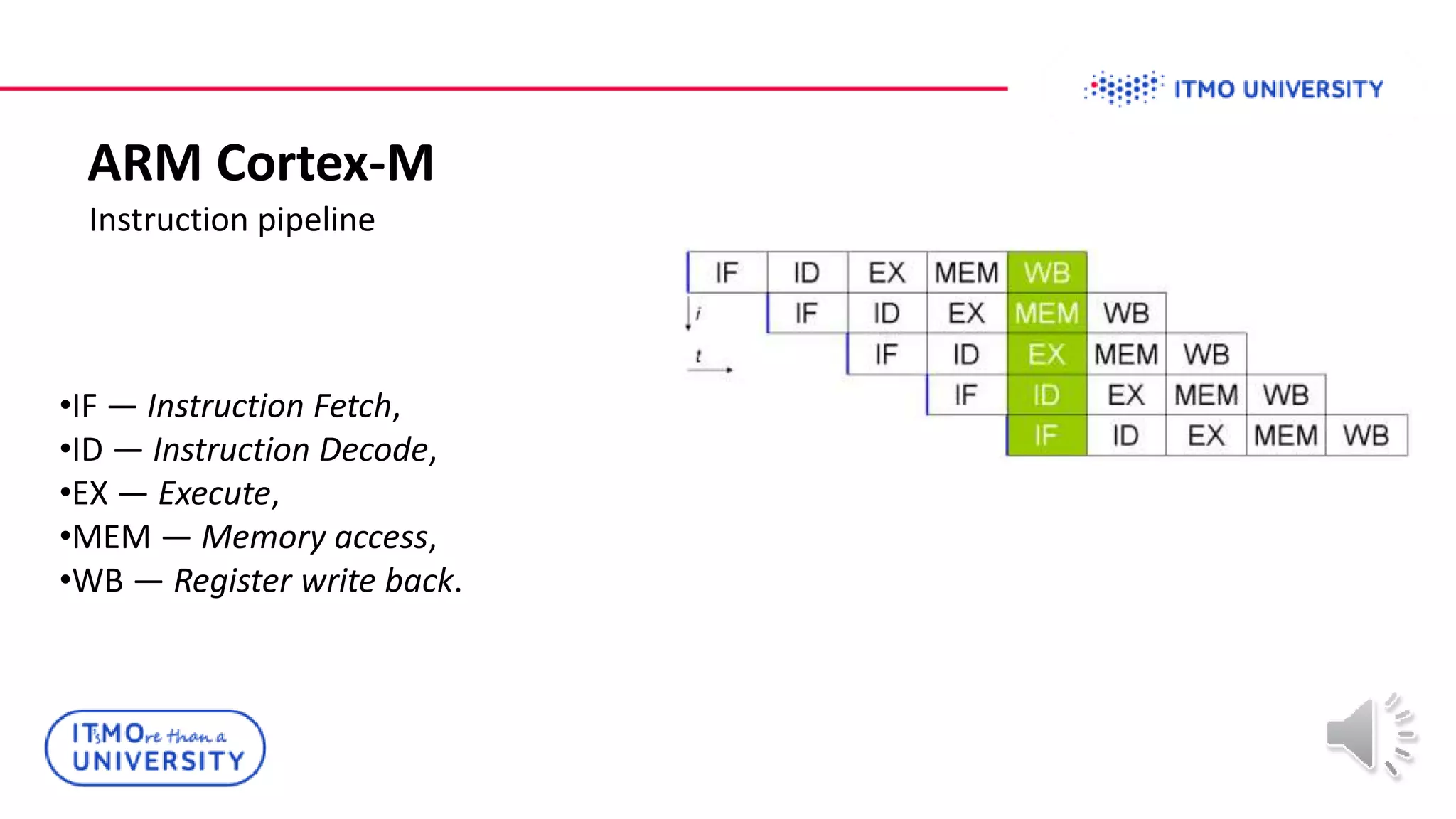
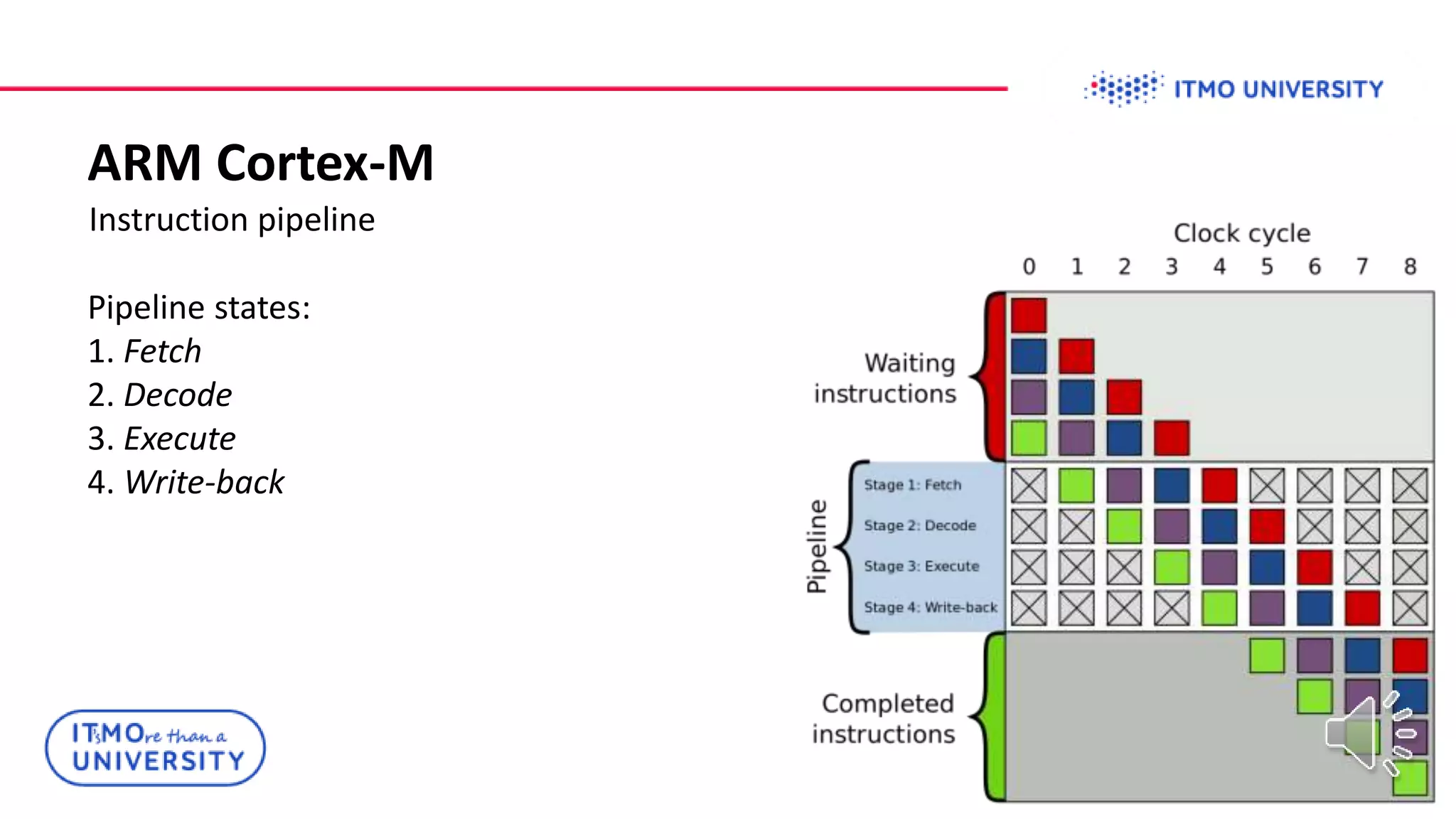
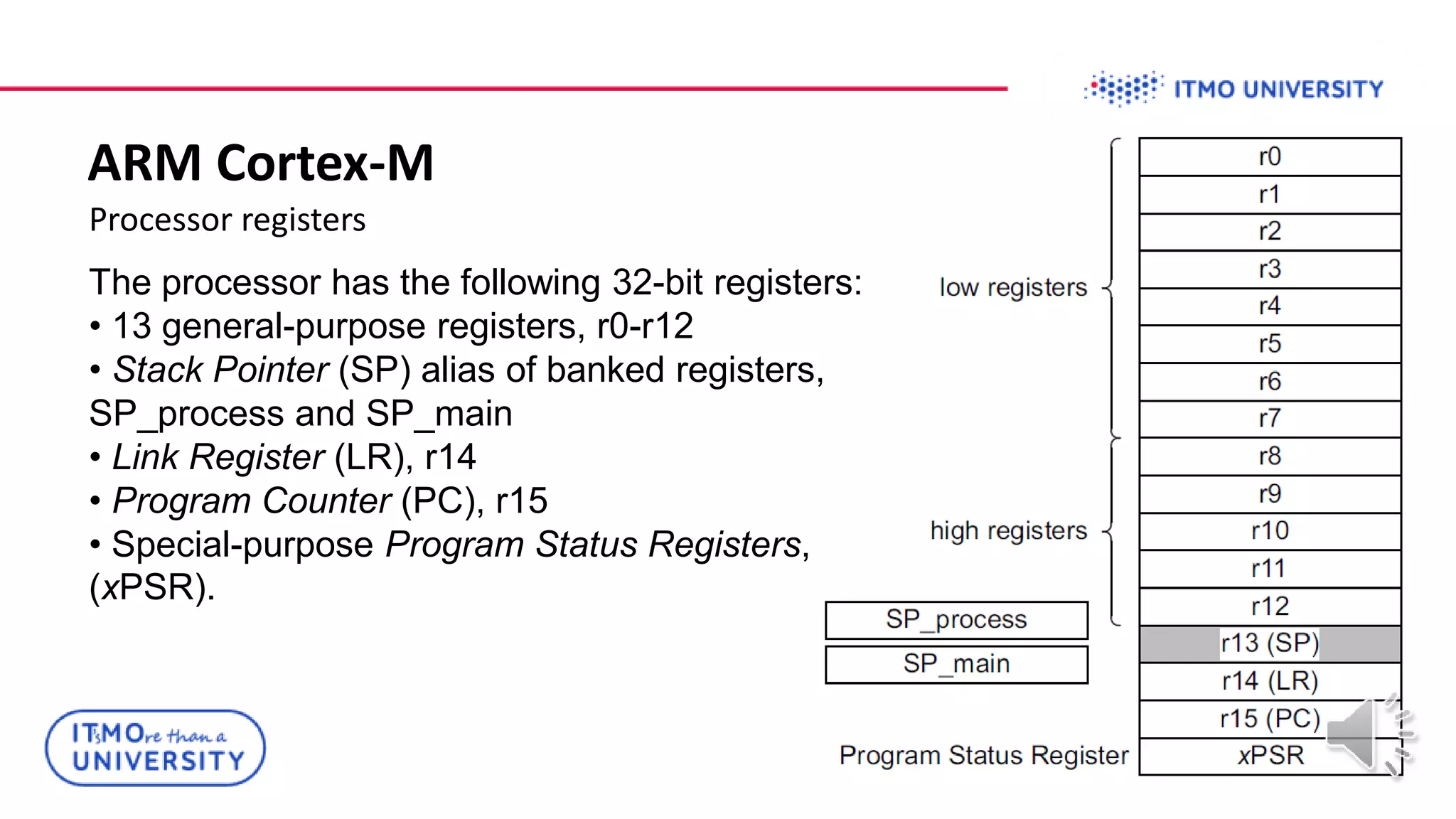
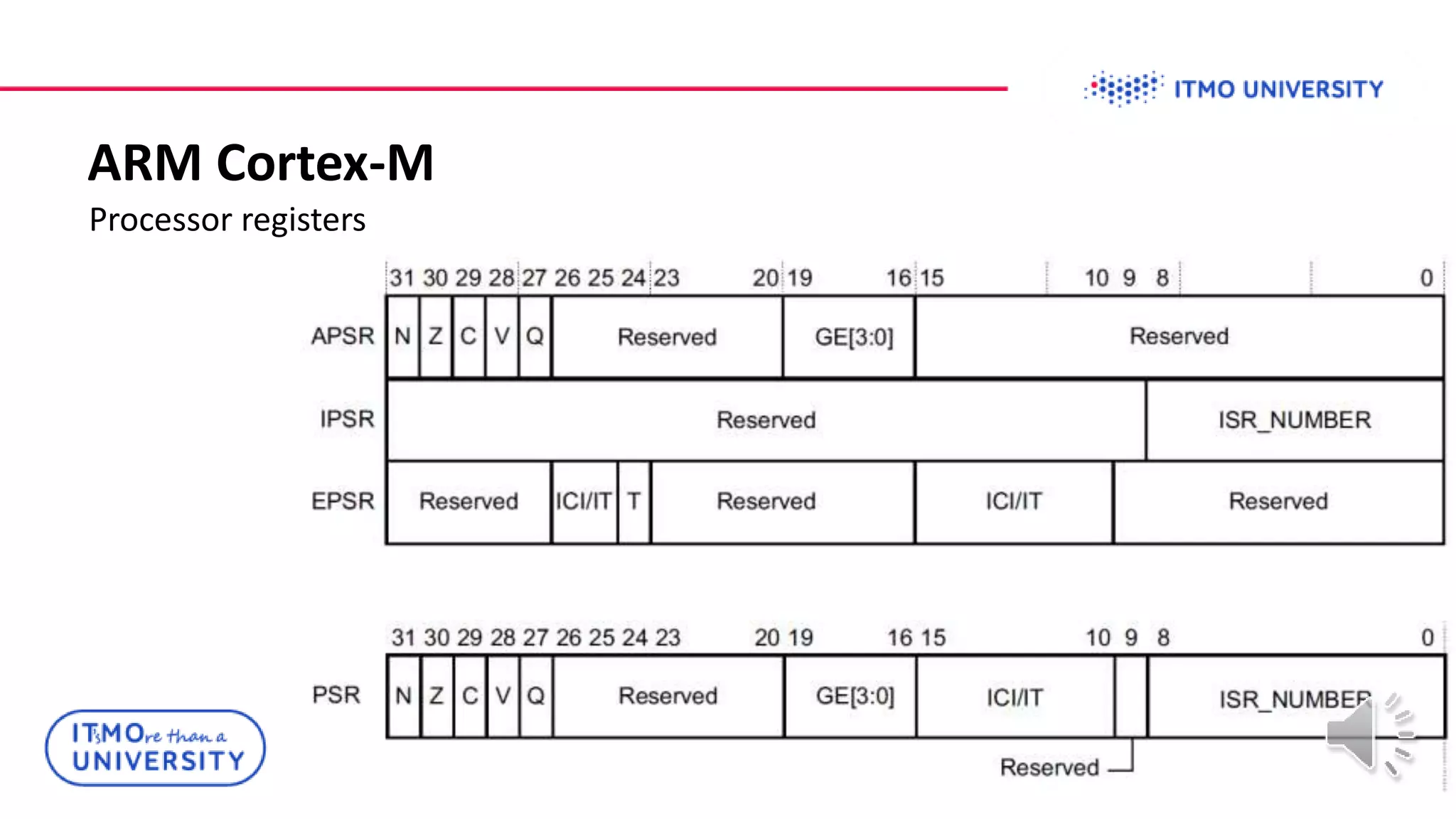
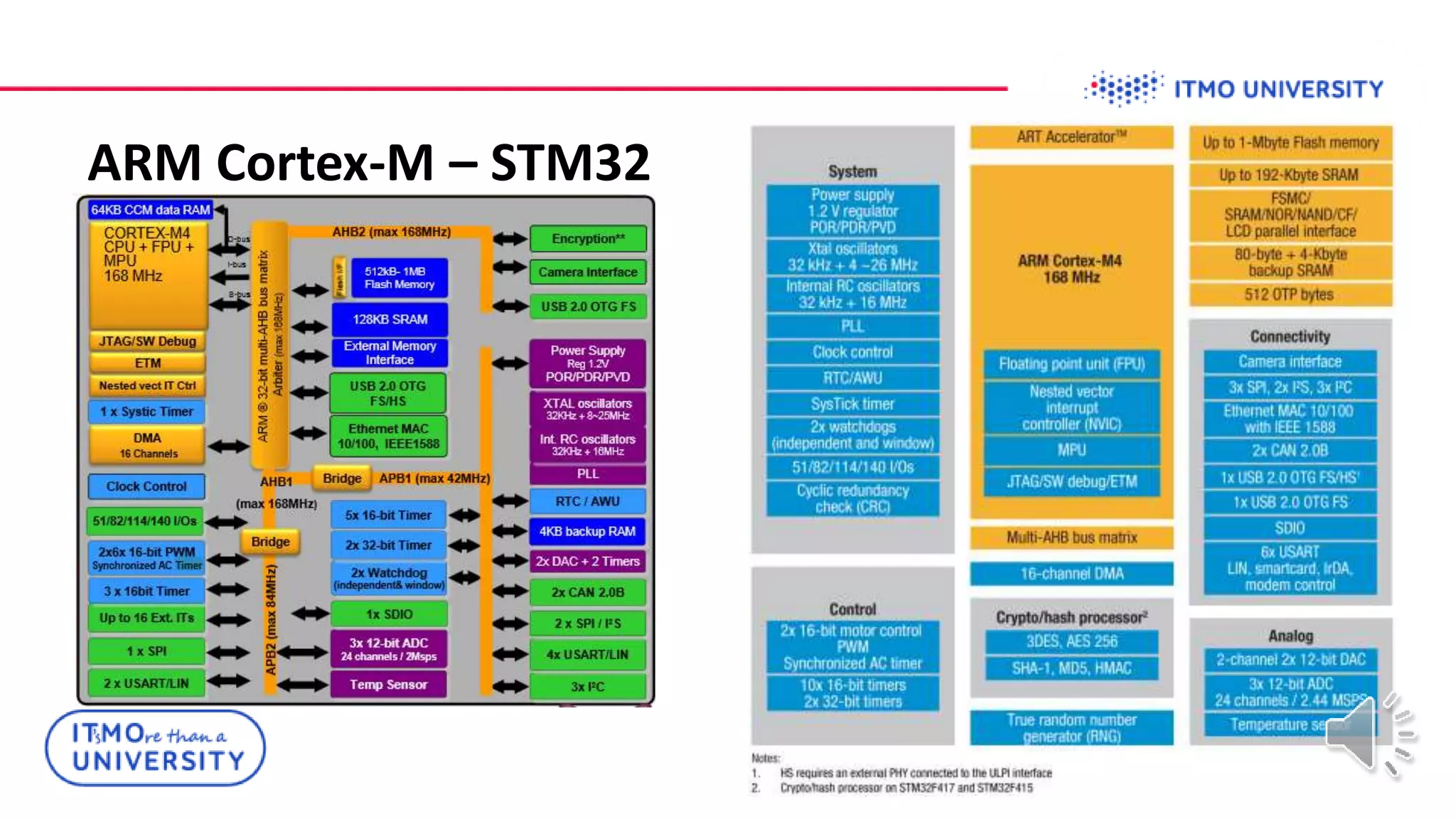
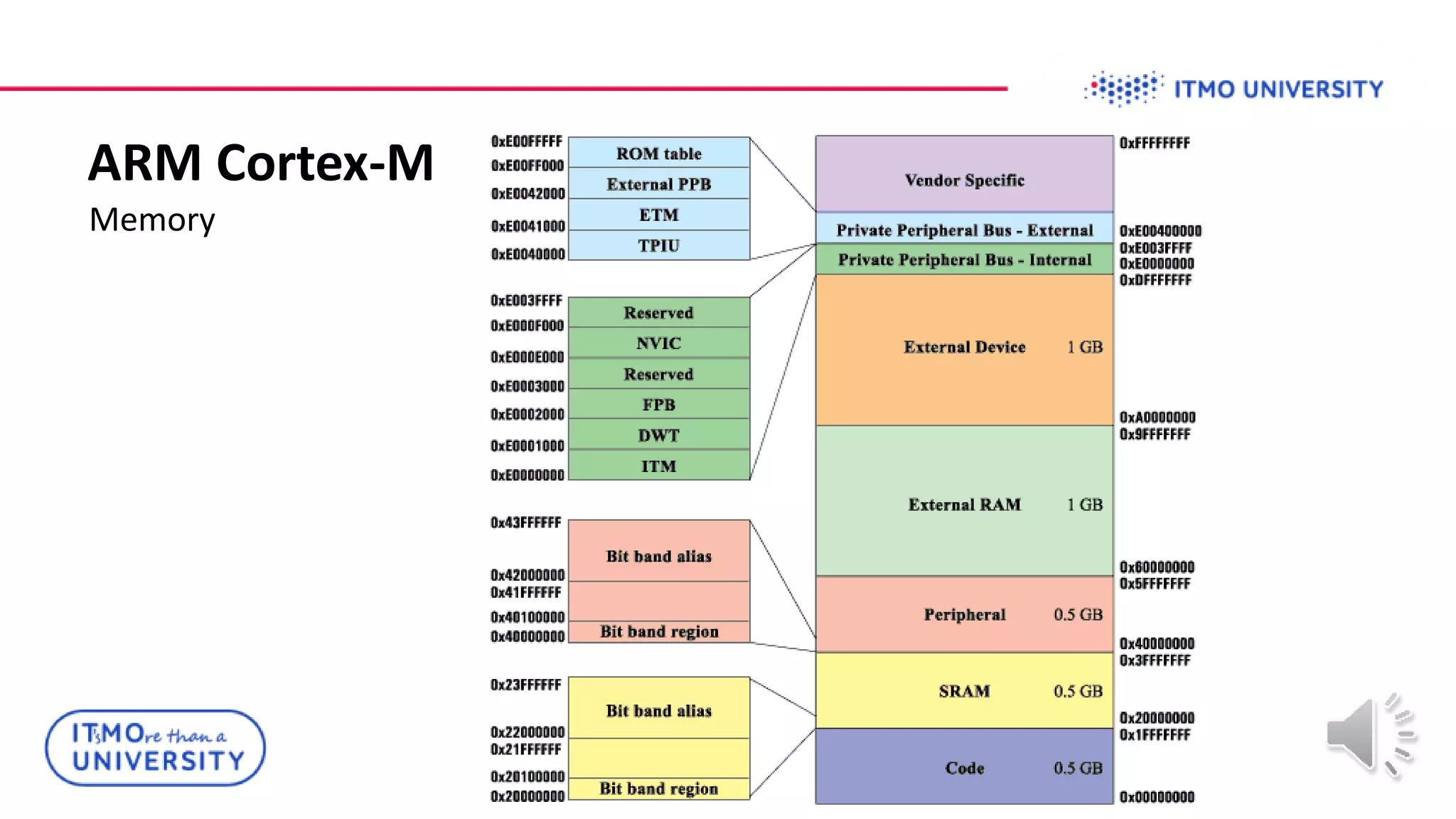
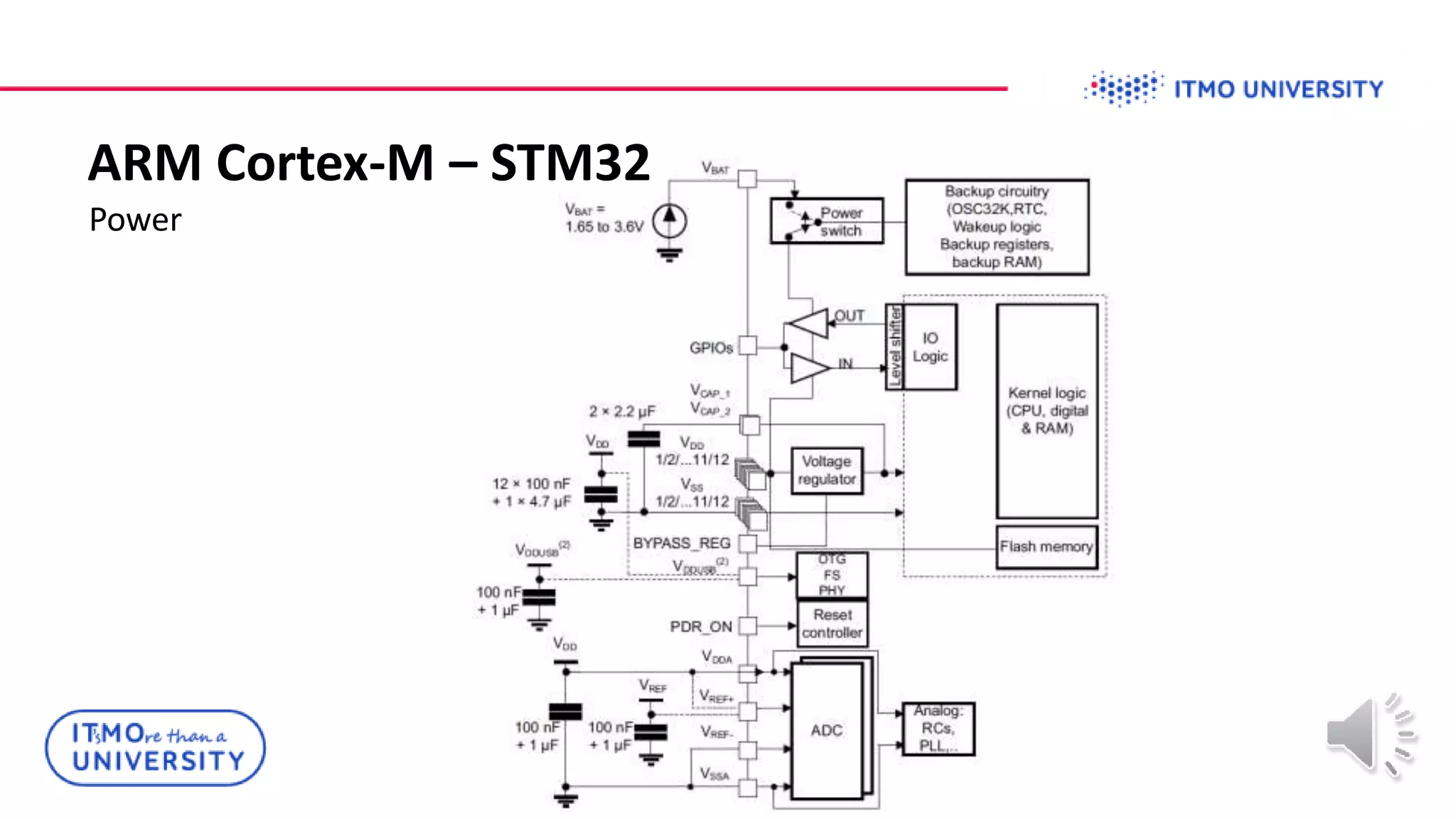
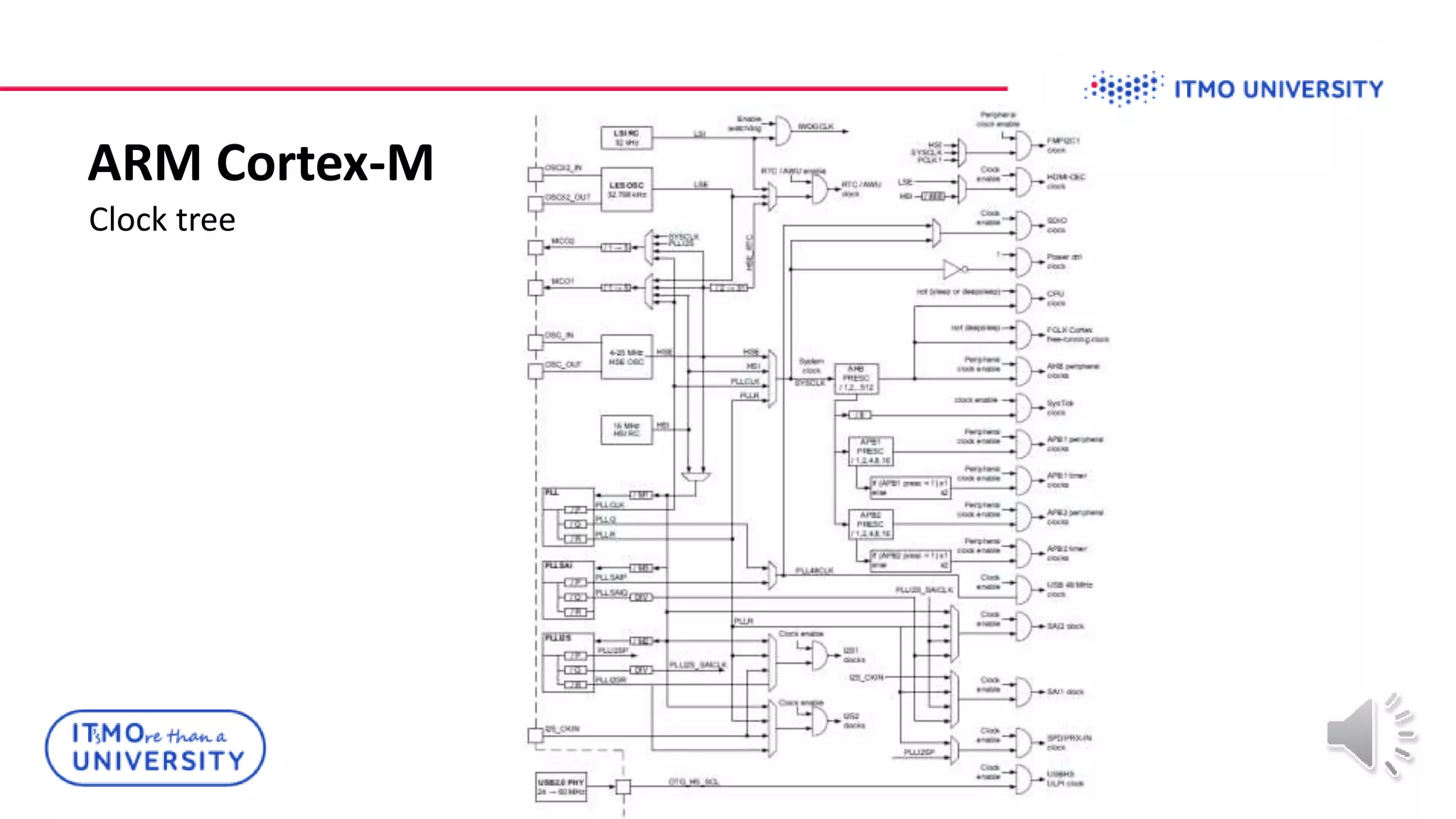
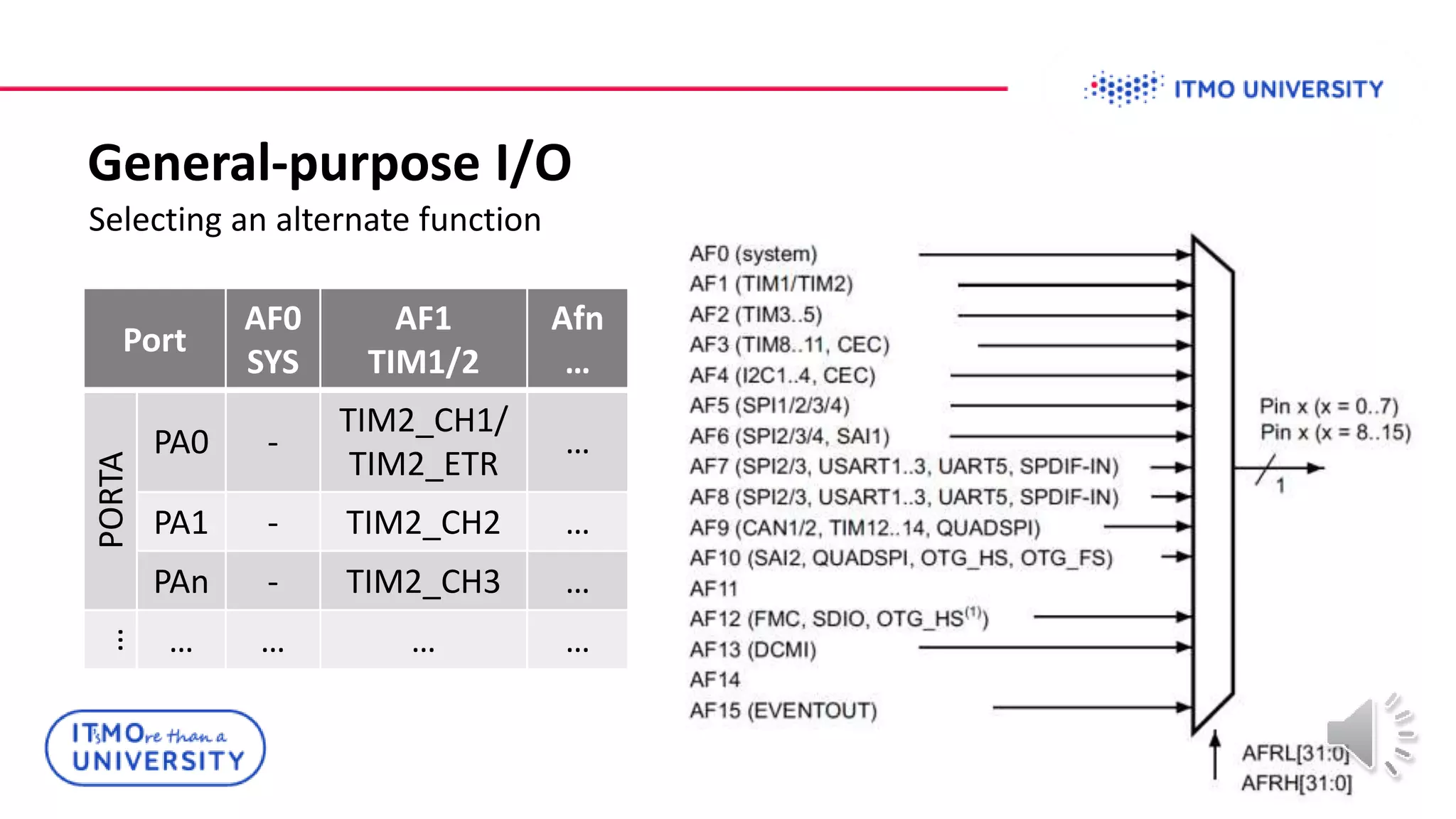
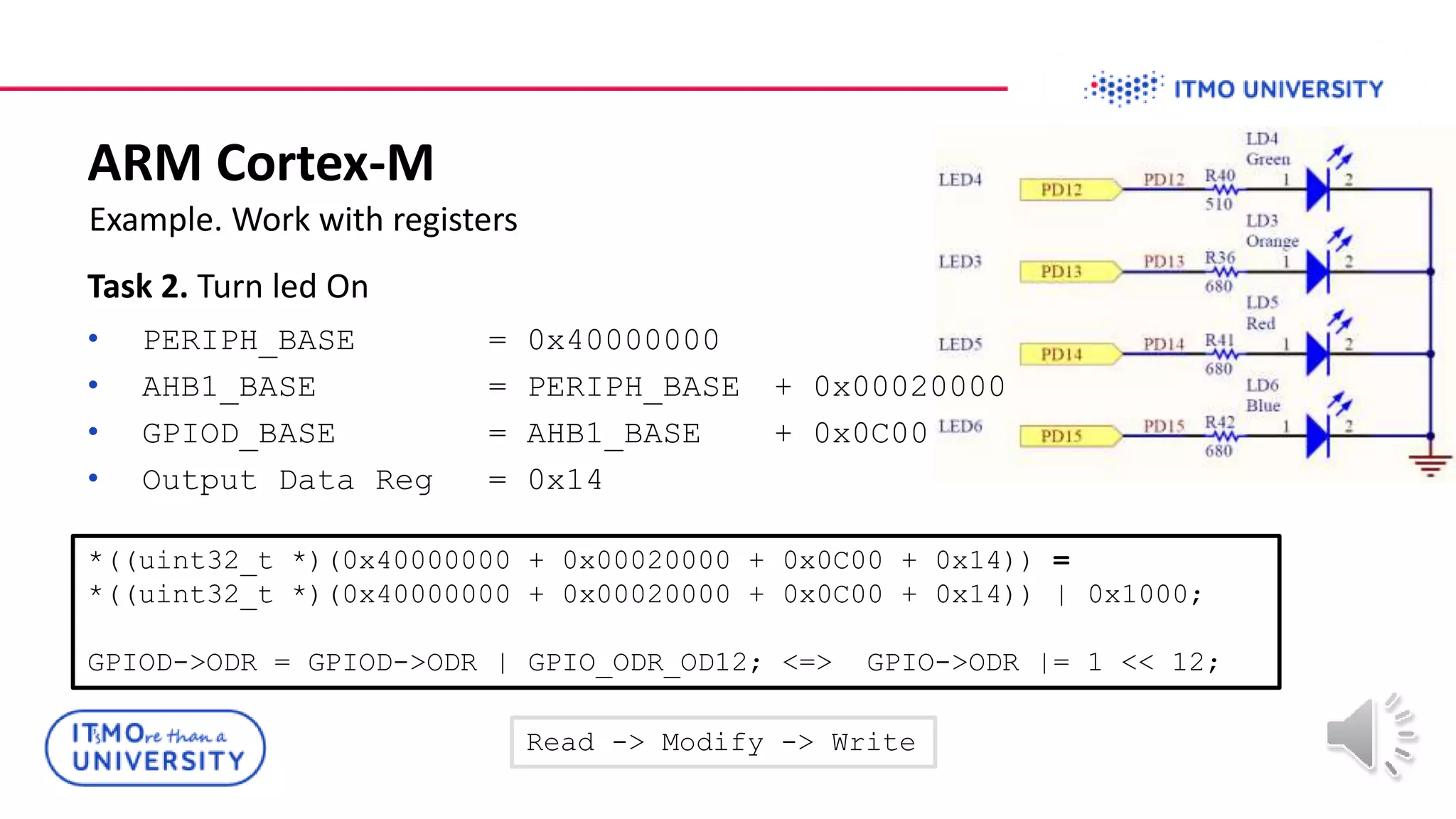
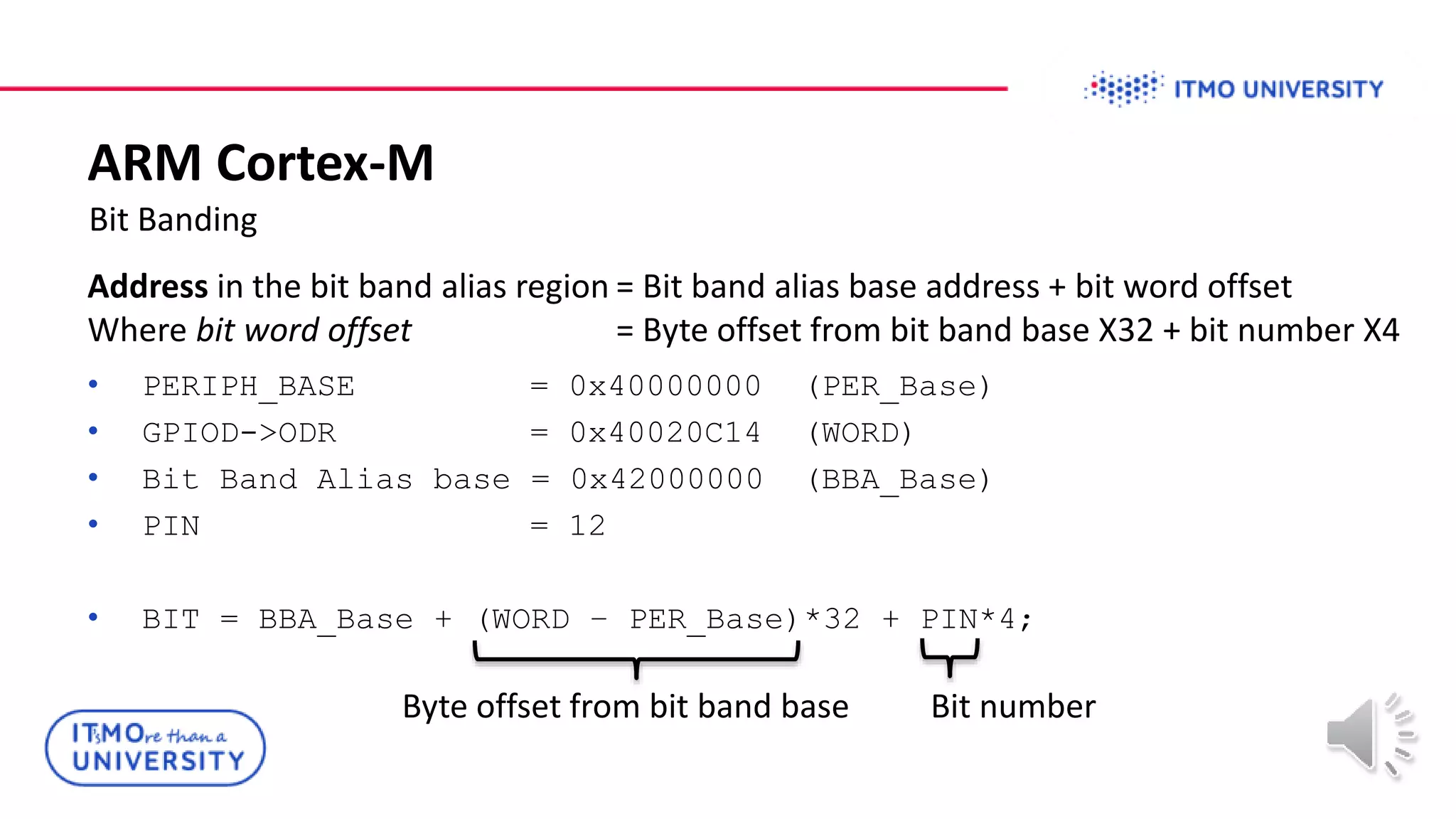
This document discusses ARM Cortex-M microcontrollers and their features. It provides information on ARM architecture and RISC processors. Specific Cortex-M models are described including their instruction sets, pipelines, registers and memory architecture. STM32 microcontrollers are mentioned. General purpose input/output and how to configure pins for different functions like GPIO, analog or alternate functions are explained. Examples of working with registers to read button states and toggle LEDs are provided. The concept of bit banding memory is also introduced.