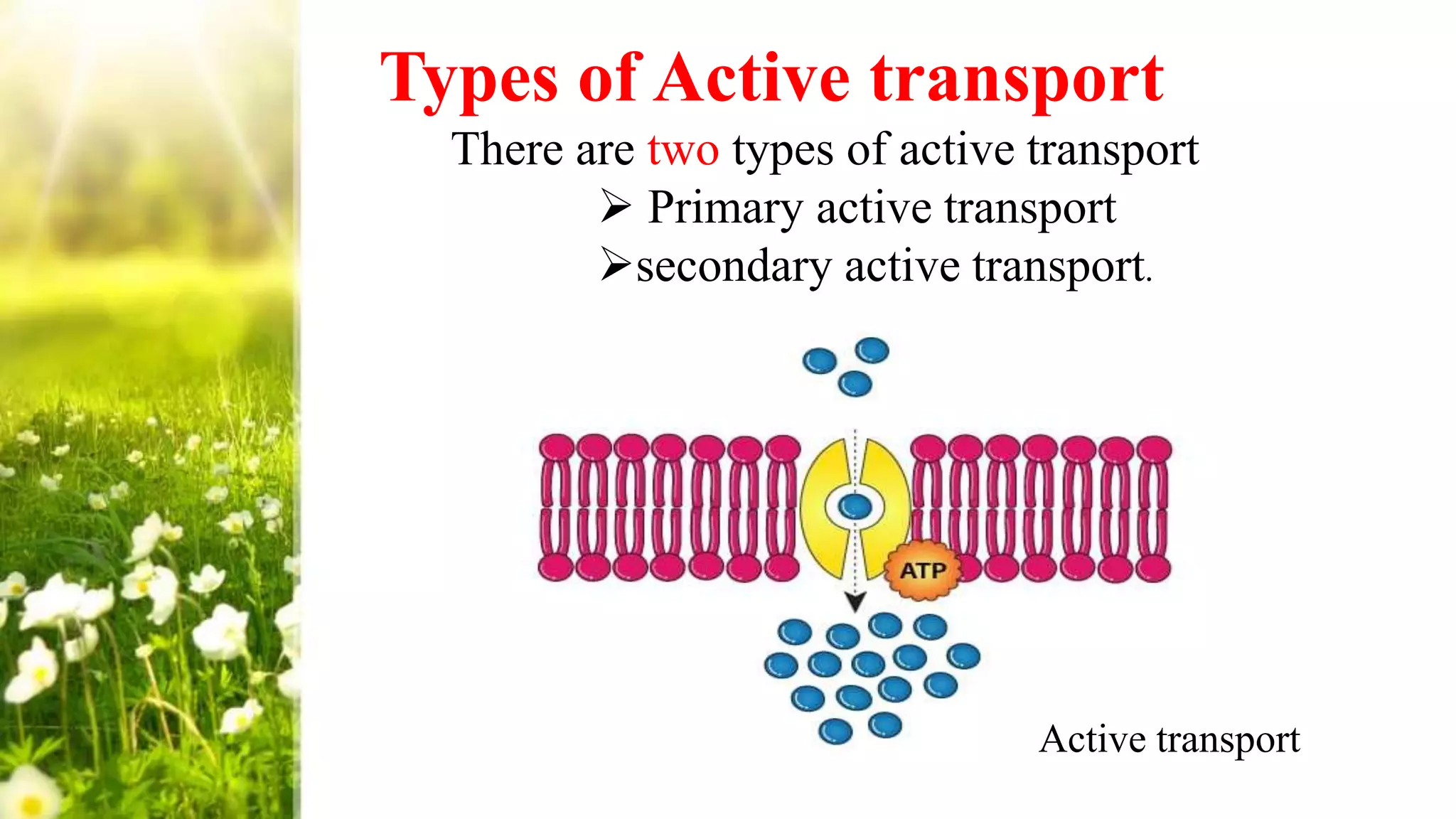
Membrane transport is the process by which molecules move across cell membranes. There are two main types of membrane transport: passive transport, which does not require energy, and active transport, which does require energy. Passive transport includes simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. Active transport includes primary active transport, which uses ATP as an energy source, and secondary active transport, which uses ion gradients. Membrane transport is essential for cells to import nutrients and export waste.