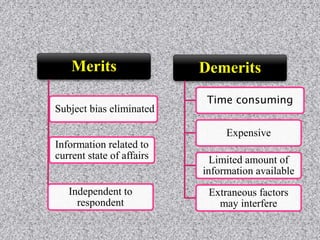
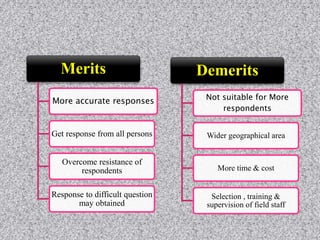
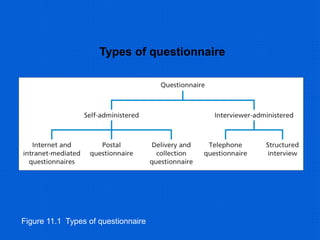
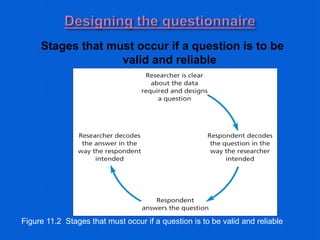
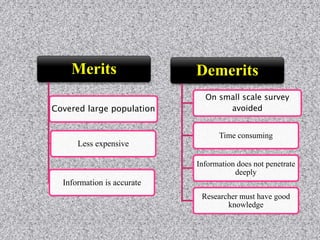
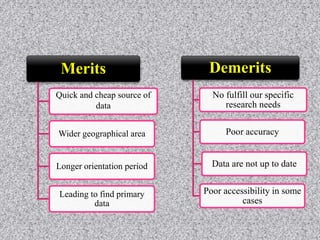
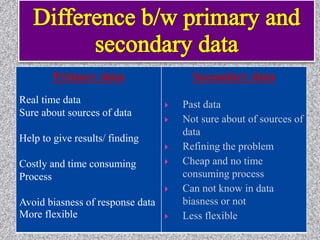
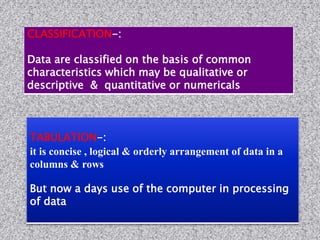
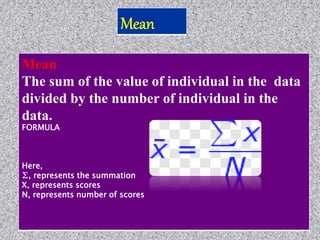
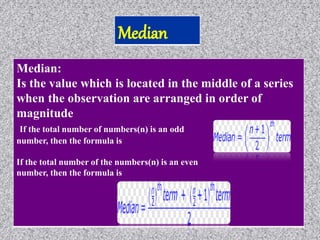
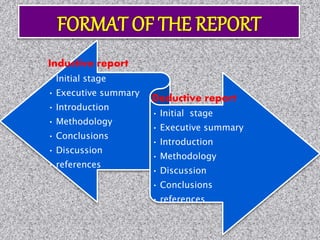
This document provides information about data collection and analysis. It discusses the purpose and types of data collection, including primary and secondary sources. It also outlines various methods of data collection like surveys, interviews, questionnaires and observation. The document then discusses data processing steps like editing, coding, classification and tabulation. It describes various techniques for data analysis including parametric and non-parametric tests. It also discusses measures of central tendency, dispersion and different types of graphical representations. Finally, it touches upon report writing and the key elements of a good report.