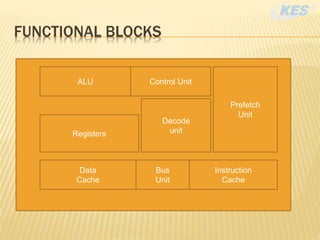
A microprocessor is a multi-programmable logic device commonly referred to as the brain of the computer, responsible for processing data through an input-process-output cycle. Its functionality relies on several primary blocks, including the arithmetic and logic unit and control unit, while its speed is influenced by factors like the number of instructions, bandwidth, clock speed, and the number of transistors. Additionally, multitasking technology allows the processor to run multiple programs at once, enhancing efficiency.