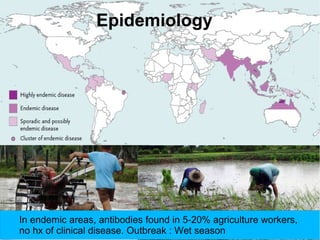
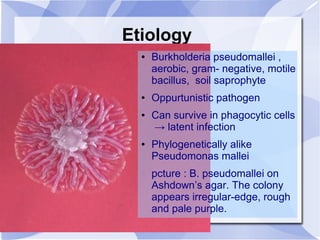
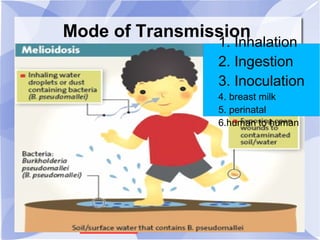
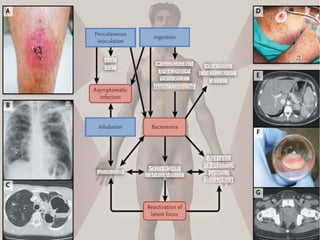
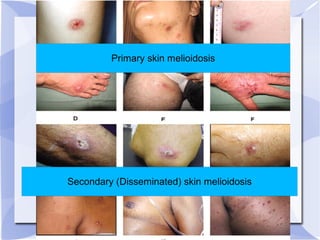
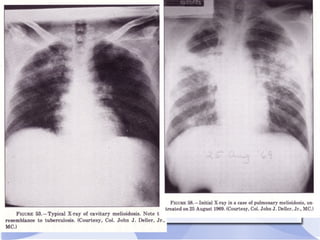
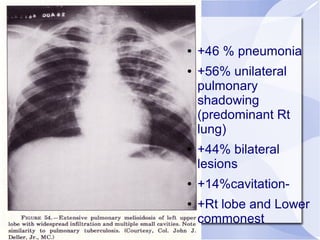
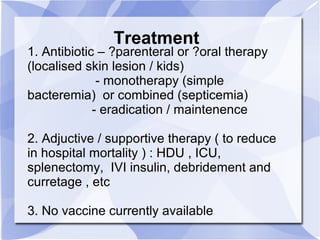
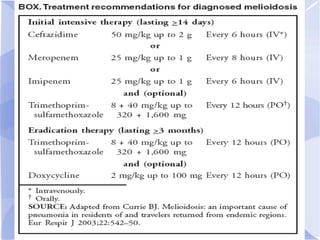
Melioidosis is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei, commonly found in soil and water in Southeast Asia and northern Australia. It most often infects the lungs and symptoms are non-specific, including fever. It is diagnosed through culturing the bacteria from blood, urine, sputum or skin lesions. Treatment involves long-term antibiotics such as ceftazidime and co-trimoxazole, with an overall mortality rate of 50-70% even with treatment.