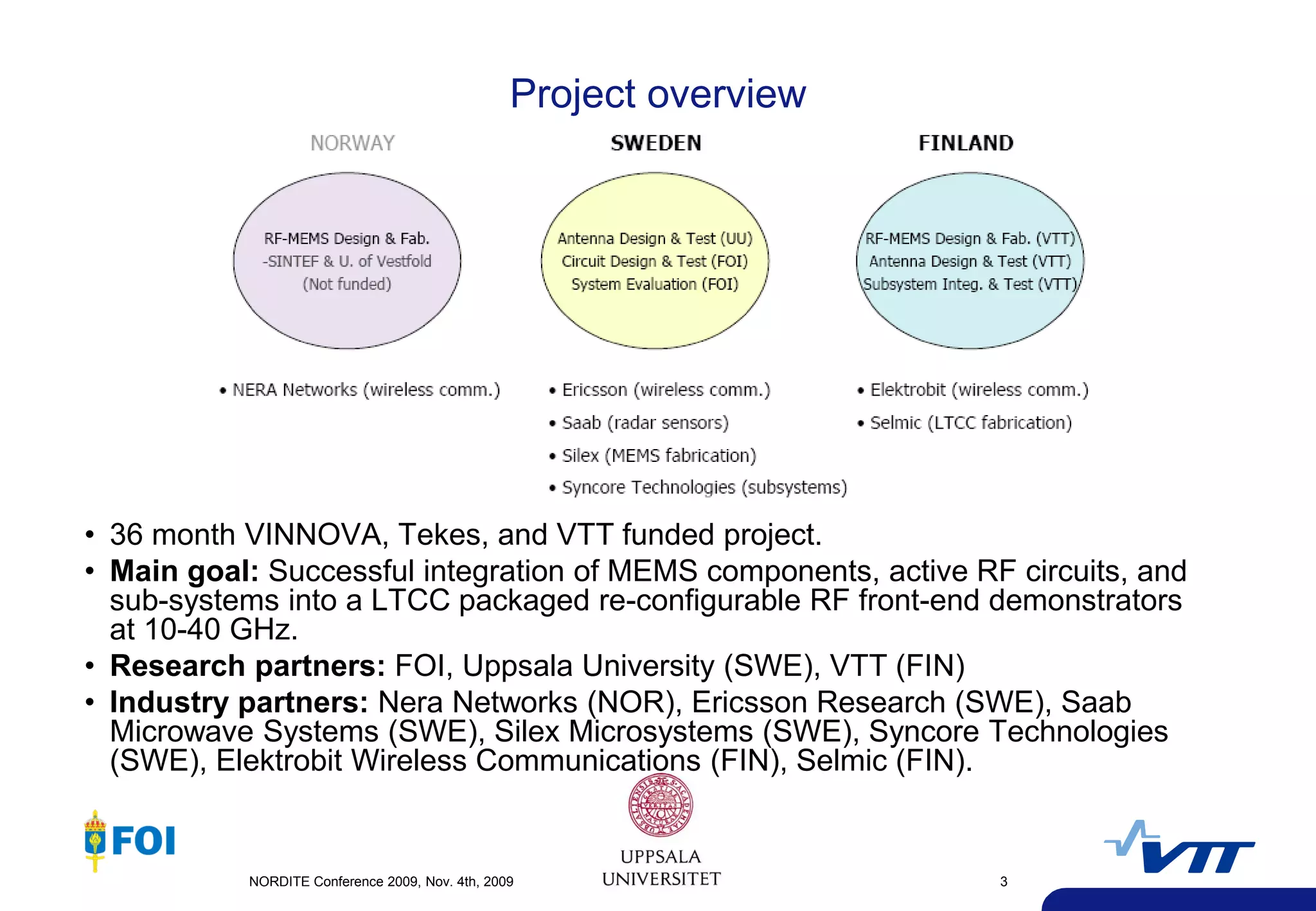
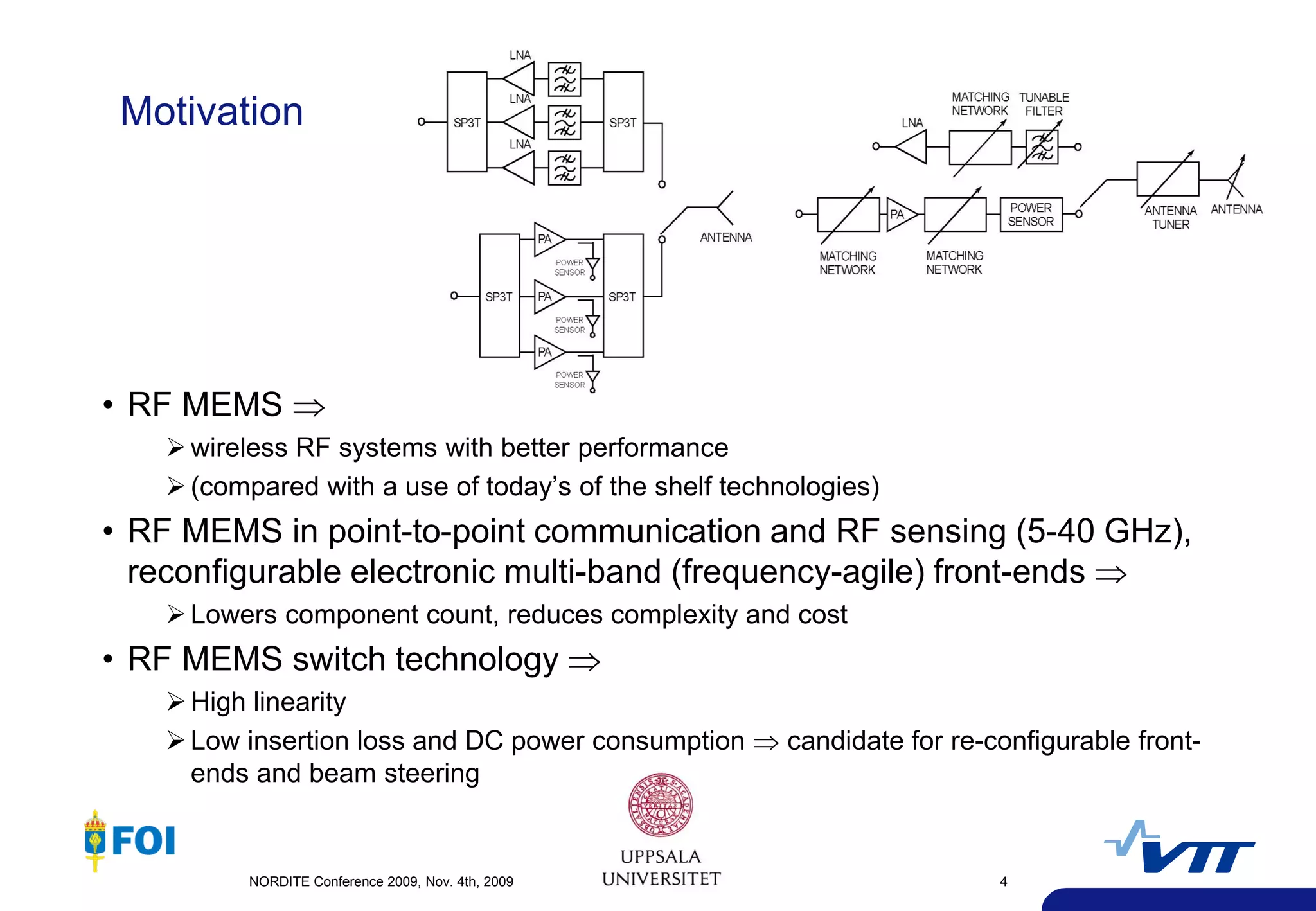
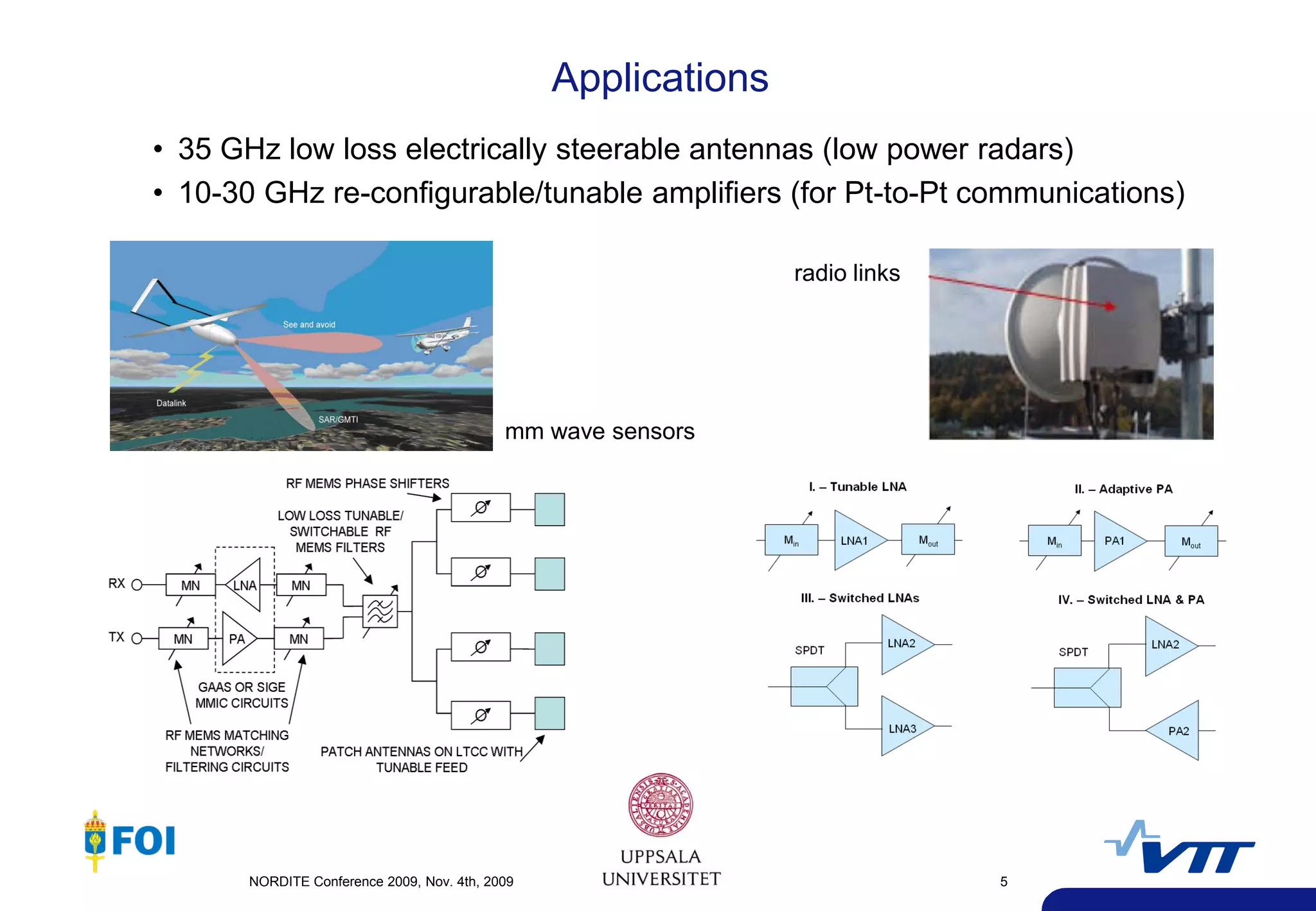
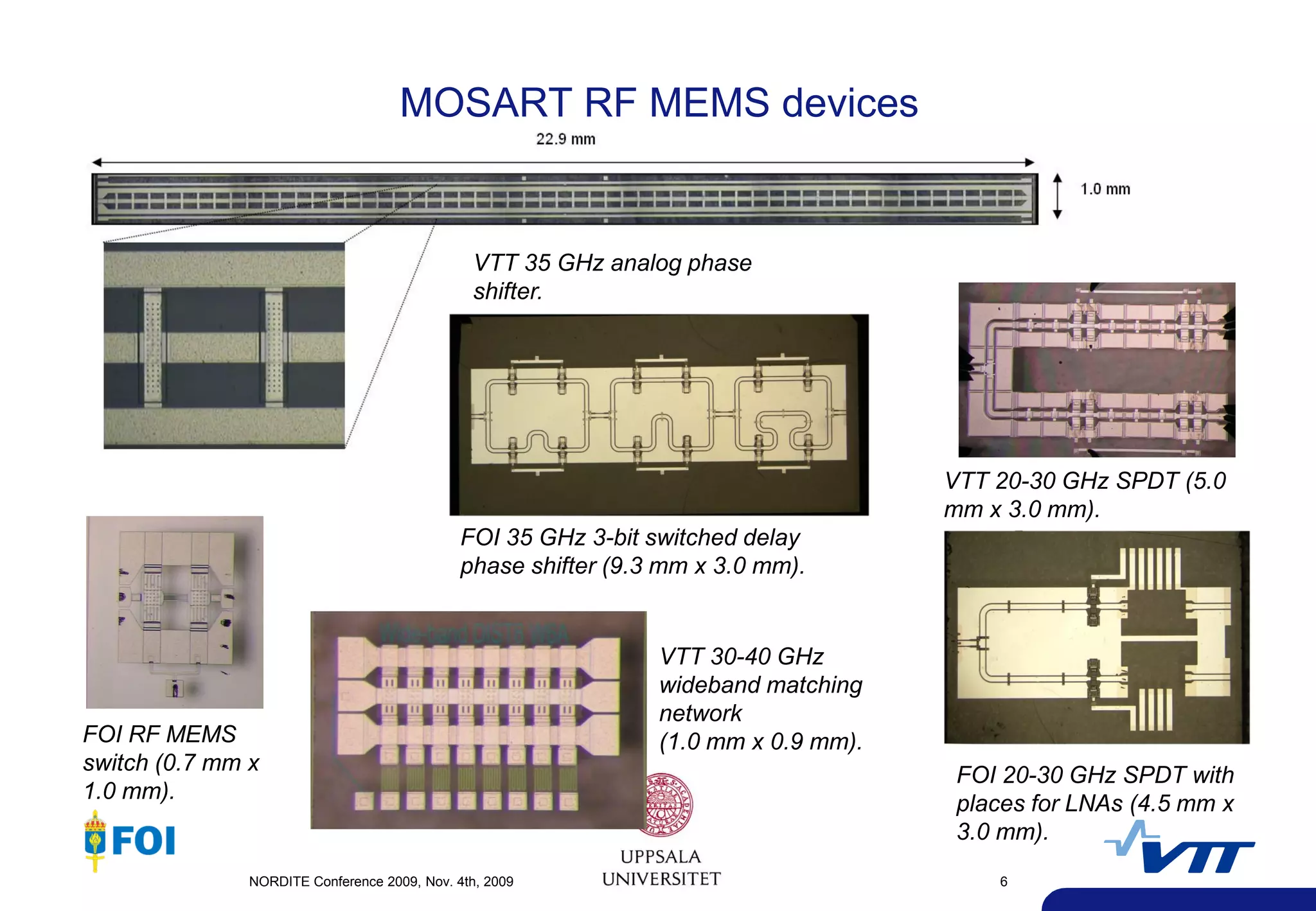
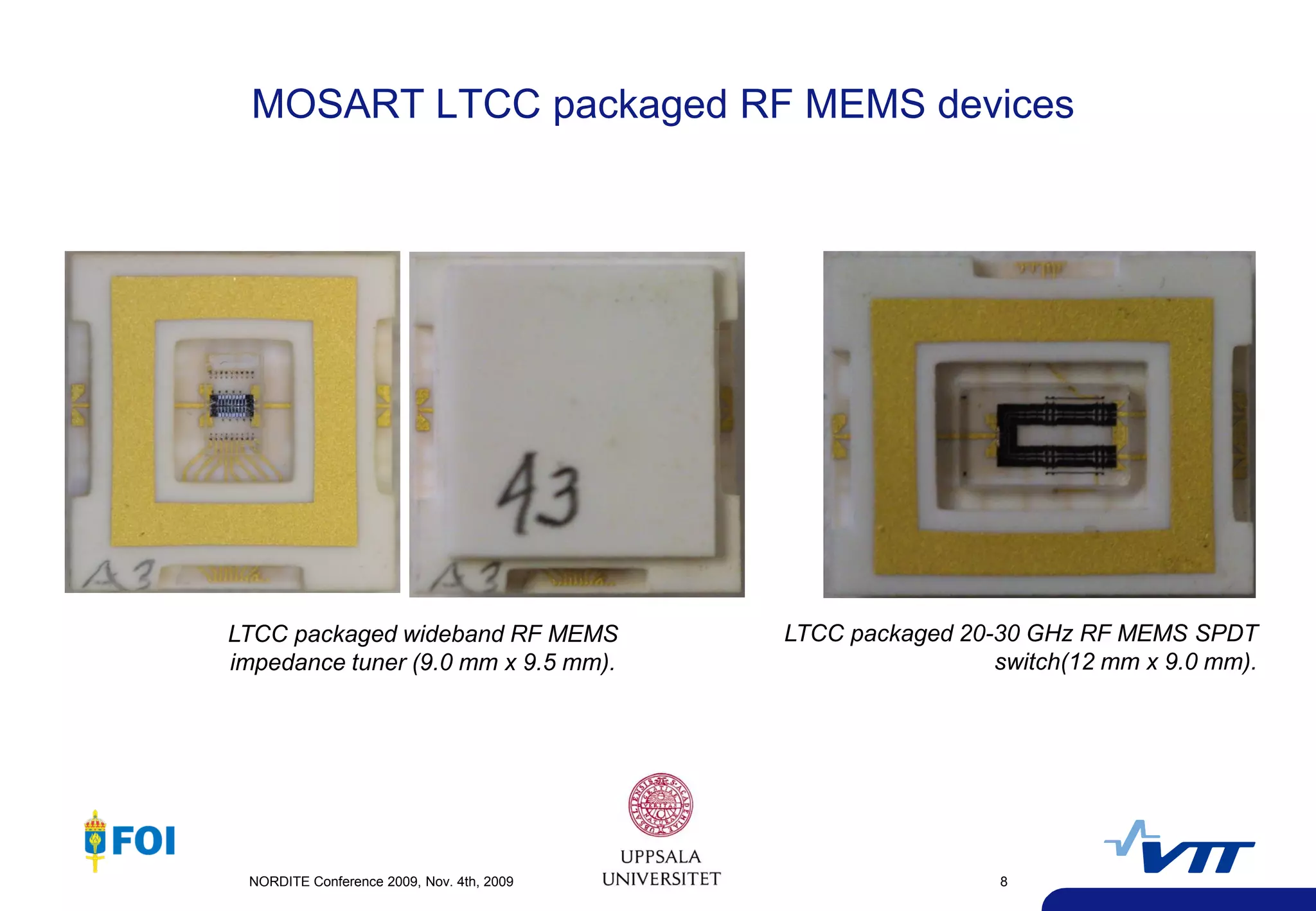
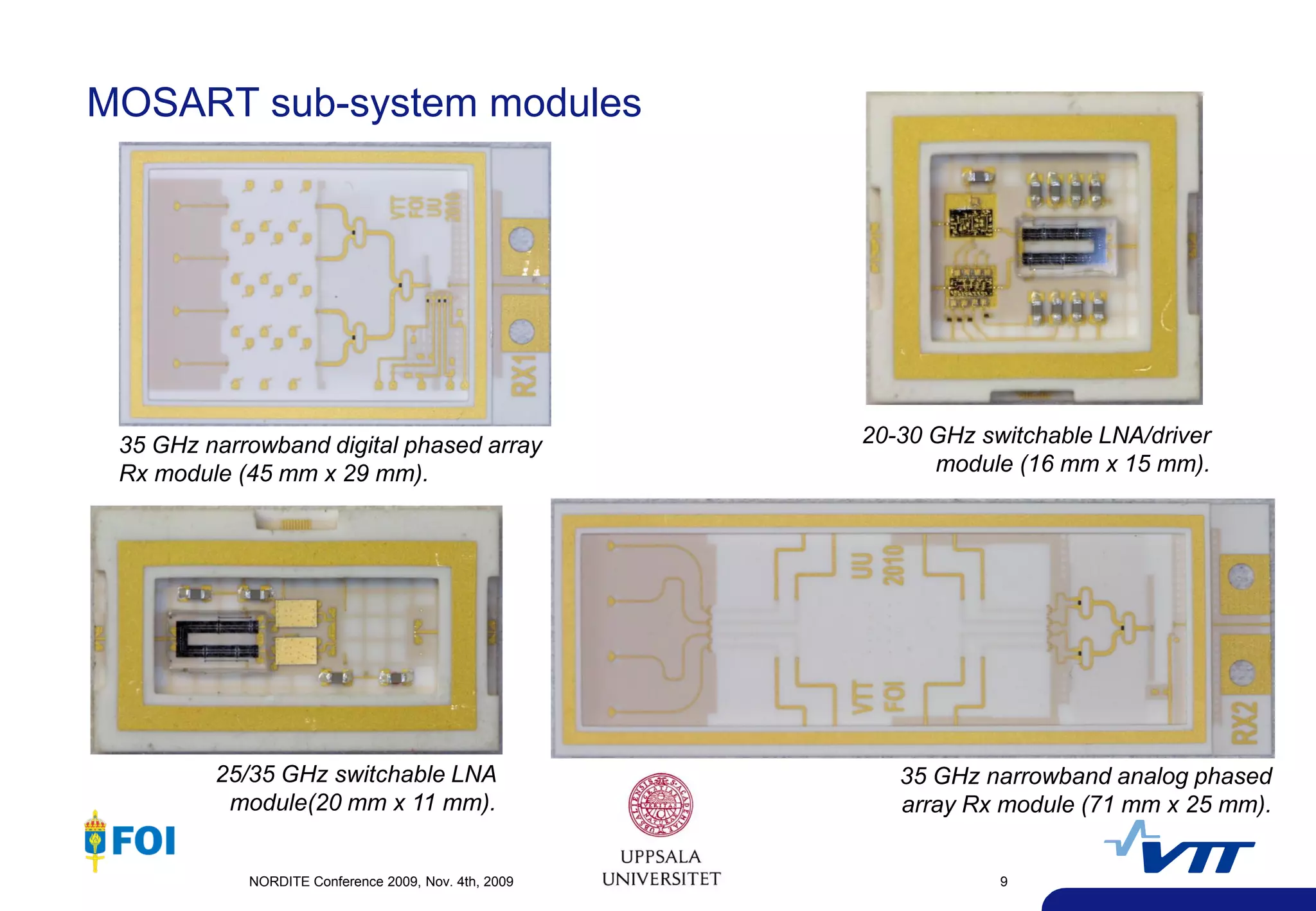
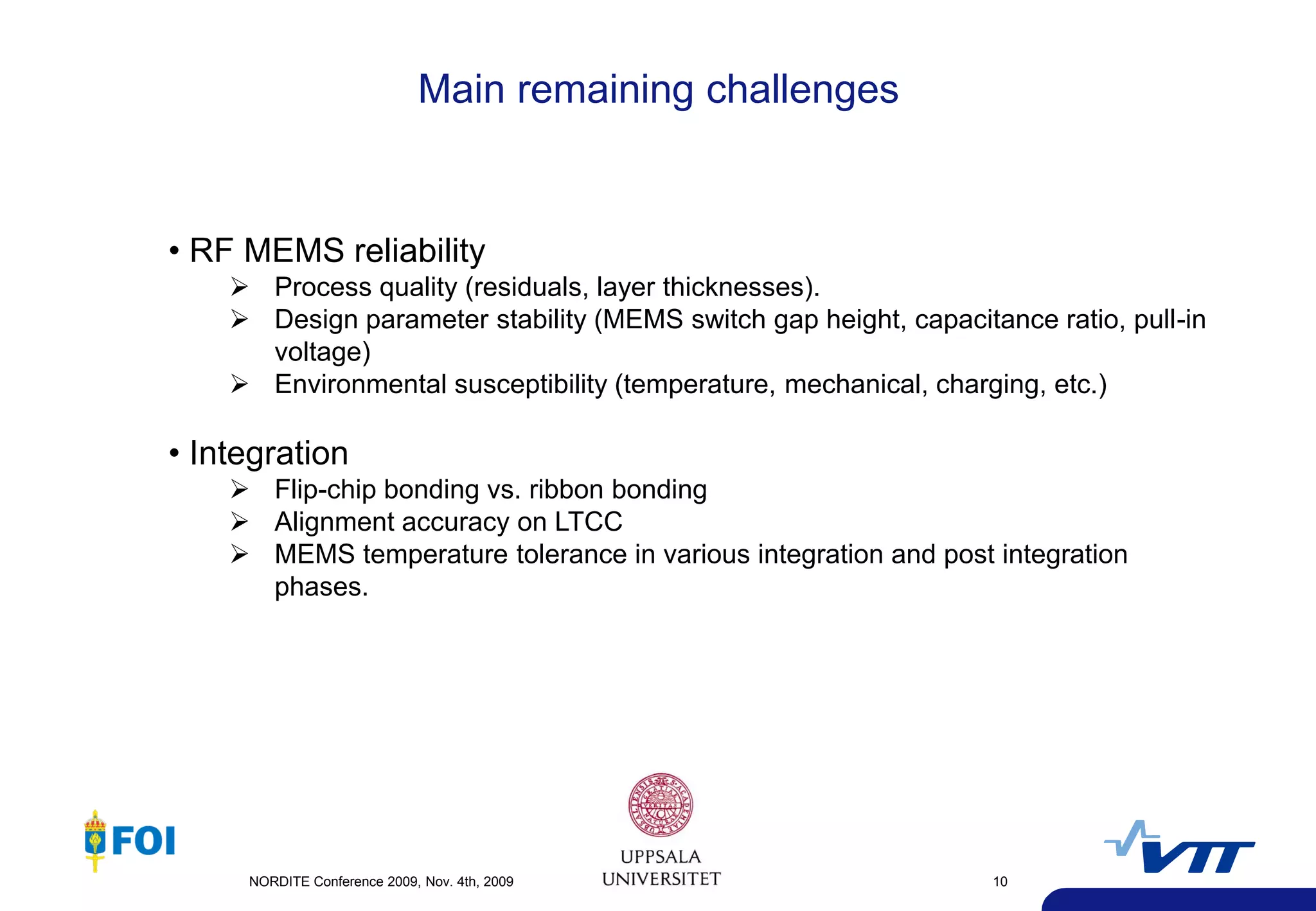
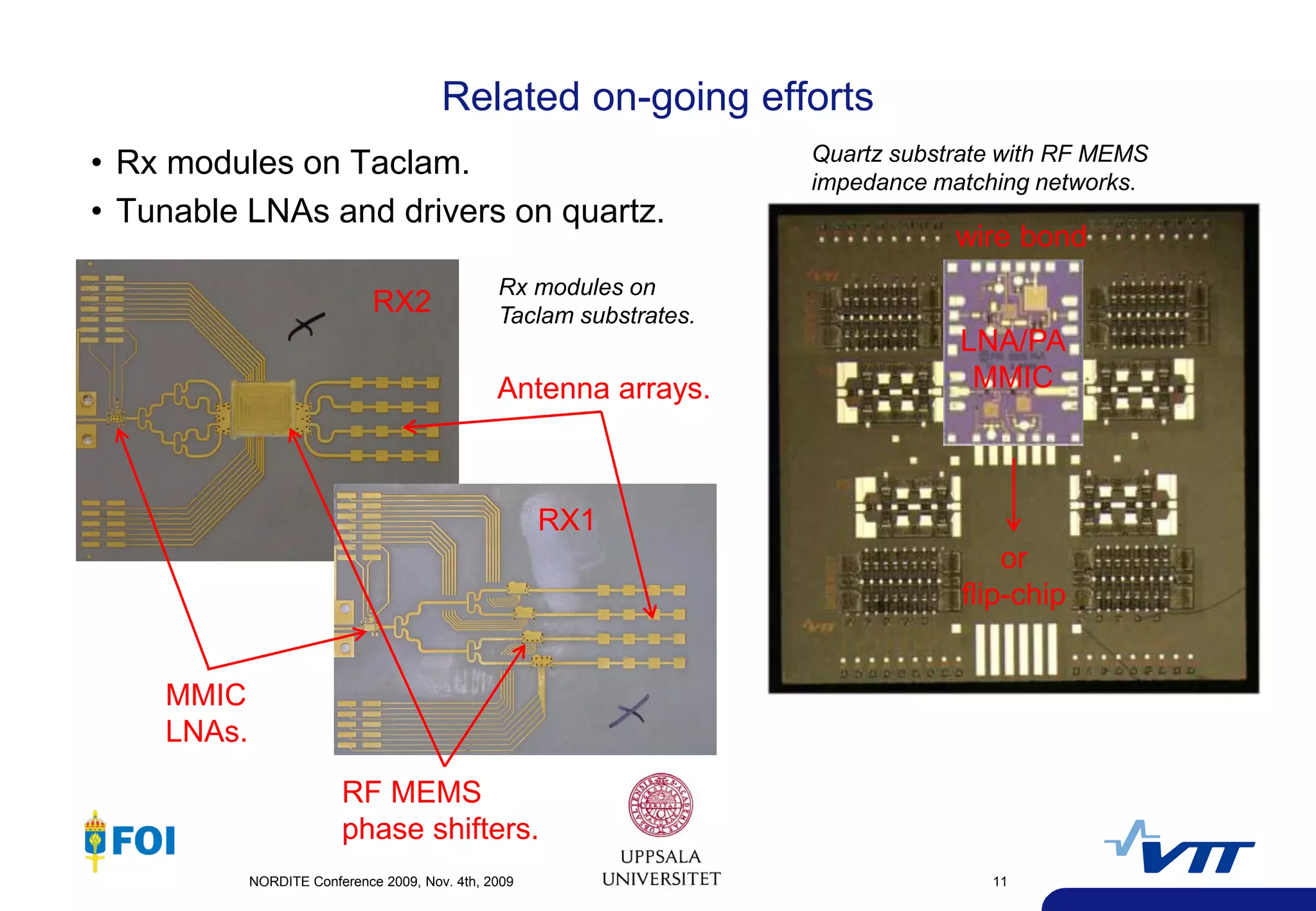
The document summarizes a presentation given at the NORDITE Conference in 2011 on MEMS-based reconfigurable RF systems. It discusses a project between research institutions in Finland, Sweden, and Norway to develop RF MEMS devices, antennas on LTCC substrates, and integrated sub-system modules for applications such as software radios and wireless sensors from 10-40GHz. Challenges in RF MEMS reliability and integration were identified. Commercialization opportunities and related European projects were also mentioned.