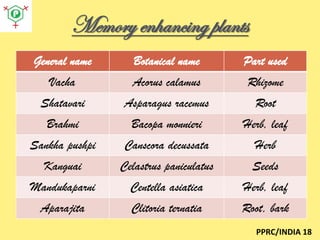
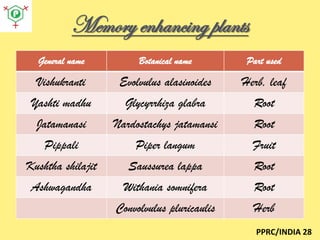
The document, presented by Dr. Sudhakar Kokate, discusses the nature of memory as a complex function of the central nervous system, emphasizing its importance for all individuals, including students and professionals. It also highlights various Ayurvedic drugs and dietary choices that can enhance memory and mitigate degeneration, particularly focusing on plants like Brahmi and Ashwagandha. The document advocates for a holistic approach to memory improvement through regular intake of these natural remedies, along with a positive lifestyle and psychological health.