Embed presentation
Downloaded 174 times

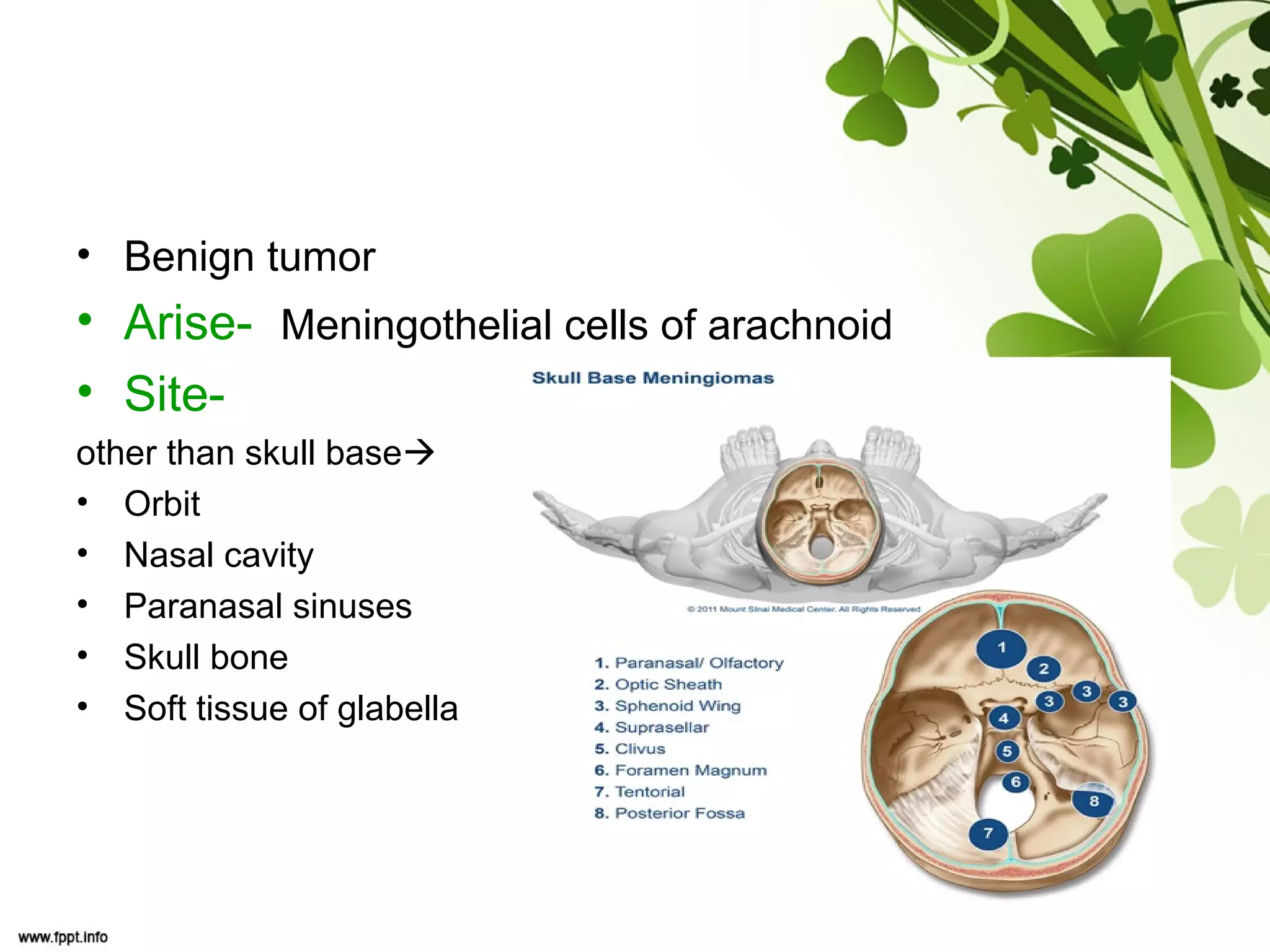

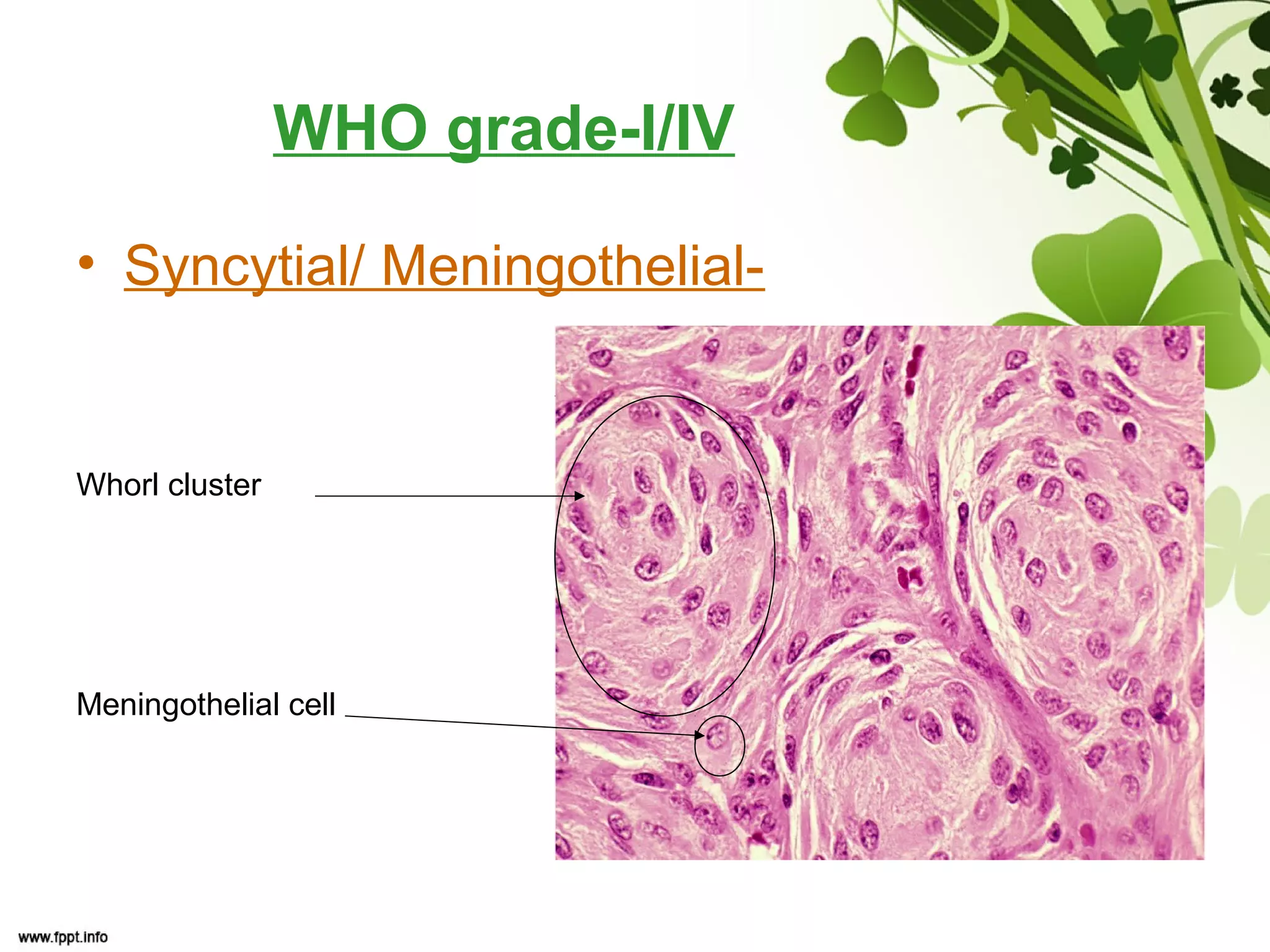
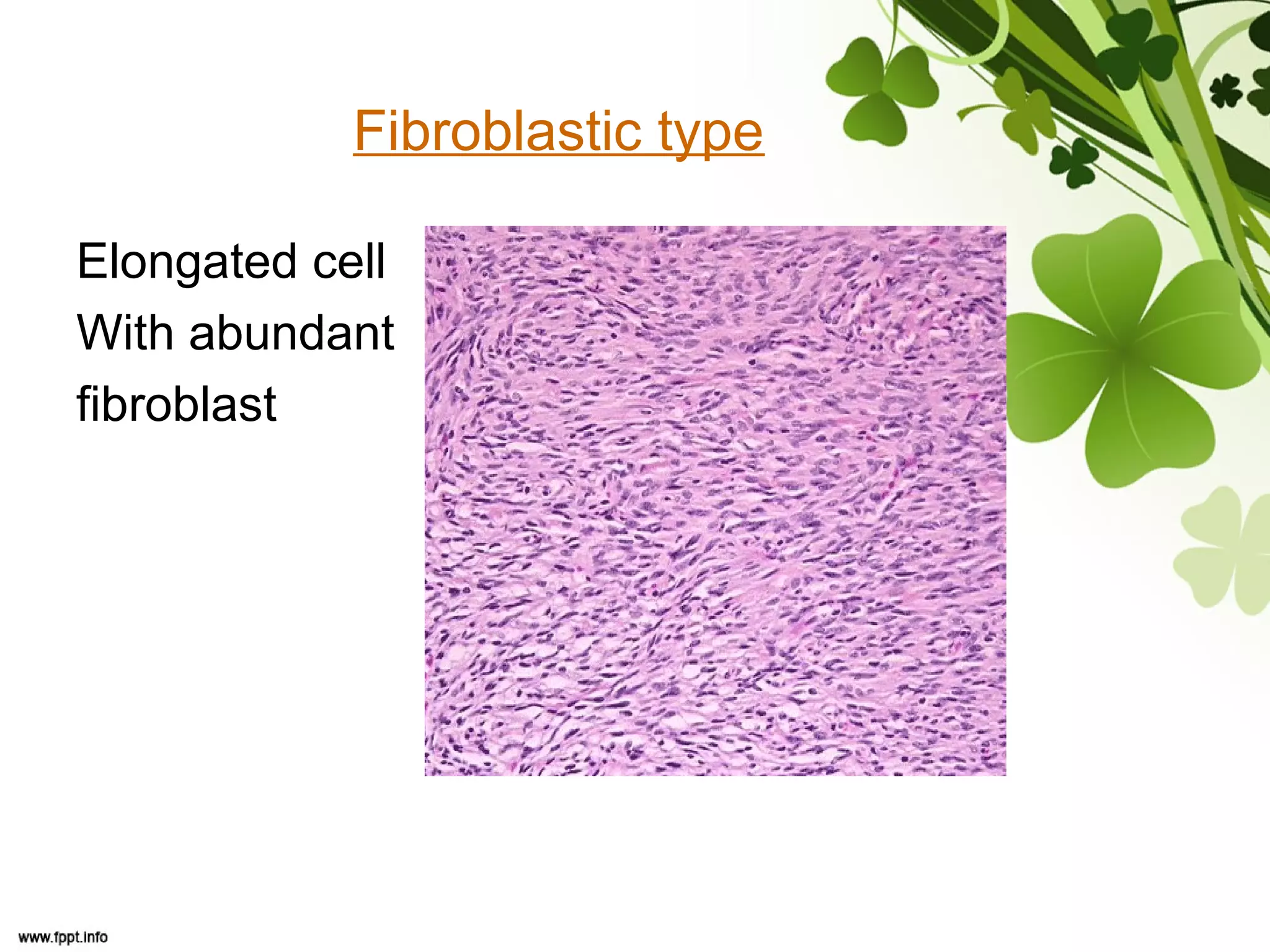
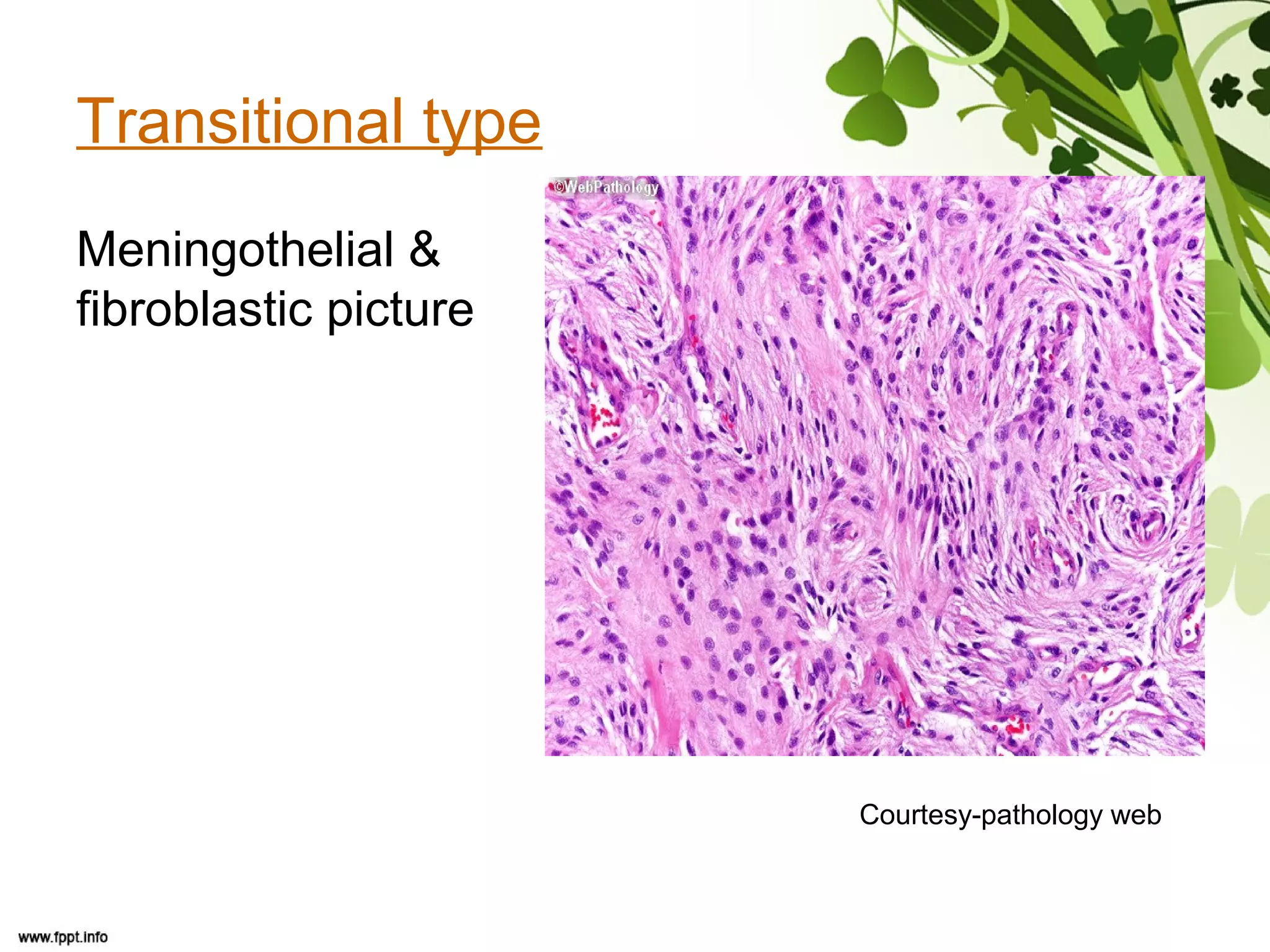
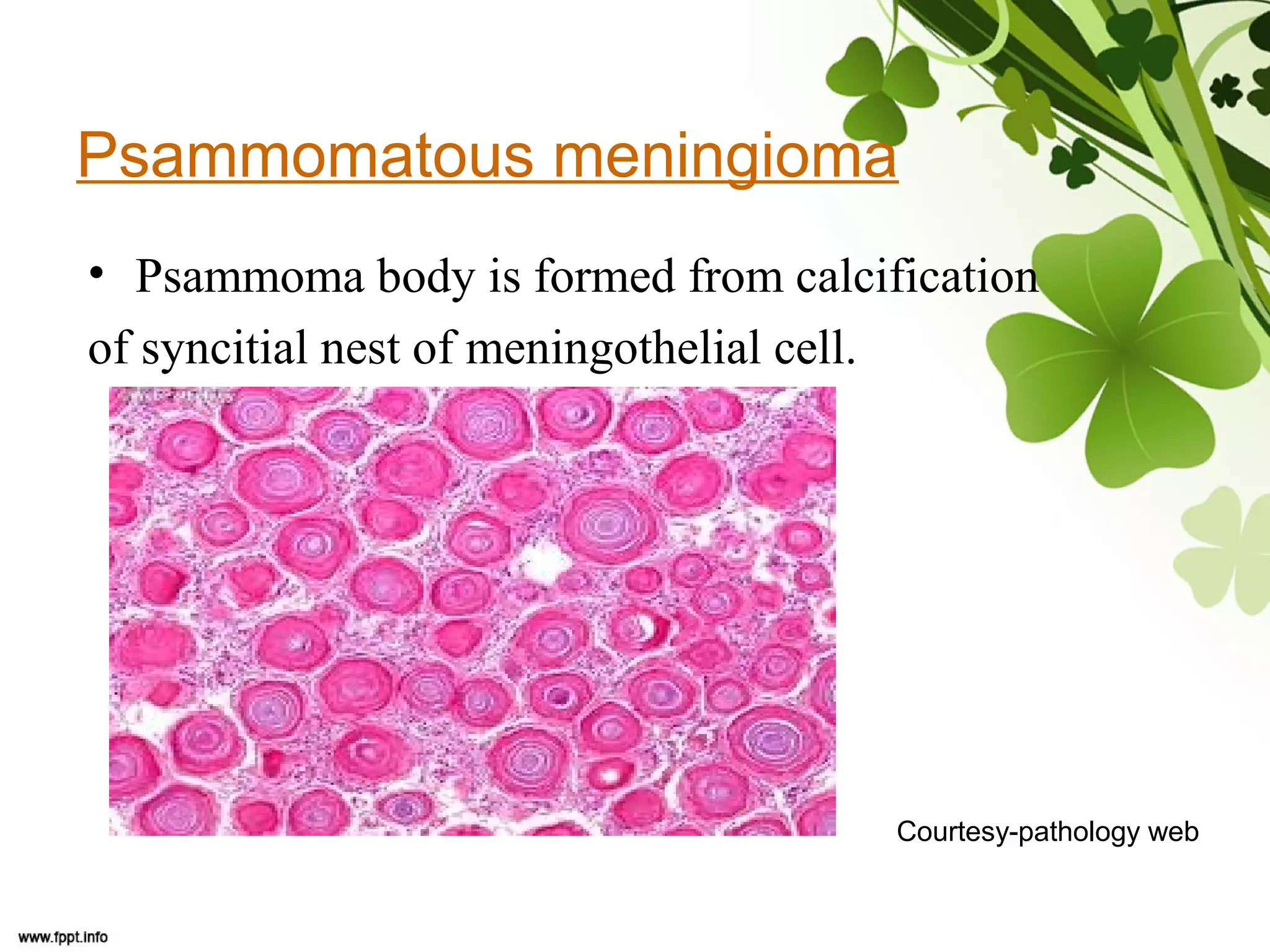
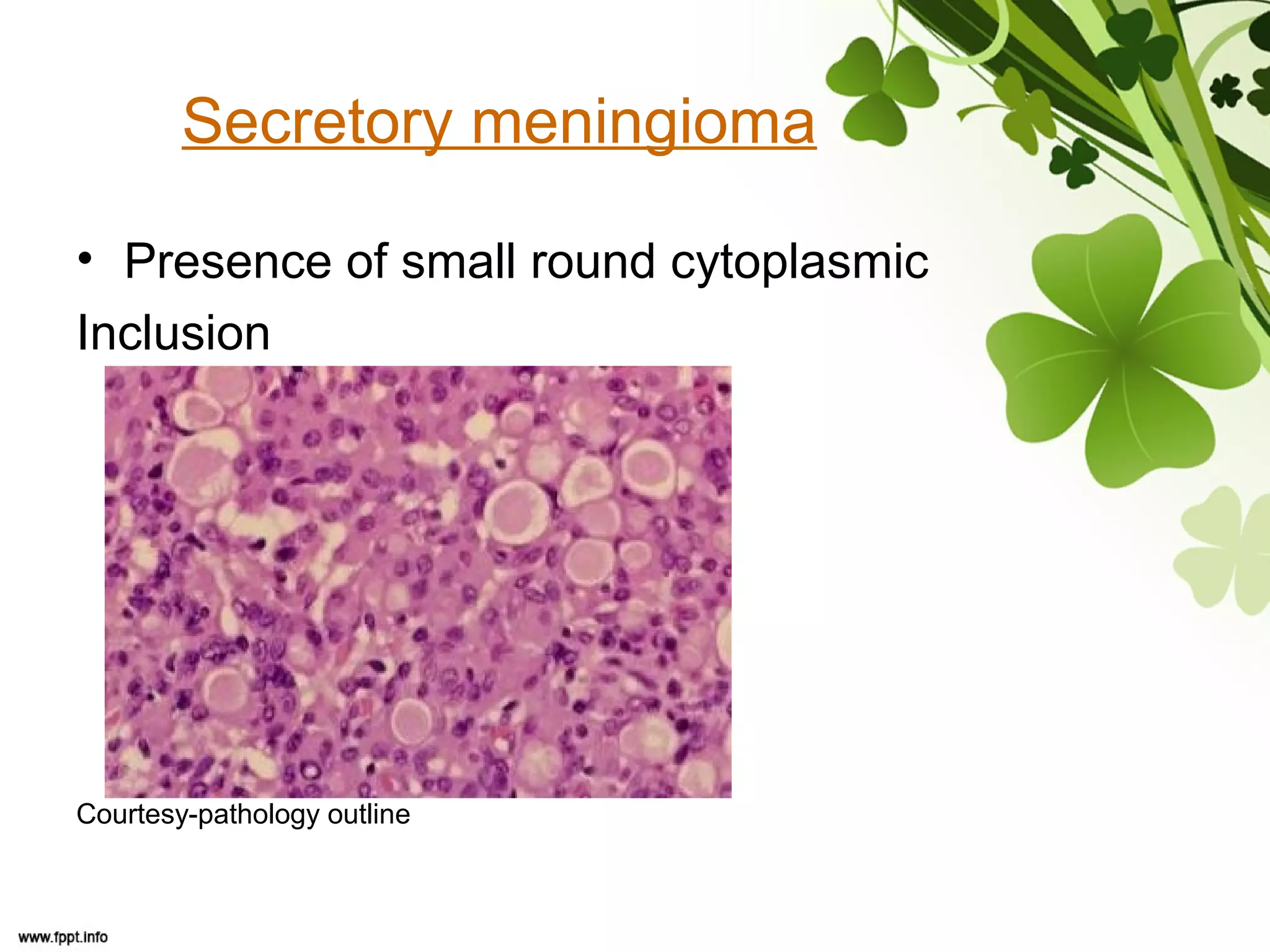
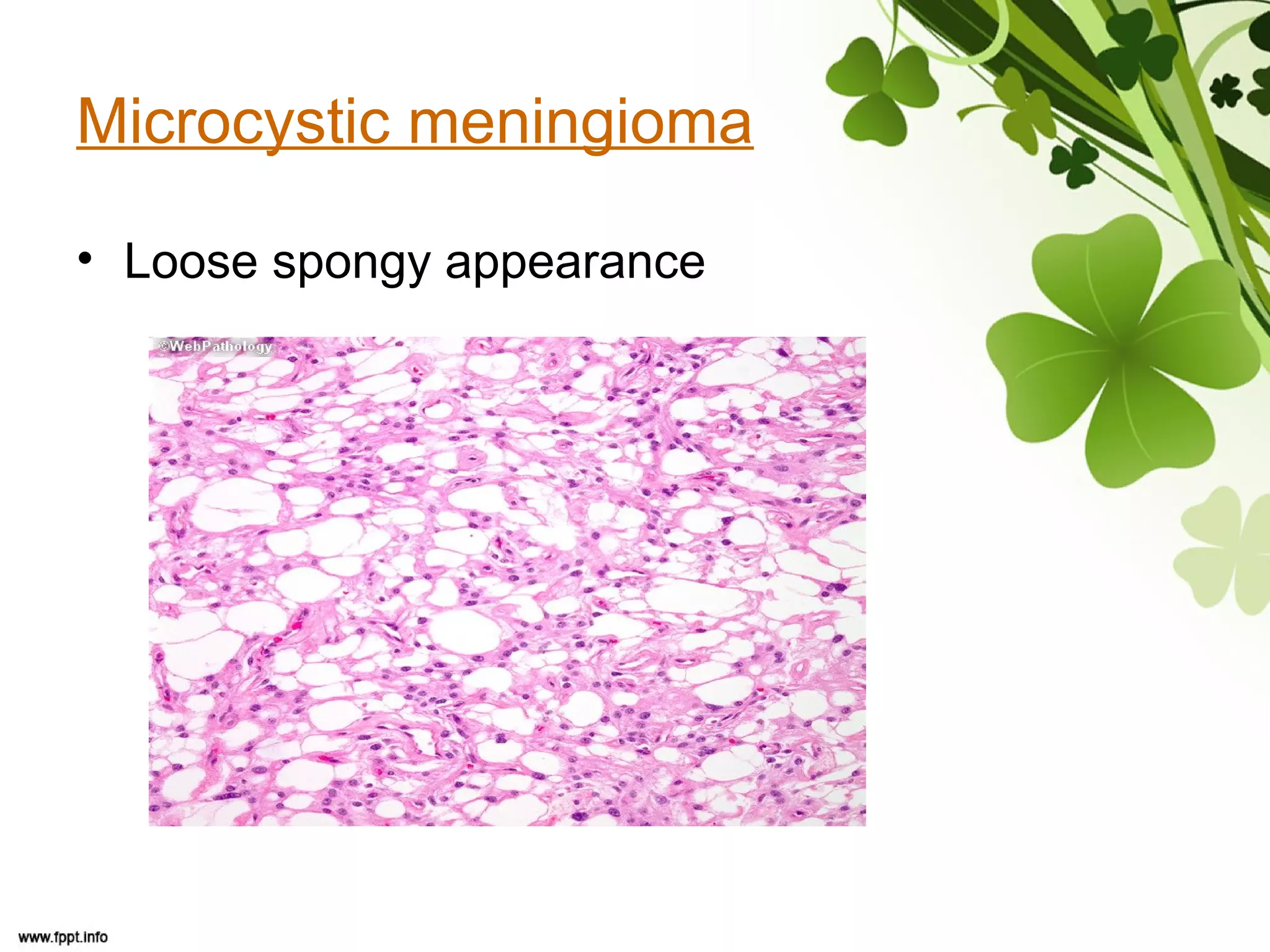
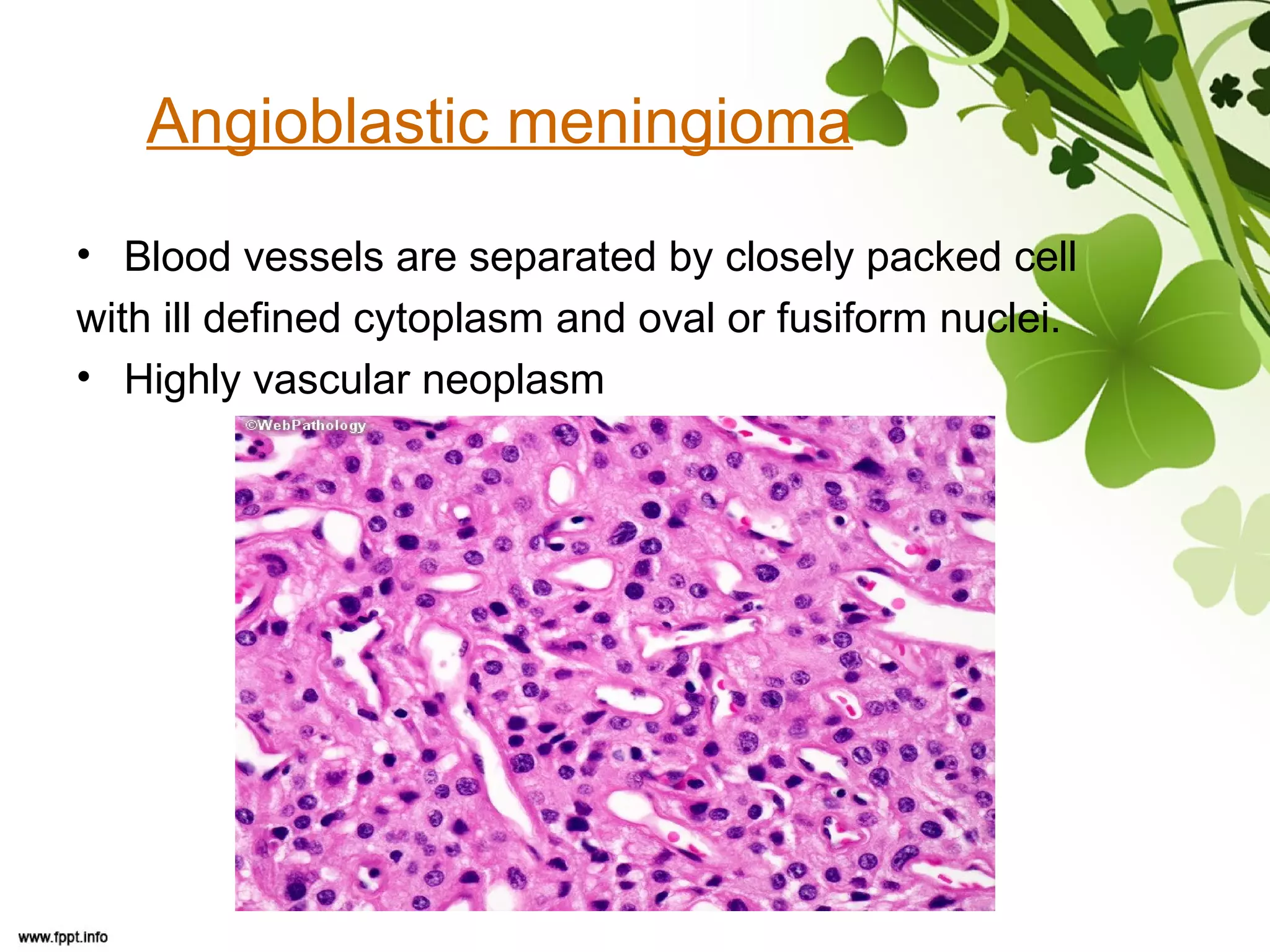
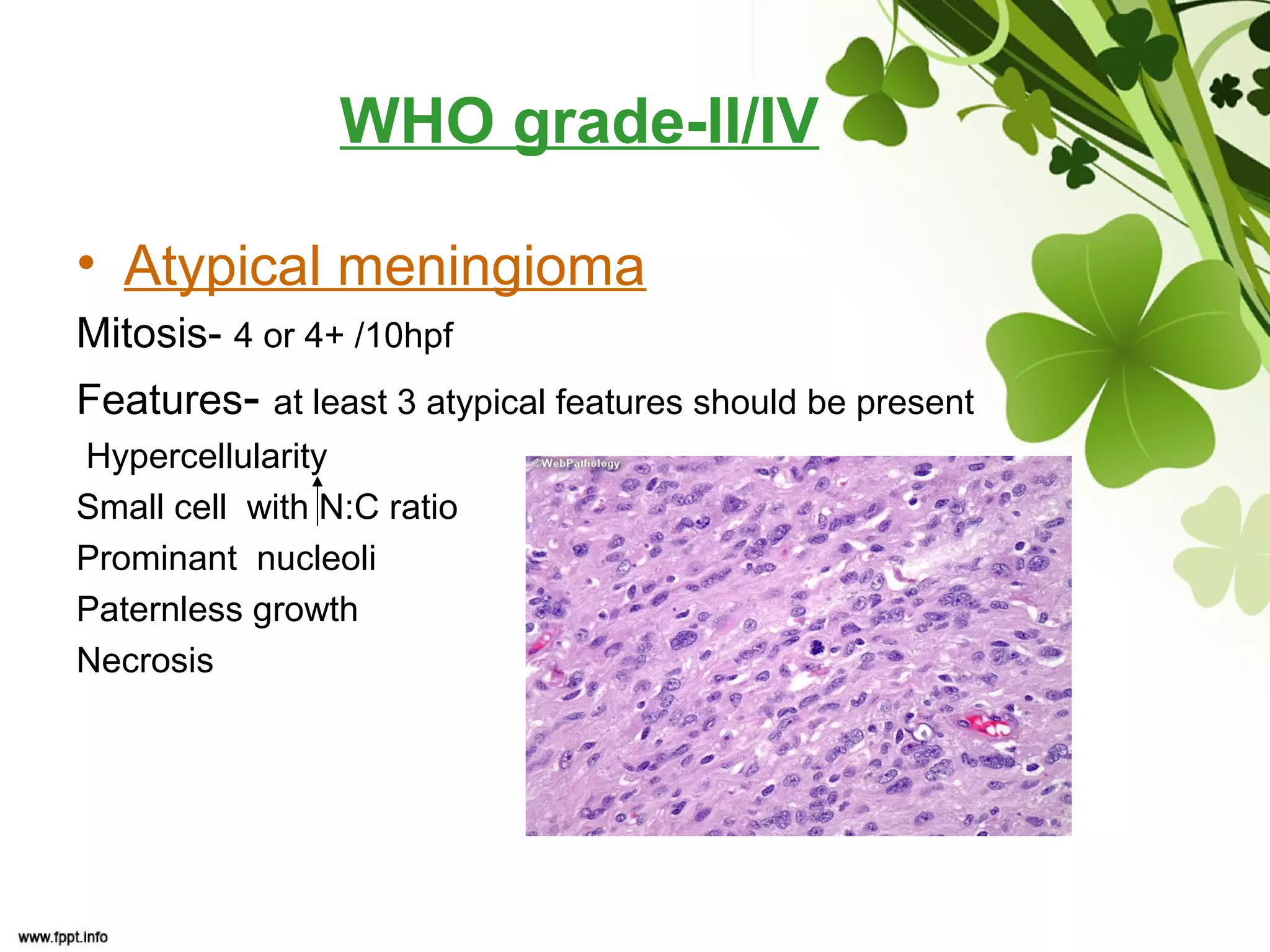
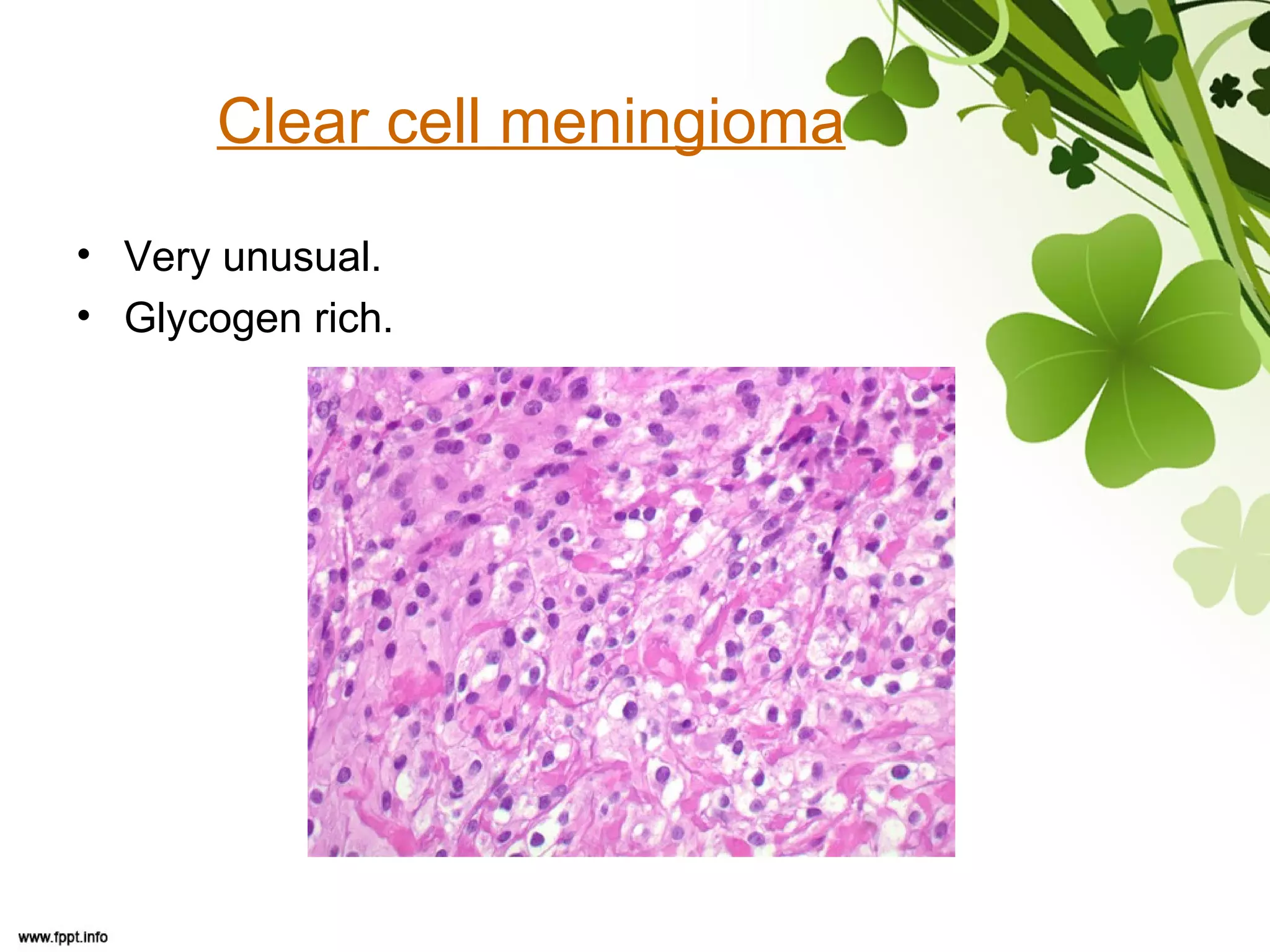
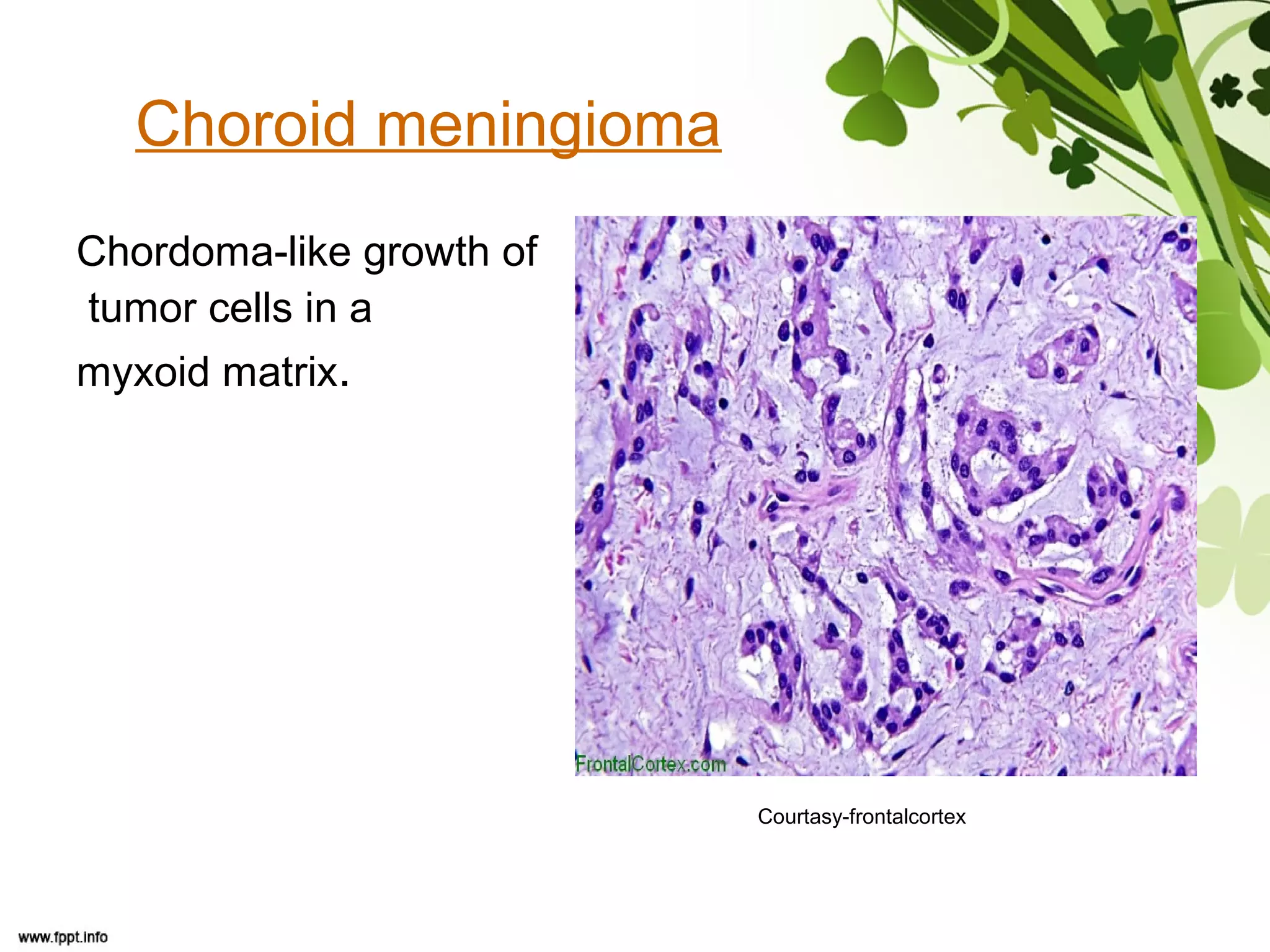
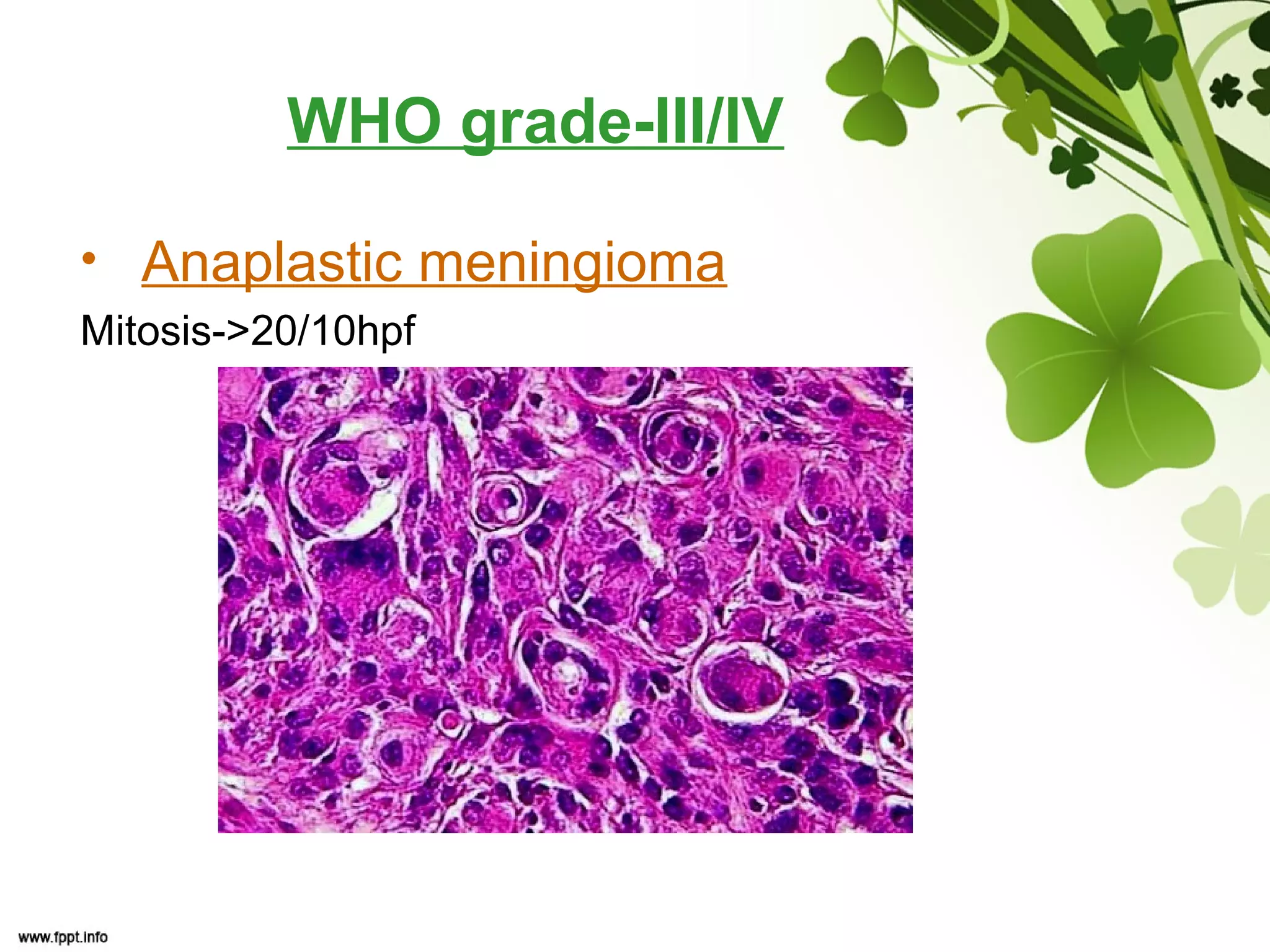
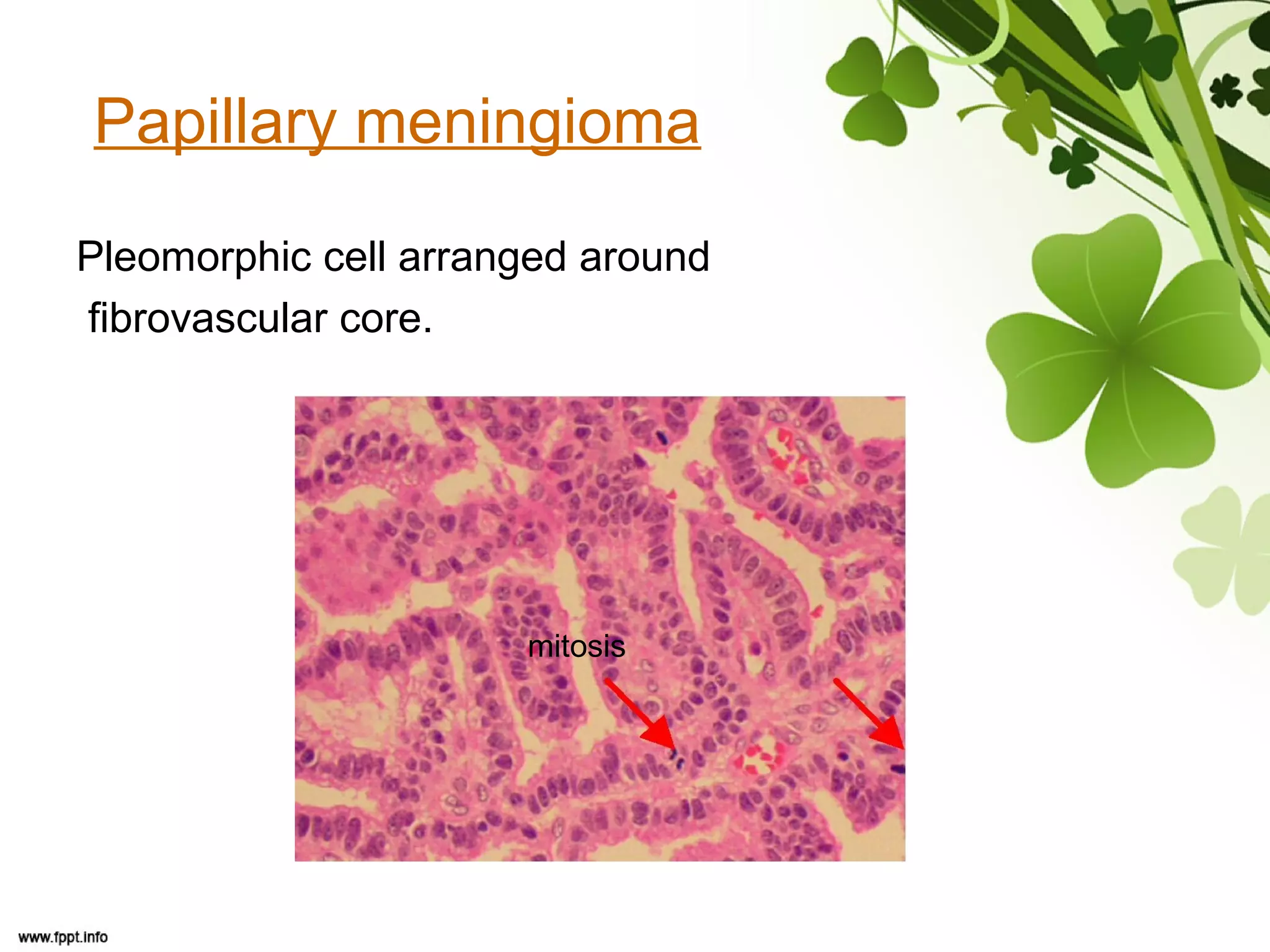
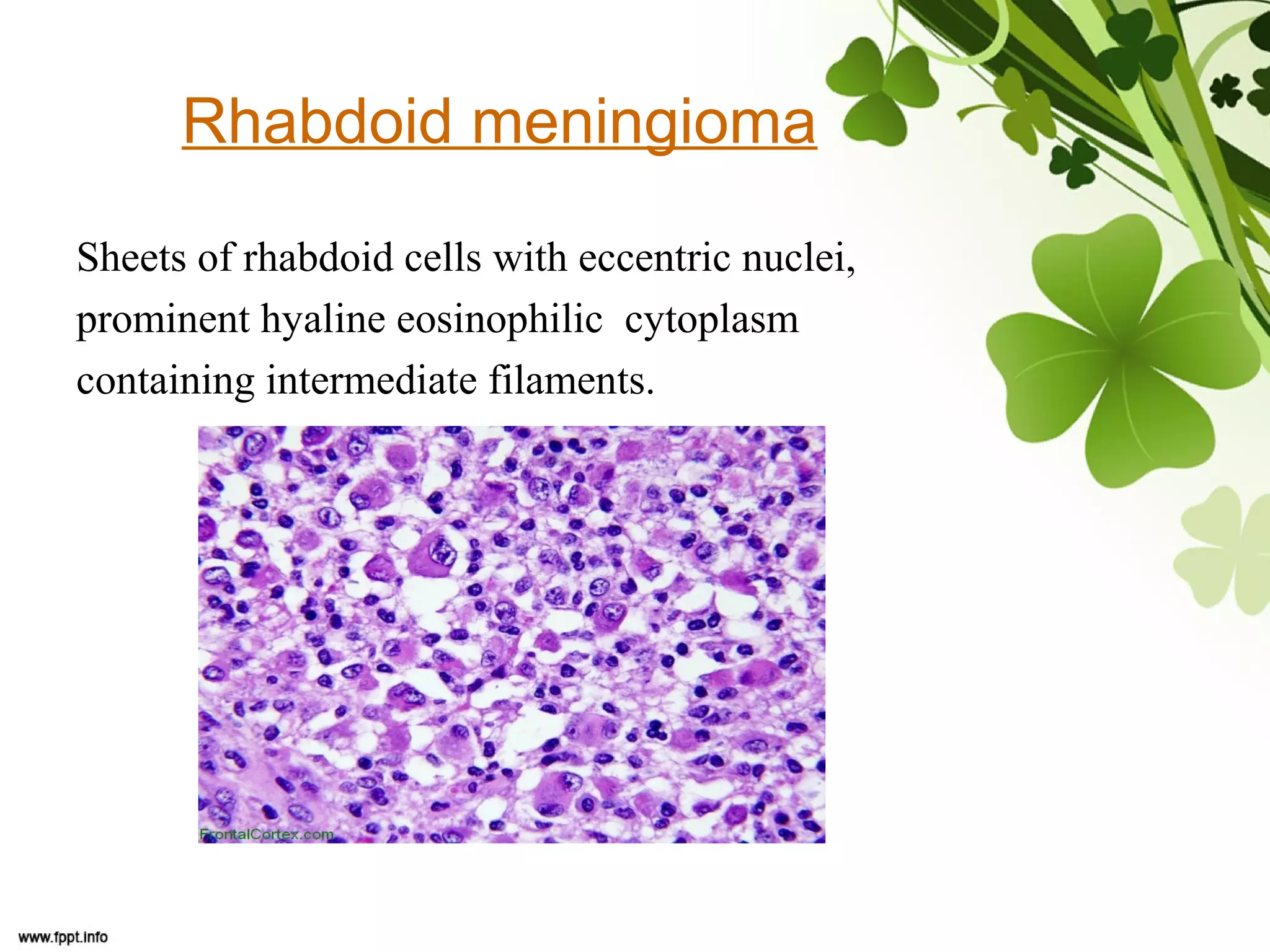


This document discusses meningioma, a benign tumor that arises from meningothelial cells of the arachnoid membrane. It can occur in locations other than the skull base, such as the orbit, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and soft tissues. Meningiomas are classified by their WHO grade, from grade I-IV, with higher grades indicating a higher rate of recurrence and more aggressive behavior requiring radiation therapy. Common subtypes include syncytial, fibroblastic, transitional, psammomatous, secretory, microcystic, angioblastic, atypical, clear cell, choroid, anaplastic, and rhabdoid meningiomas.

















