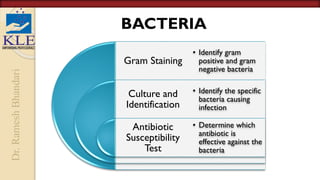
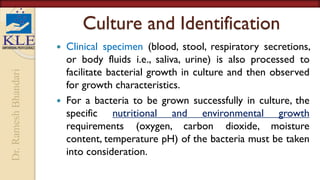
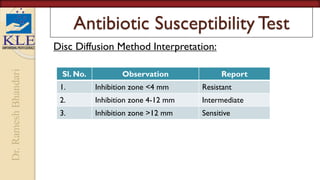
This document discusses microbiological culture sensitivity tests, which are used to identify bacteria causing infections and determine effective antibiotic treatment. The tests include gram staining to classify bacteria, culturing samples to grow bacteria and identify the specific species, and antibiotic susceptibility testing to see which antibiotics will inhibit or kill the bacteria. Gram staining provides a rapid preliminary analysis, while culturing can identify bacteria within hours to days. Antibiotic susceptibility testing then determines the most effective antibiotics through measurement of inhibition in dilution or disk diffusion assays. Together these tests guide appropriate antibiotic selection for treating bacterial infections.