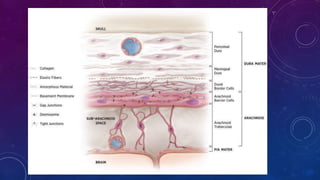
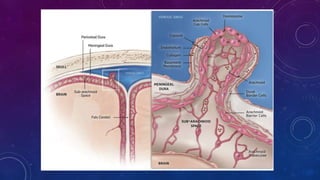
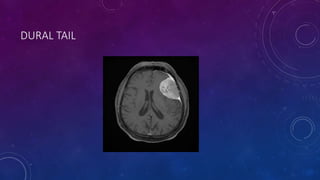
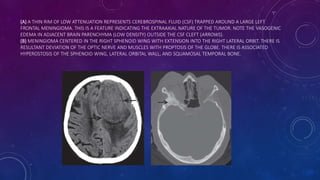
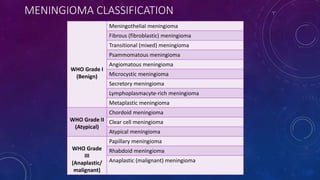
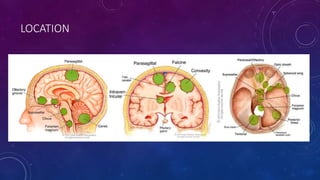
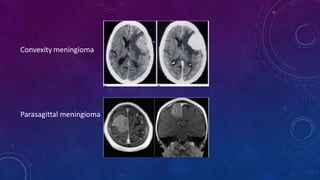
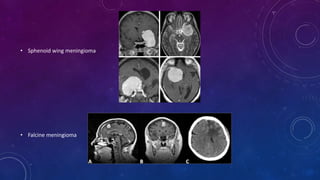
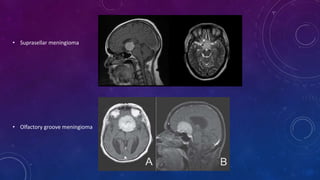
Meningiomas are tumors that arise from meningothelial cells in the arachnoid membrane. They are typically benign slow-growing tumors that compress the underlying brain. The highest rates occur in females and incidence increases with age. Risk factors include radiation exposure, hormones like estrogen, and possibly viruses. Imaging shows characteristic hyperostosis, calcification, and dural tail signs. Most are surgically resected for cure, with recurrence more likely if brain invasion occurs. Observation is common for asymptomatic cases with follow up imaging to monitor for growth.