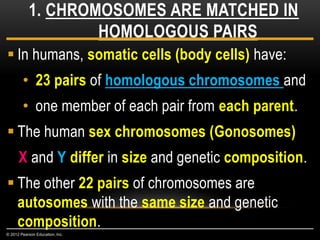
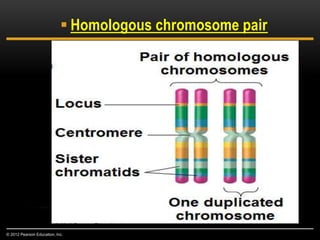
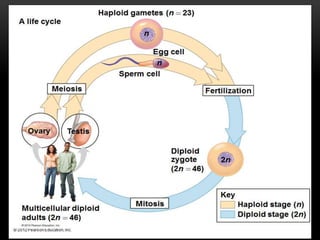
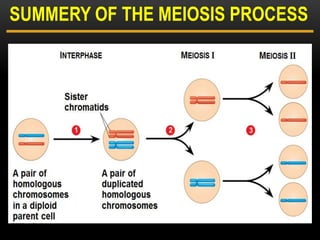
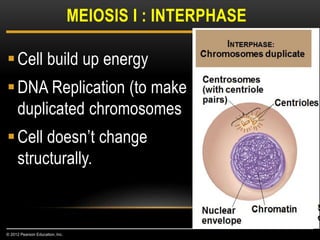
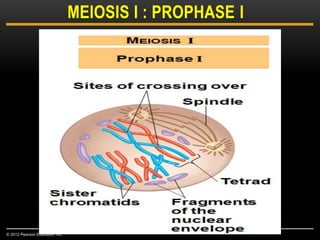
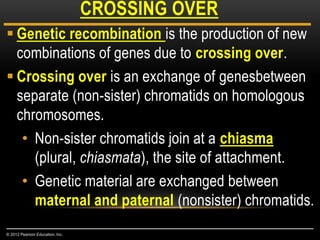
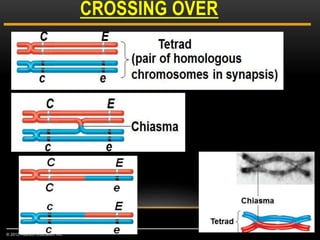
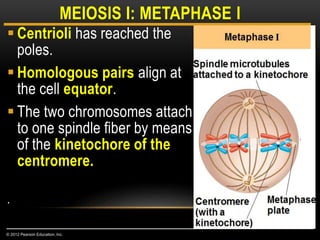
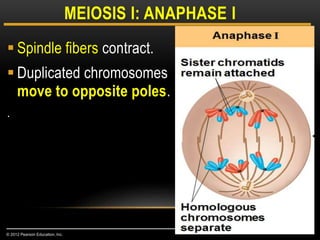
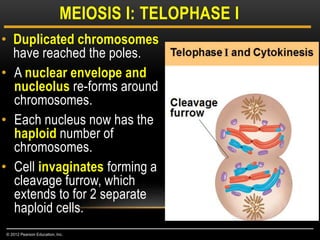
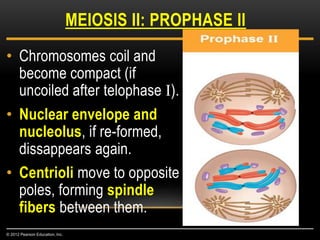
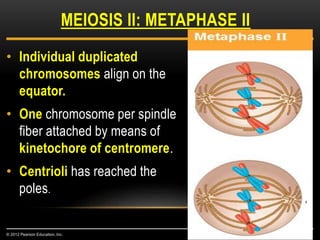
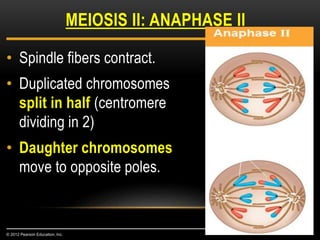
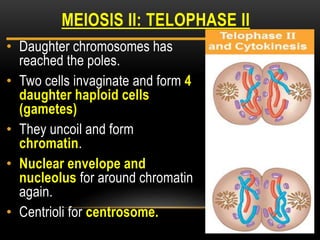
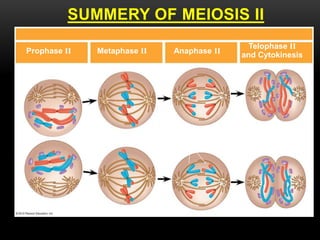
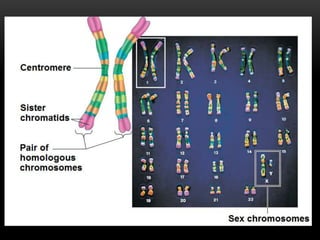
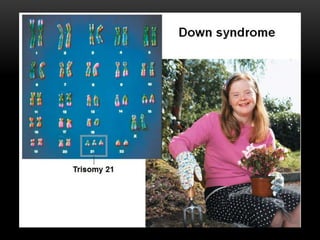
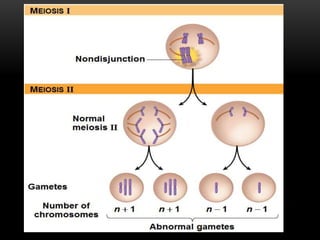
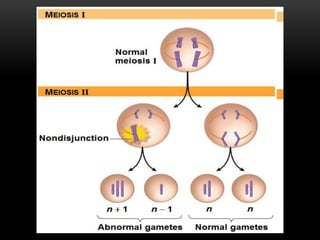
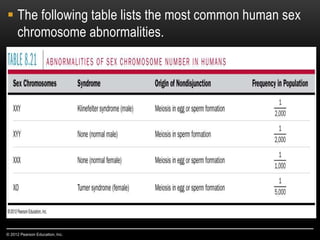
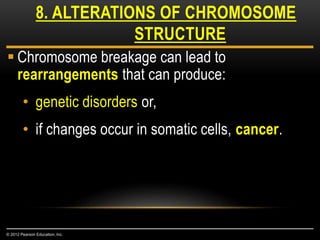
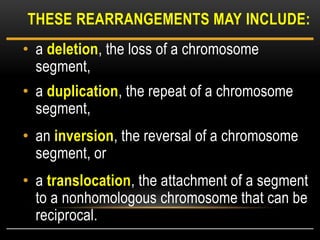
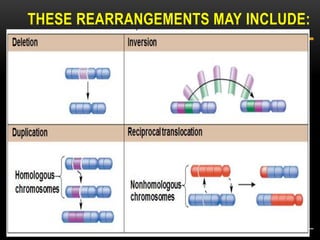
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces haploid gametes from diploid cells in two stages. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair and undergo crossing over before separating, resulting in haploid daughter cells. Meiosis II then follows without intervening DNA replication to generate four haploid gametes. This ensures each gamete has a single set of chromosomes and allows for genetic variation from independent assortment and recombination during meiosis I.