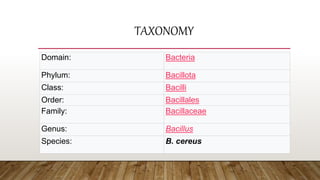
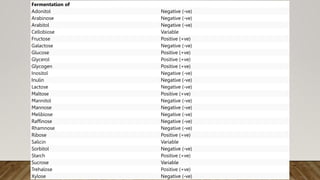
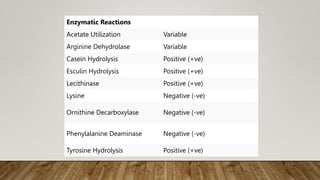
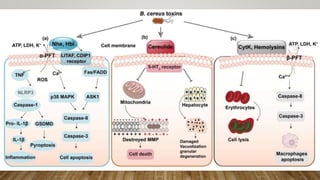
The document provides information about Bacillus cereus, including its taxonomy, morphology, cultural properties, biochemical properties, toxins, virulence factors, epidemiology, clinical symptoms, laboratory diagnostics, treatment, and prevention. B. cereus is a gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil and foods. It can cause two types of food poisoning - an emetic syndrome caused by a toxin and a diarrheal syndrome caused by three enterotoxins. Diagnosis involves microscopy, culture, and PCR detection of toxin genes. While usually self-limiting, treatment may include rehydration and antibiotics for invasive infections. Prevention relies on proper food handling and storage.