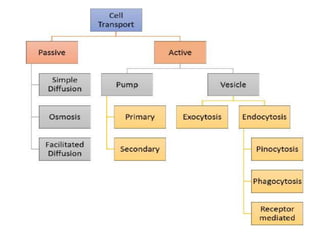
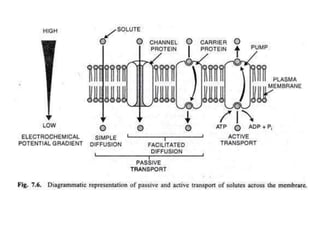
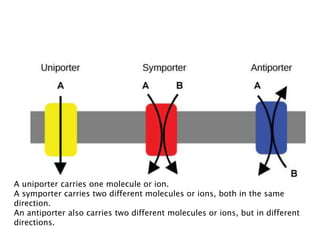
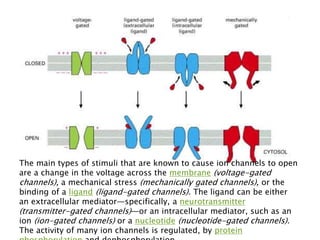
The document summarizes transport across the cell membrane. There are two main types of transport - passive transport (diffusion) and active transport. Passive transport involves the movement of substances down their concentration gradient without energy expenditure, and can occur through simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion via channel or carrier proteins. Active transport moves substances against their concentration gradient by expending cellular energy in the form of ATP. Key examples discussed are the sodium-potassium pump, which actively transports sodium out and potassium into cells.