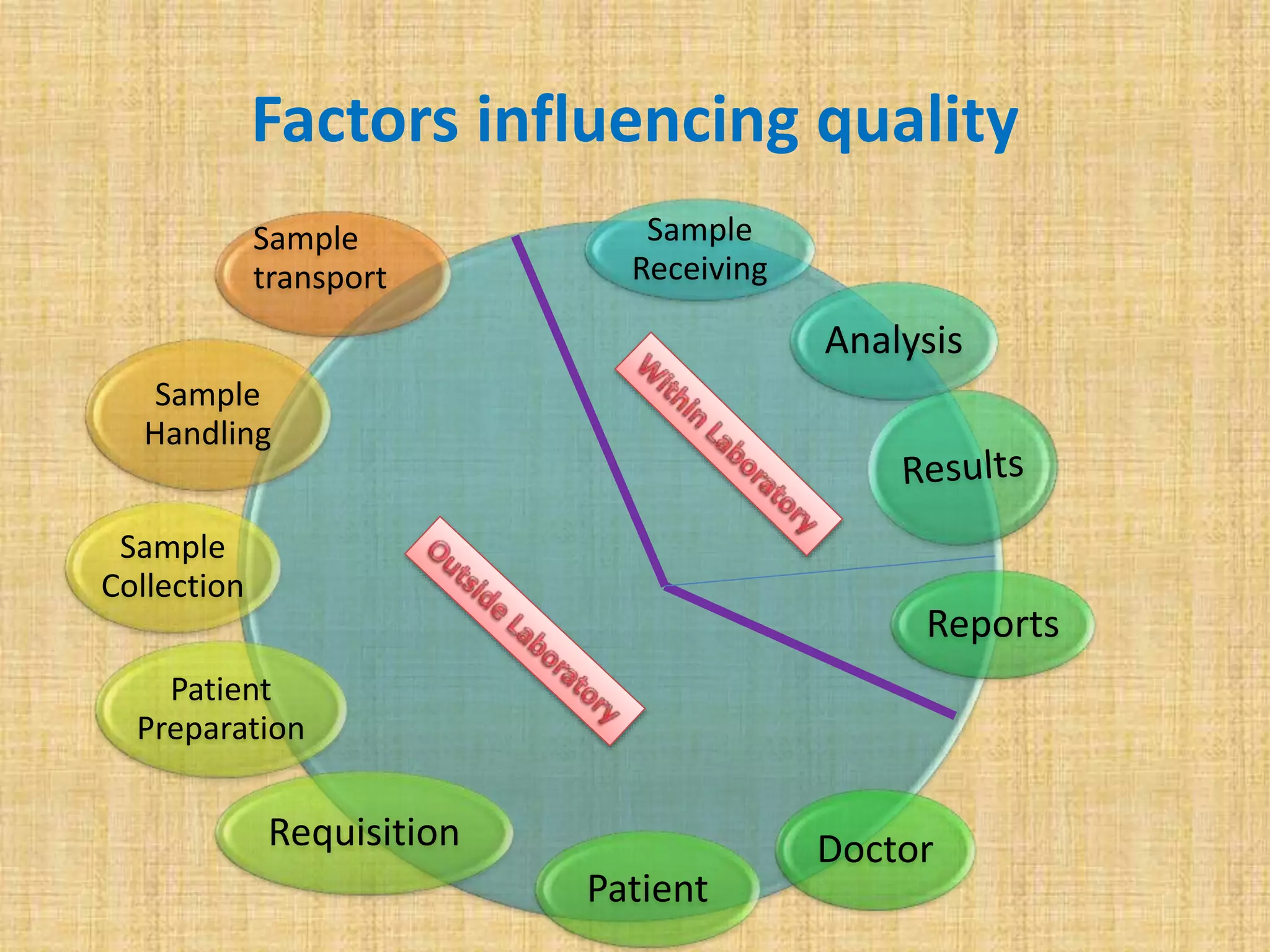
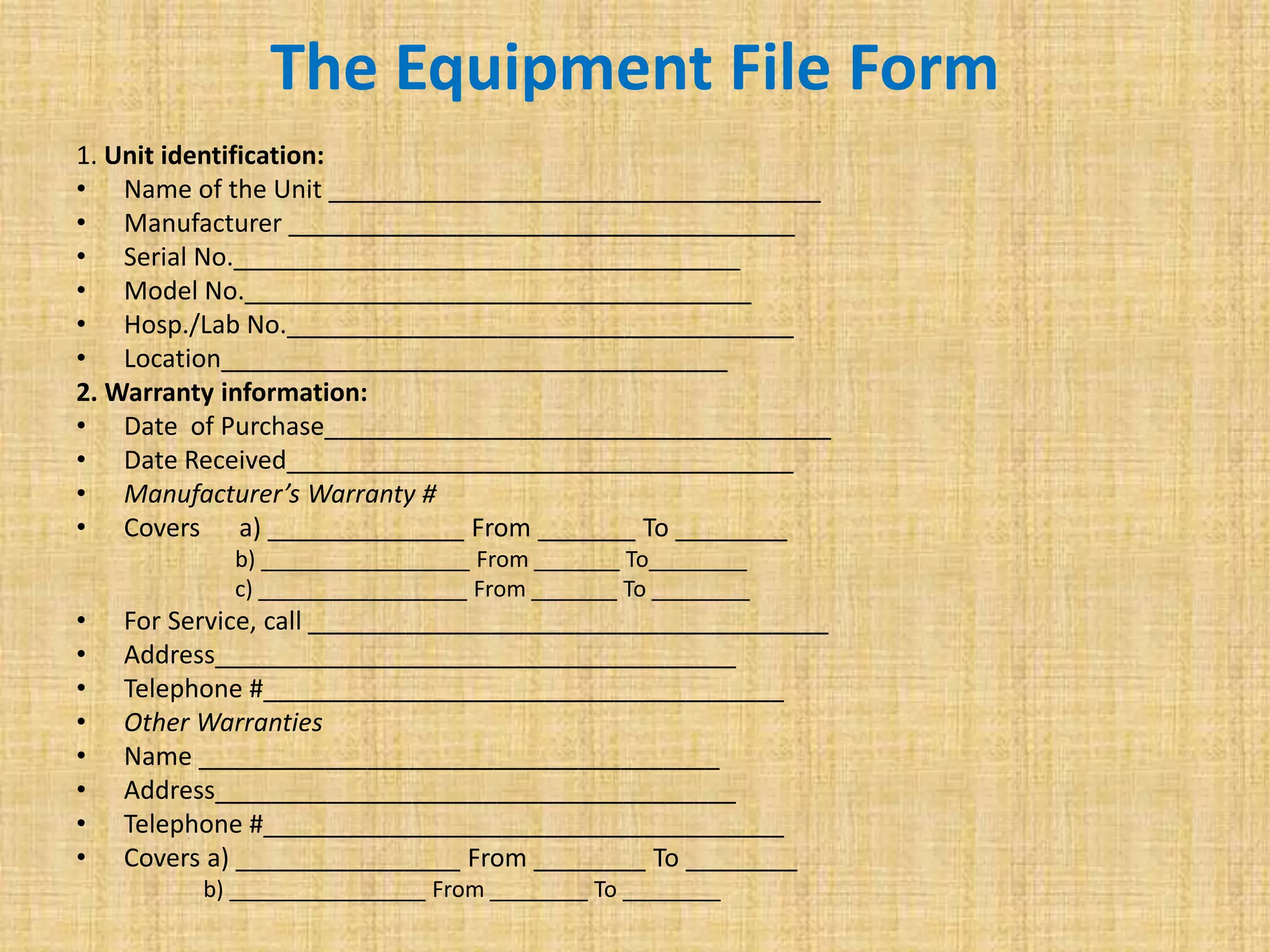
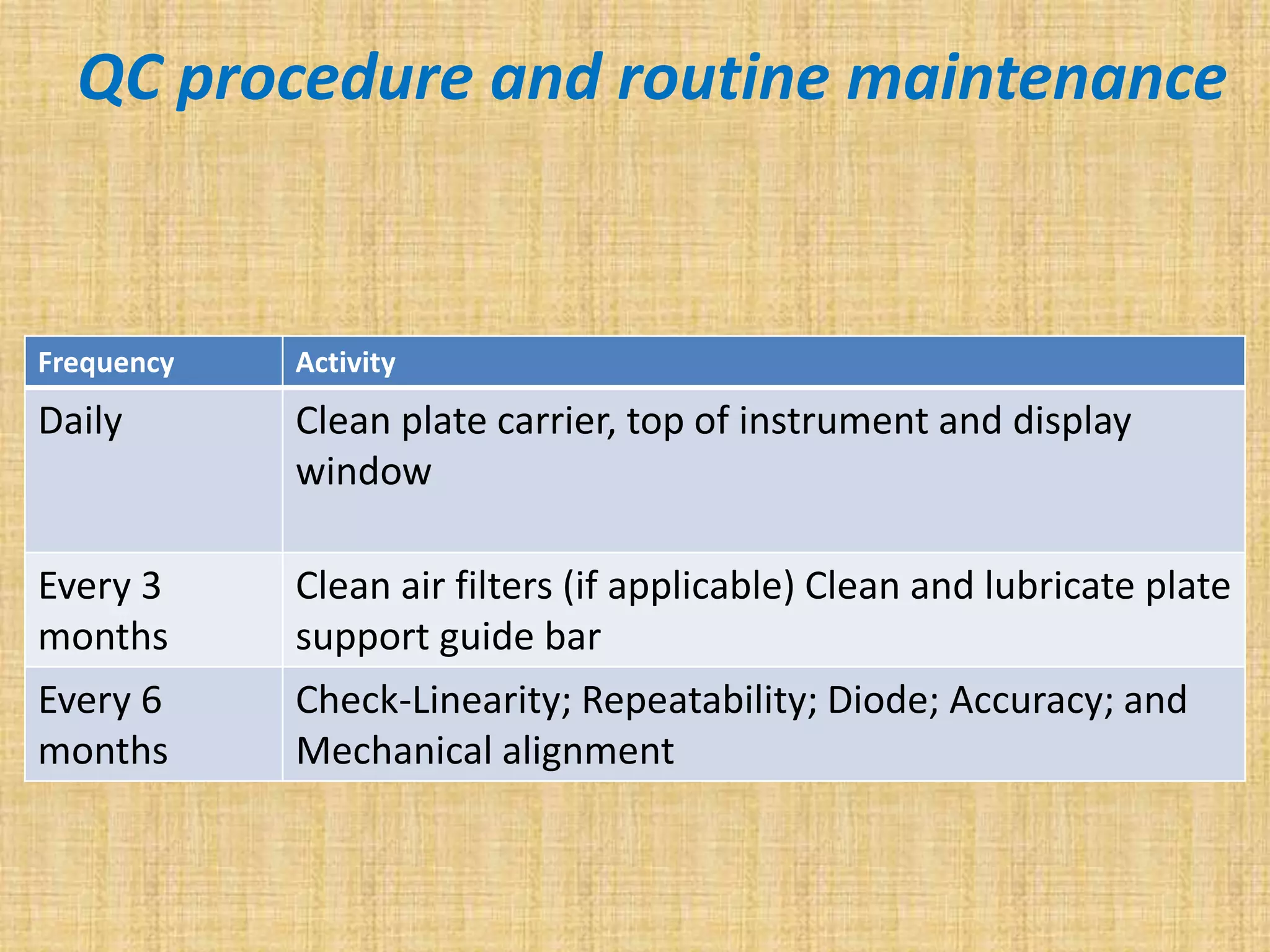
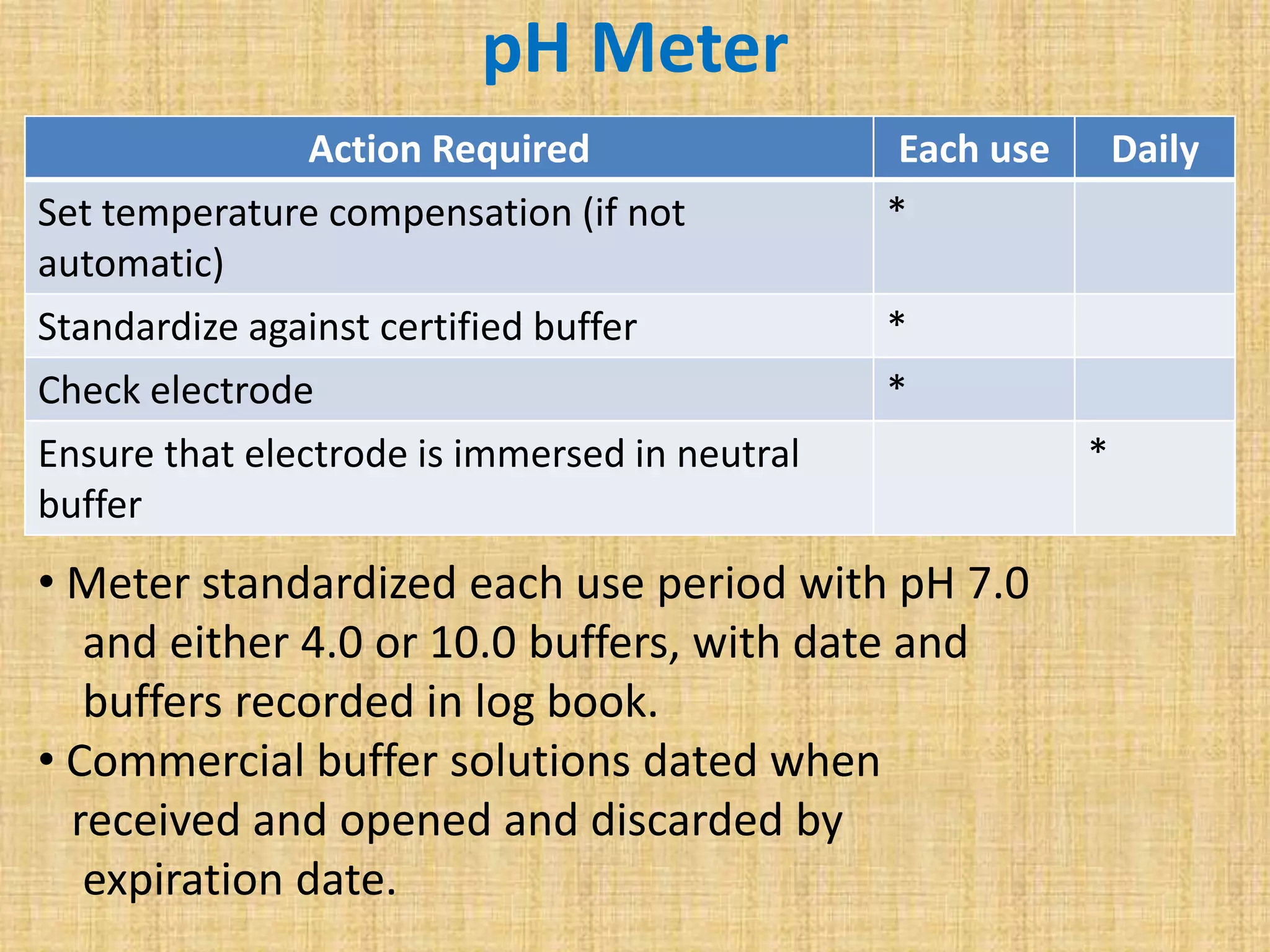
This document discusses quality assurance and quality control procedures for microlaboratories. It defines quality and quality management, and explains how quality is ensured in laboratories through controlling all factors that influence reliable test results. Quality assurance aims to ensure accurate and reliable data generation and use. Key quality control procedures discussed include regular equipment maintenance and calibration, sterilization validation methods, reagent and media quality control, and environmental monitoring. Adhering to these standardized quality control protocols is important for generating credible results and safeguarding patient health.