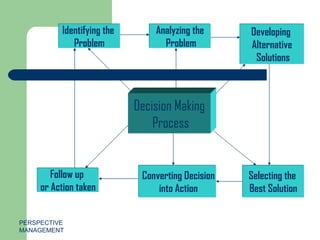
Decision making is a fundamental aspect of management that involves choosing between alternative courses of action to achieve desired results. Managers must make decisions to solve problems, and monitor the consequences to determine if further decisions are needed. There are different types of decisions like basic one-time decisions, routine repetitive decisions, programmed structured recurring decisions, and non-programmed unique situation decisions. Decision making can also be classified as personal, organizational, strategic, operational, problem-solving, opportunity-based, structured, unstructured, crisis-based, research-based, initiative, and referred. The typical decision making process involves awareness of a problem, diagnosing and stating the problem, developing alternatives, analyzing alternatives, selecting the best solution, and implementing and