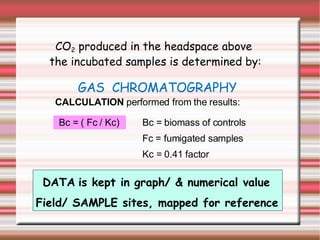
Microbial biomass in soil is affected by land use and management practices that influence microbial processes and soil nutrient availability. The document outlines a method for measuring this biomass through soil extraction, chloroform fumigation, and subsequent incubation to analyze carbon and nitrogen concentrations. It highlights the importance of monitoring soil quality for sustainable agriculture and details analytical techniques and tools used in the measurement process.