This document provides an overview of topics related to environmental science and sustainability. It includes sections on:
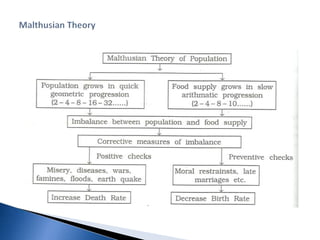
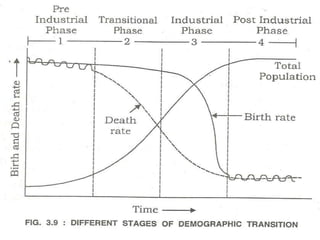
1. Human population and demographics like growth rates, structures, and projections.
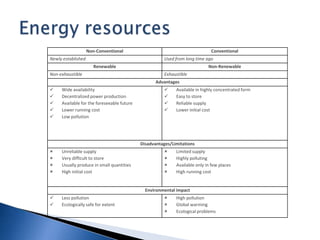
2. Renewable and non-renewable resources like forests, water, and energy. It discusses uses, conservation, and problems from overexploitation.
3. Key concepts in environmental science like habitats, pollution, and effects of deforestation. Diagrams, definitions, and exam strategies are also provided to help students understand and apply the content.



















![ Forest Types
◦ Tropical Rain forest – (rain whole year) [Tropical = Near Equator]
◦ Tropical Deciduous forest – (rain only in monsoon)
◦ Tropical Shrub Forest – (longer dry season less rain)
◦ Temperate Deciduous forest – (Moderate temperature & rainfall throughout
the year)
◦ Evergreen Coniferous forest (Boreal forests)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationes-130908090038-/85/Population-growth-and-Natural-resources-22-320.jpg)