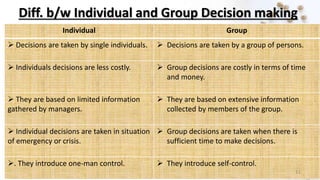
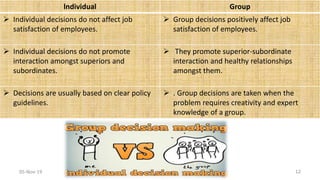
This document discusses individual and group decision making. It defines decision making as selecting a course of action from alternatives to achieve an objective or solve a problem. Decision making has three components: objectives/problems, alternatives, and choice. The process of decision making involves identifying the decision, gathering information, identifying alternatives, evaluating alternatives, choosing, taking action, and reviewing the decision. Individual decision making is done by a single manager for small problems, while group decision making utilizes the expertise of multiple people. Advantages of individual decisions include speed while group decisions benefit from diverse perspectives and acceptance of the decision.