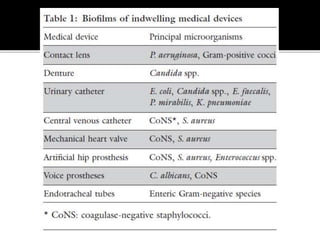
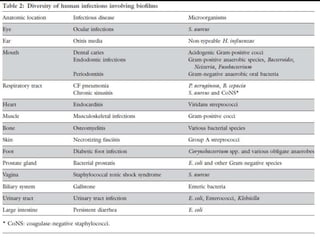
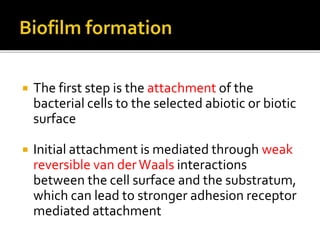
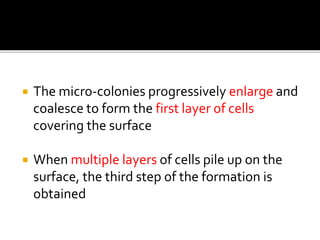
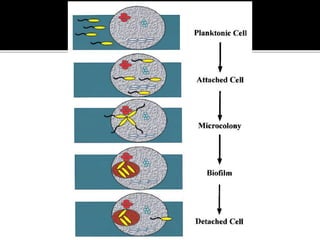
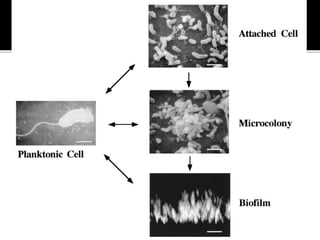
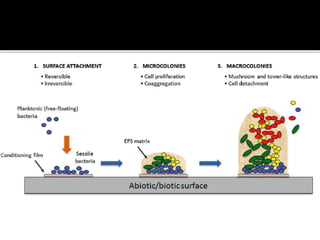
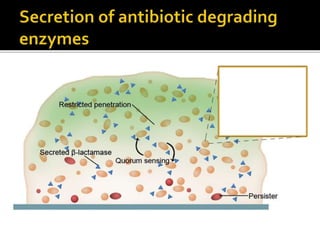
The document discusses biofilms and their antibiotic resistance. It notes that biofilms are assemblages of surface-attached microbial cells encased in an extracellular matrix. This matrix provides protection from antibiotics by acting as a diffusion barrier and binding antimicrobial agents. Additionally, the heterogeneous conditions within biofilms, including nutrient depletion and slower growth, contribute to antibiotic tolerance in some cells. Genetic transfer of resistance genes is also facilitated within dense biofilm communities.