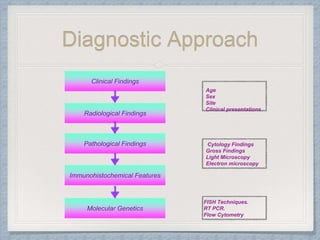
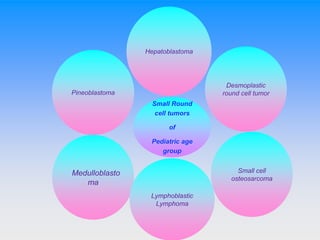
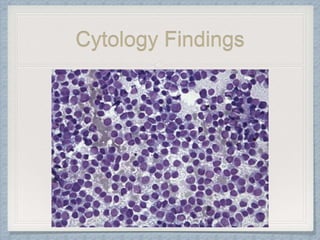
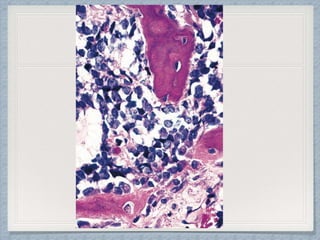
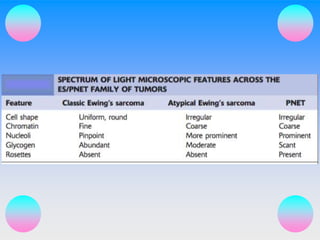
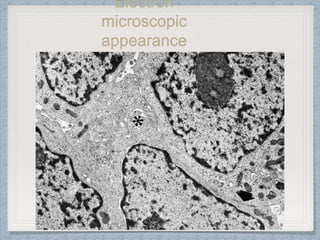
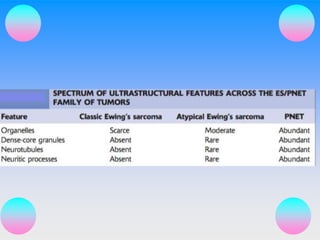
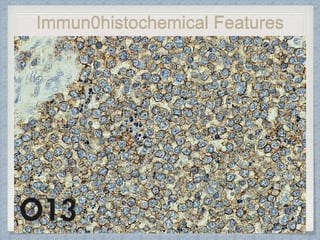
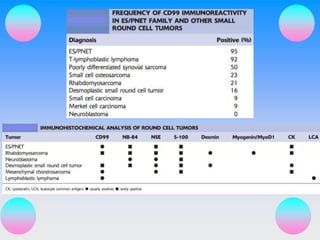
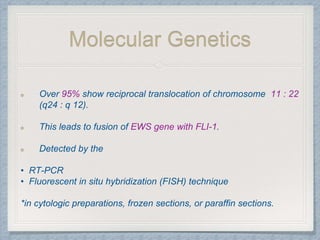
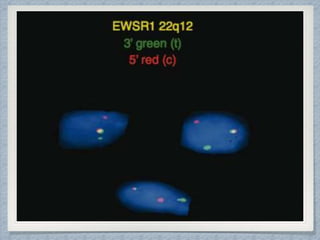
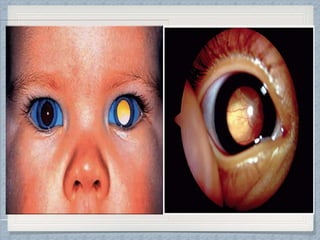
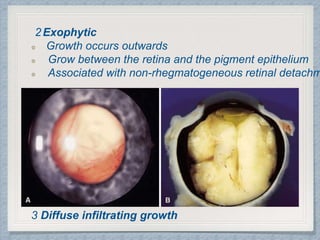
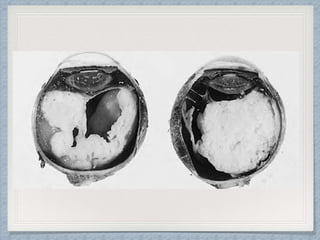
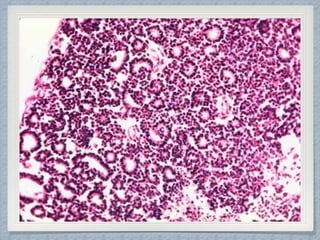
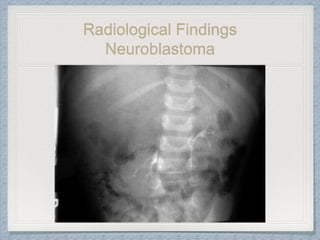
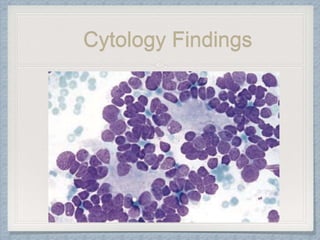
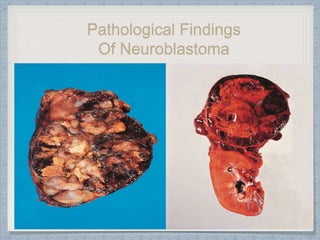
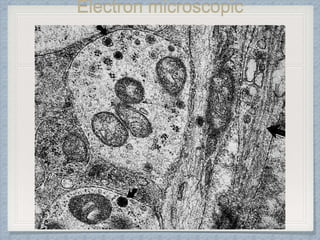
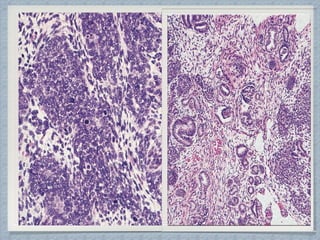
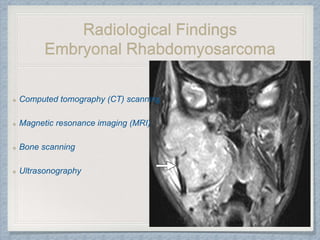
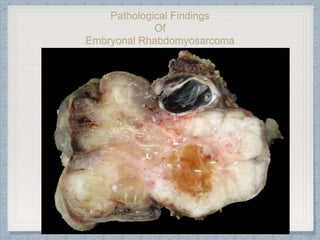
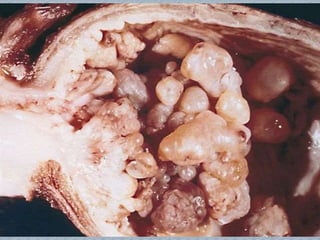
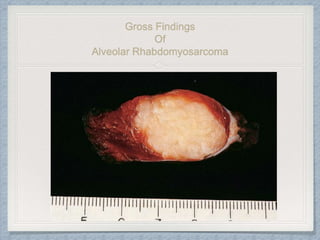
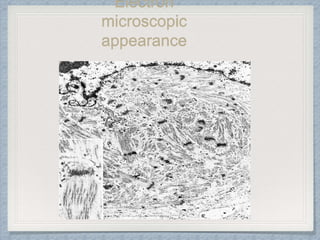
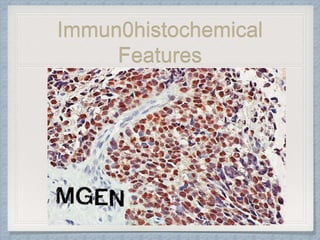
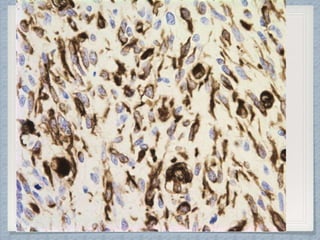
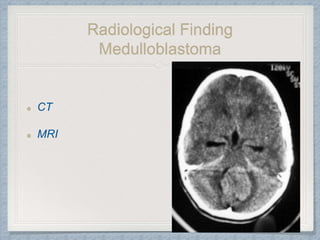
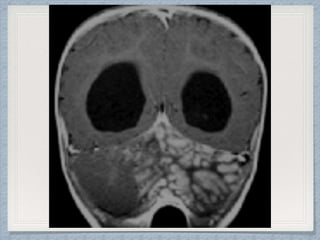
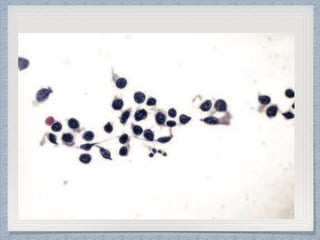
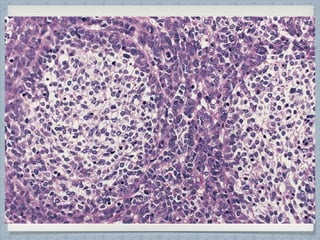
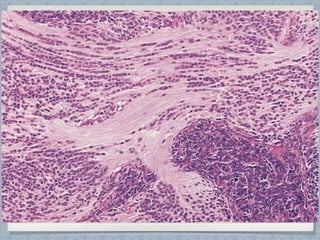
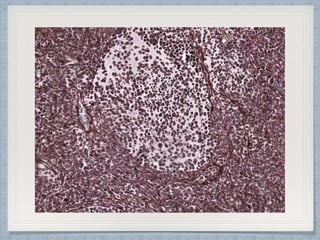
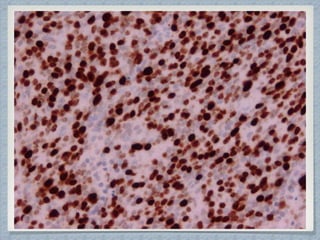
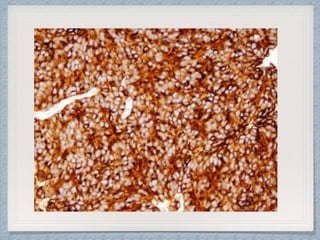
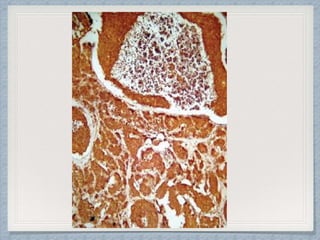
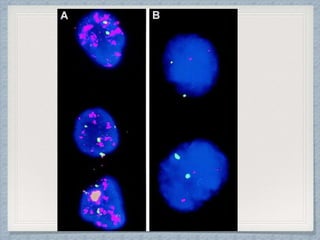
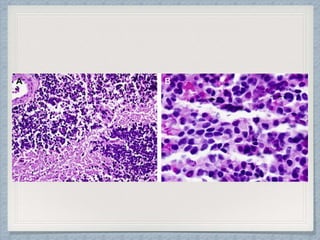
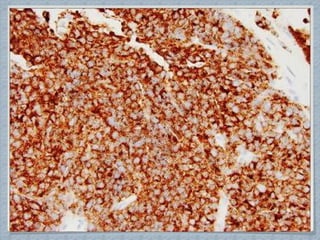
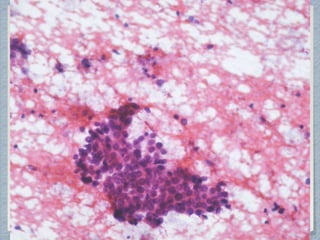
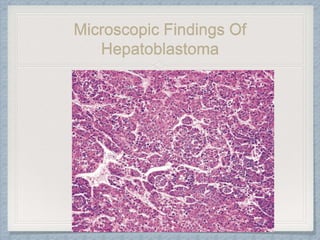
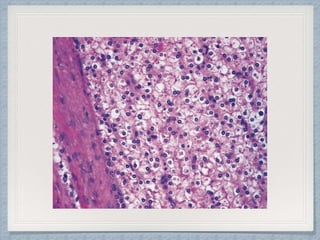
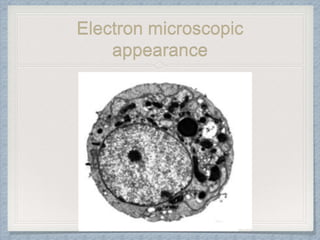
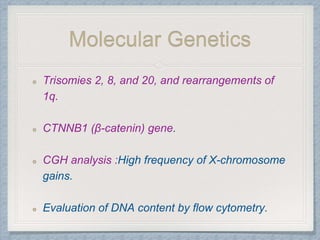
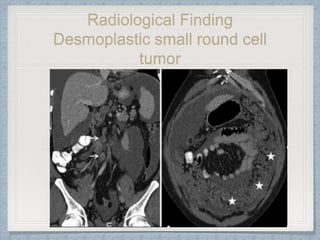
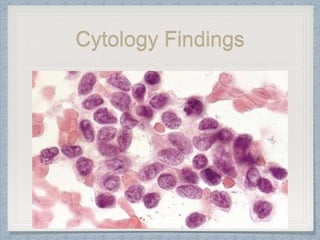
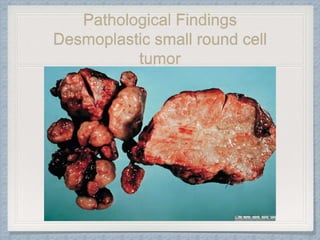
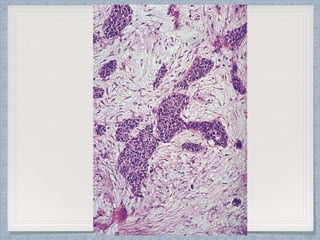
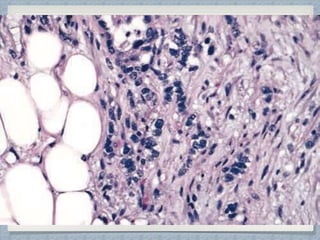
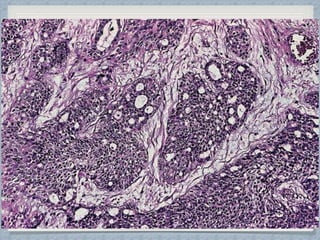
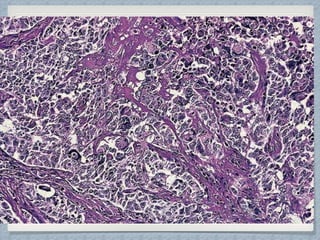
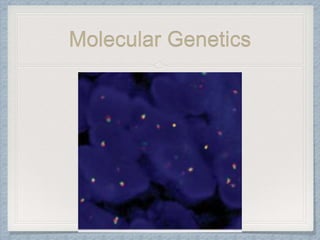
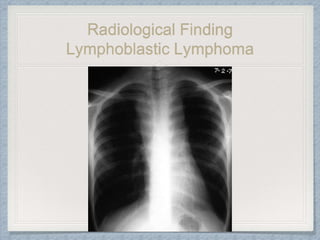
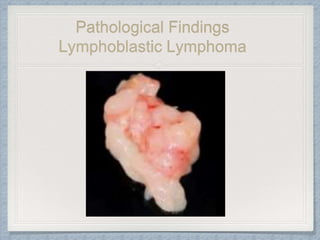
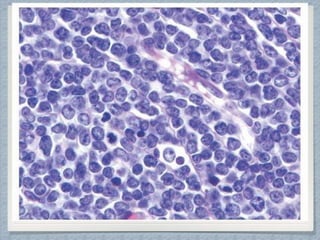
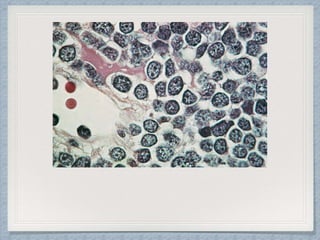
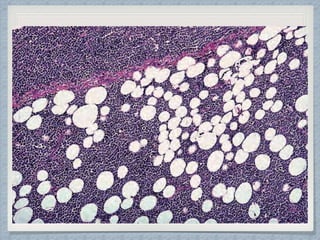
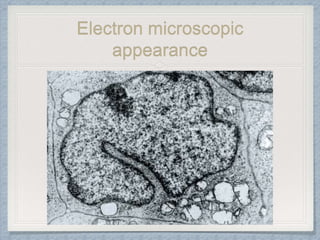
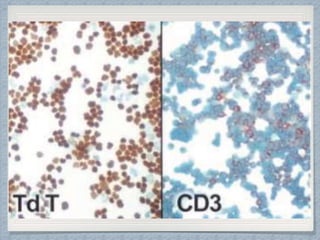
Small round cell tumors are a group of highly aggressive cancers composed of small, undifferentiated cells. The diagnostic approach involves clinical findings, imaging, pathology, and molecular genetics testing. Key small round cell tumors in pediatric patients include Ewing sarcoma, neuroblastoma, nephroblastoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, medulloblastoma, retinoblastoma, and lymphoblastic lymphoma. Immunohistochemistry and genetic testing are used to determine the specific tumor type to help guide treatment.