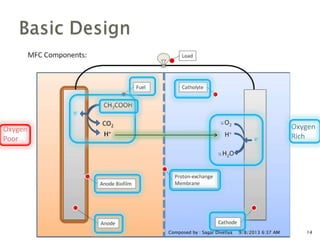
The document discusses microbial fuel cells (MFCs), which convert chemical energy from organic materials into electrical energy through the interaction of microorganisms. It highlights their basic design, components, applications, advantages, limitations, and their potential future in environmental technology, particularly in wastewater treatment and power generation. The MFC technology, while promising, faces challenges such as economic competitiveness and limited current production.