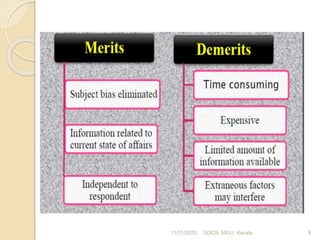
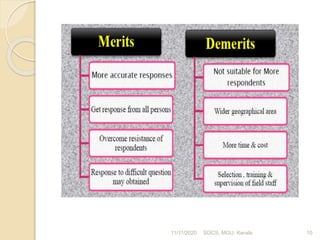
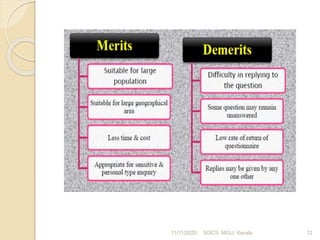
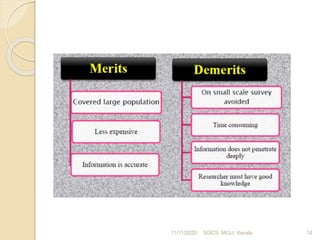
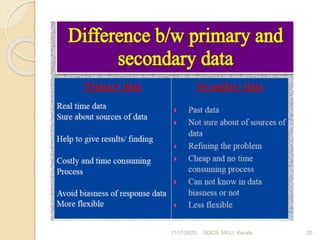
This document discusses methods of collecting data for research. It describes primary and secondary data collection. For primary data, methods include observation, interviews, questionnaires, surveys, and case studies. Observation can be structured or unstructured, while interviews are standardized or non-standardized. Secondary data involves data already collected from sources like books, journals, published websites, and organizational records. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages relating to cost, time, accuracy, and control. The document was presented by Bilal Sultan and provides an overview of key data collection techniques for research.