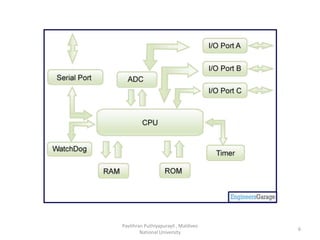
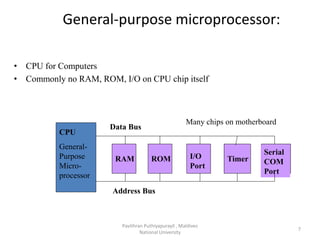
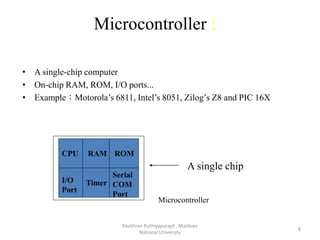
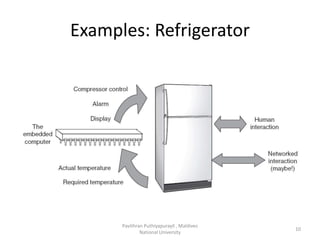
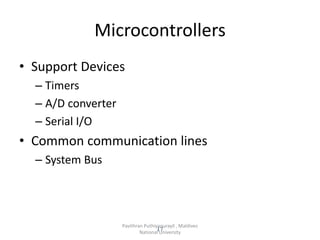
A microcontroller is a self-contained system with peripherals, memory and a processor that can be embedded in consumer products and machinery. Microcontrollers contain CPU, RAM, ROM, I/O ports, timers and counters to control input and output devices like sensors, displays and relays. They are used in applications where cost, power and space are critical constraints.