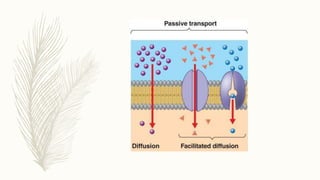
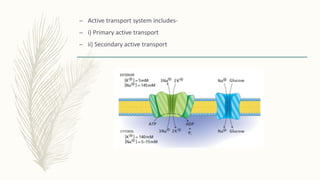
Membrane transport systems move molecules into and out of cells across cell membranes. There are two major types of membrane transport: passive transport, which does not require energy, and active transport, which uses cellular energy. Passive transport includes simple diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion. Active transport uses transporter proteins and ATP or ion gradients to move molecules against their concentration gradients. Primary active transport directly uses ATP, while secondary active transport utilizes ion gradients generated by primary transporters.