Embed presentation
Download to read offline
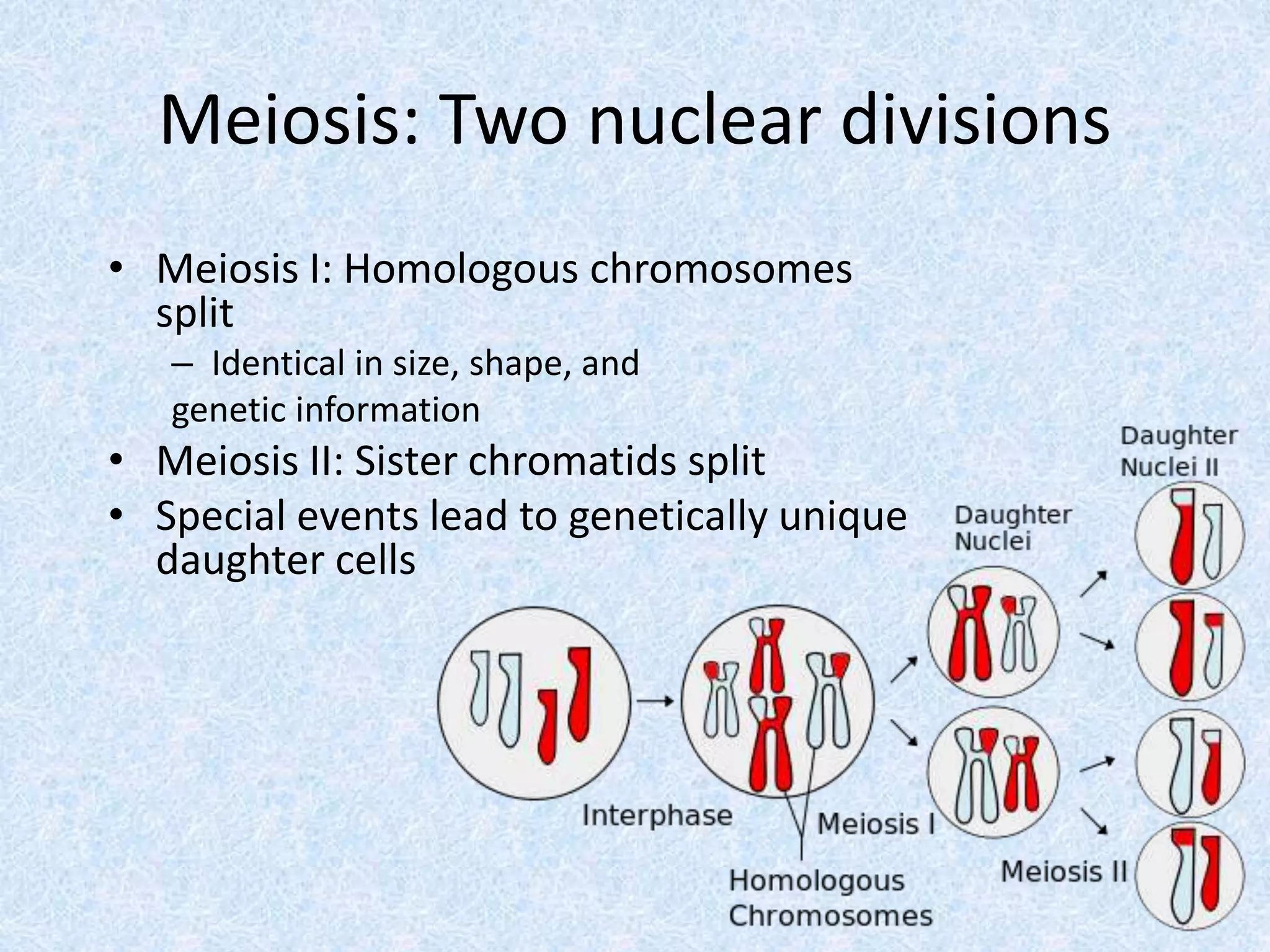
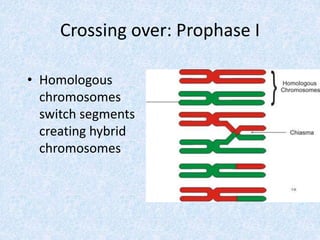

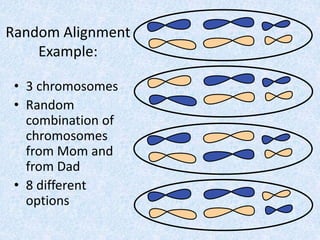

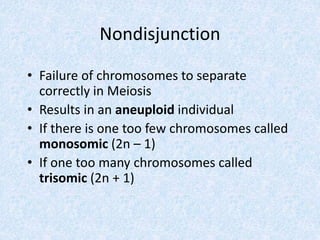
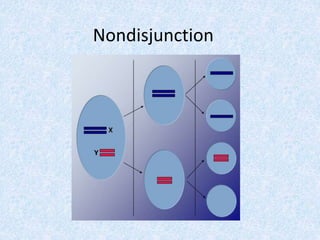


Meiosis involves two nuclear divisions that result in genetically unique daughter cells. In Meiosis I, homologous chromosomes split but identical sister chromatids remain attached. Meiosis II separates the sister chromatids, reducing the number of chromosomes by half. Special events like crossing over in prophase I and random alignment of homologous chromosomes in metaphase I contribute to genetic diversity between the daughter cells produced in meiosis.








