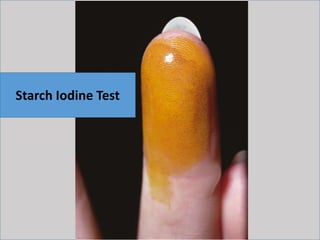
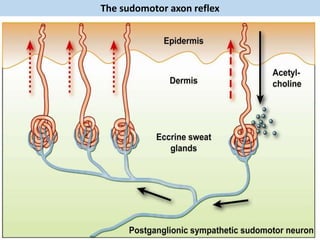
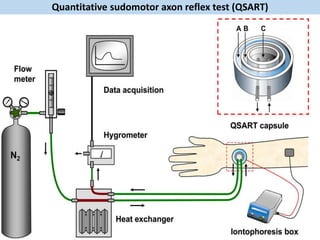
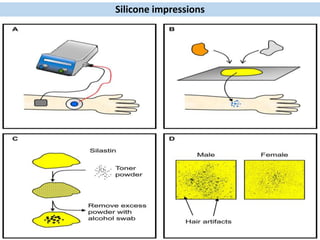
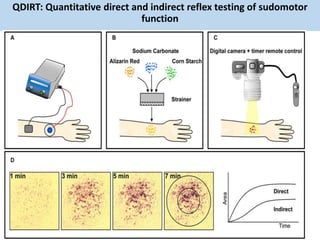
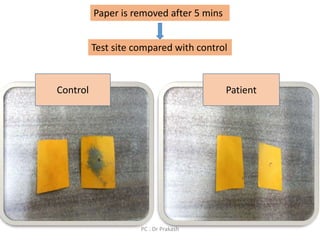
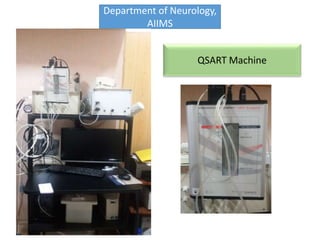
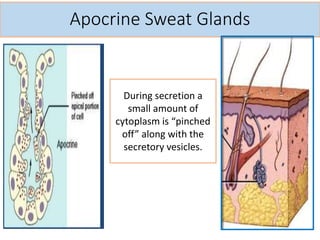
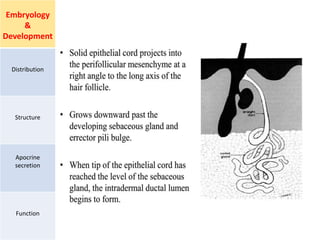
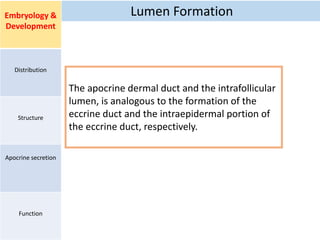
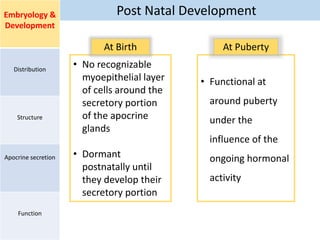
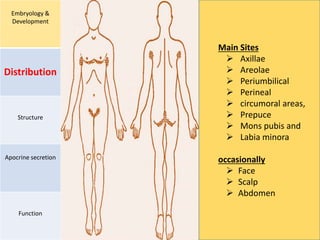
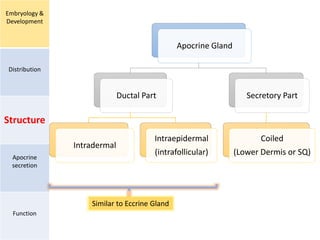
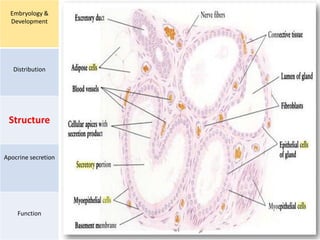
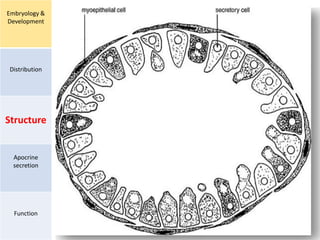
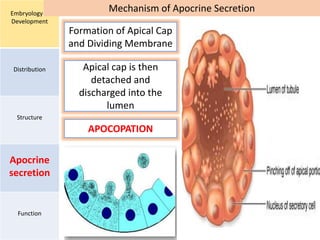
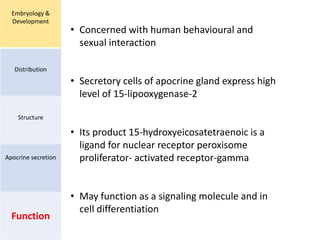
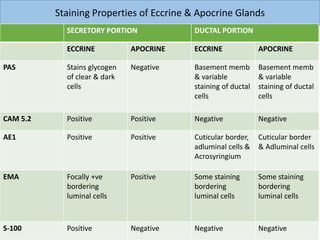
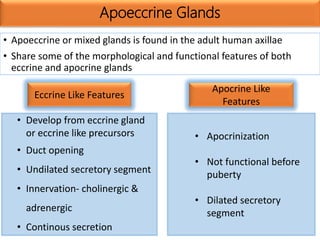
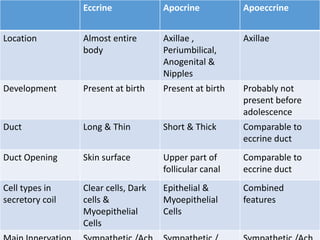
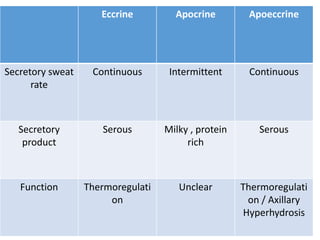
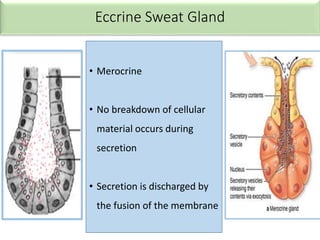
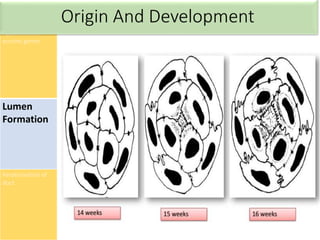
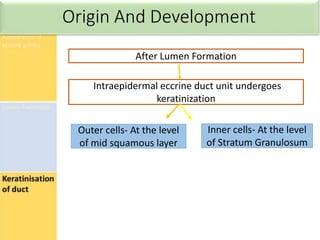
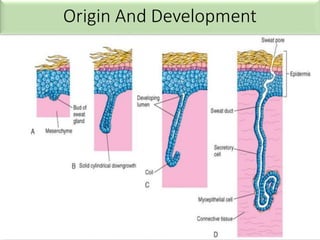
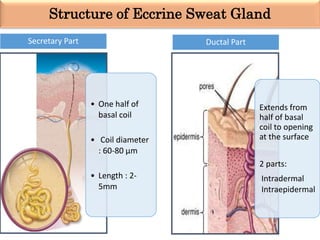
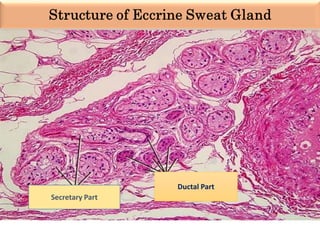
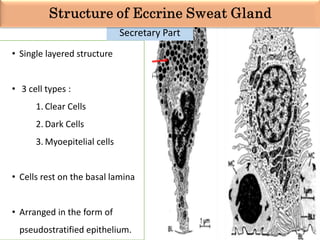
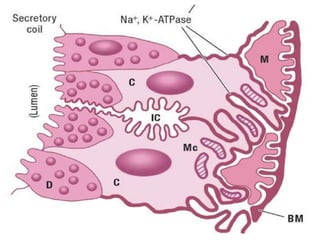
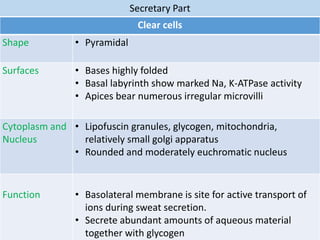
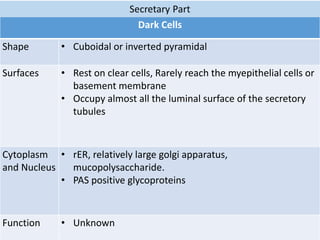
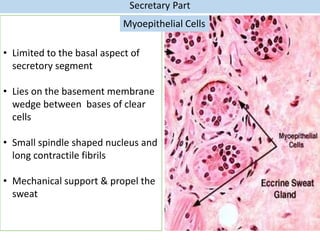
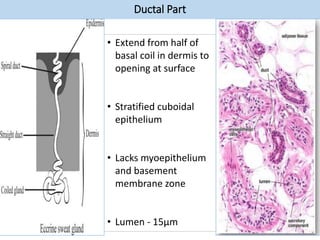
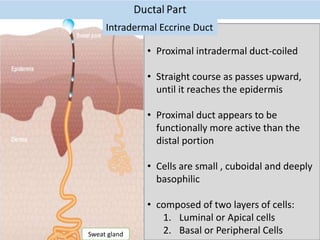
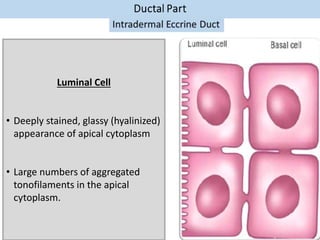
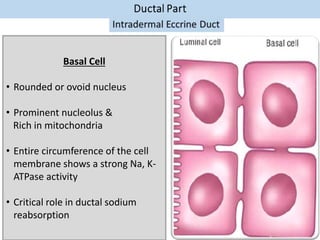
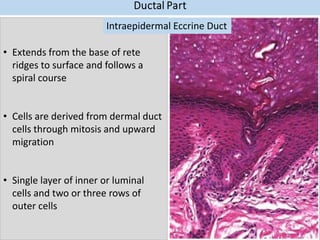
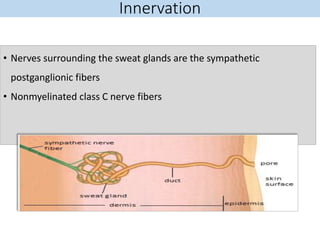
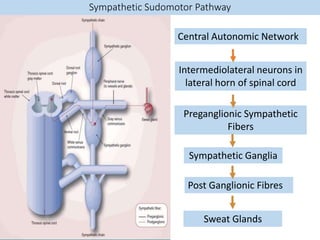
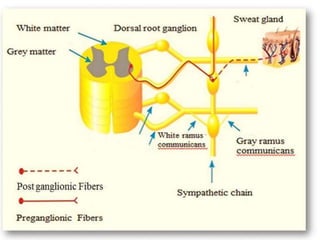
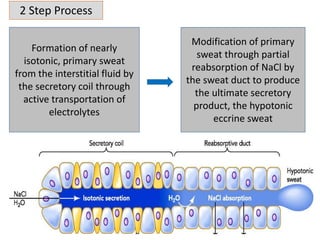
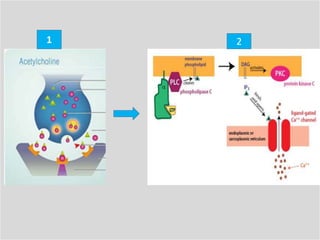
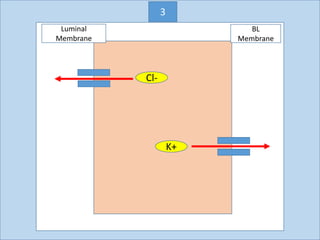
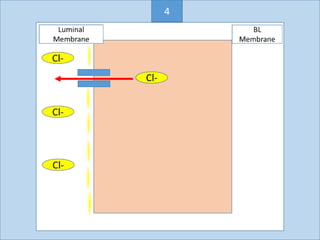
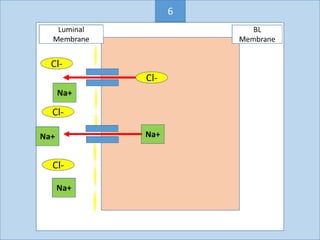
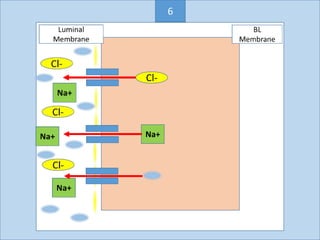
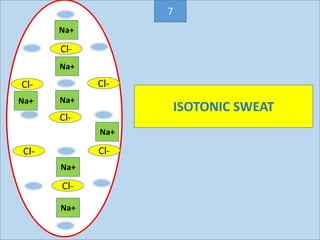
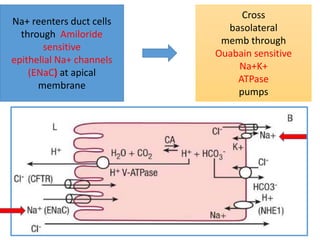
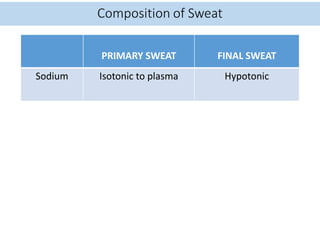
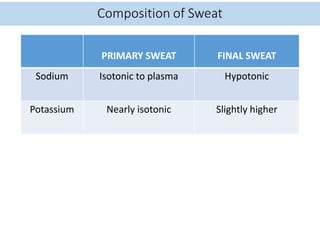
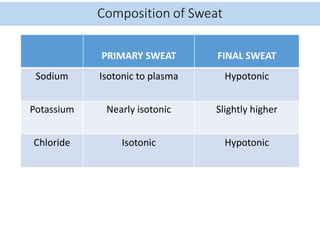
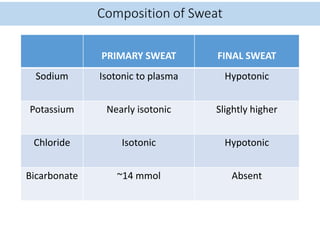
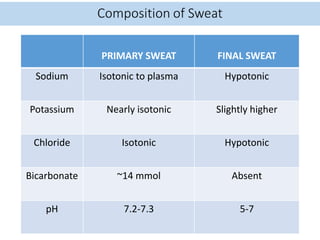
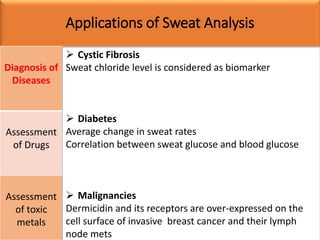
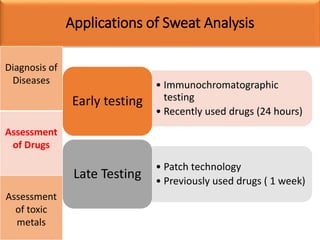
Eccrine sweat glands are the main sweat glands in humans. They produce a hypotonic sweat through active transport of ions from interstitial fluid into the secretory coil, and partial reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the ducts. Sweating is controlled by the sympathetic nervous system and helps regulate body temperature by evaporative cooling. The three main stimuli for sweating are thermal, emotional, and gustatory. Sweat contains water and low concentrations of ions similar to plasma but is hypotonic due to reabsorption in ducts.



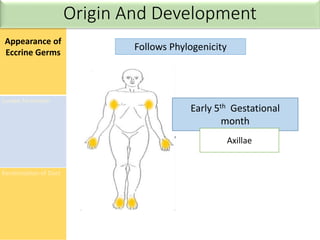
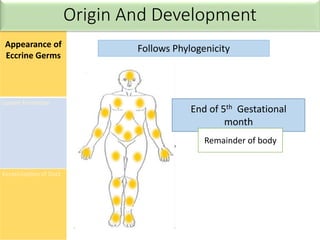








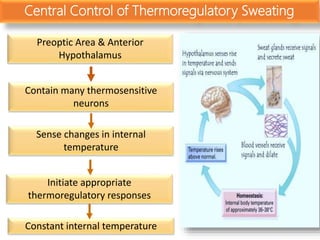
![• Maintenance of a constant body temperature is a
core element of our homeostasis
• Sweating is one of the many mechanism through which the body
dissipates heat
• Temperature setpoint [Tse]- sweating occurs at and above a
certain core temperature
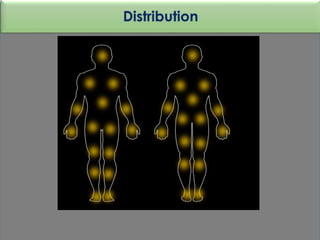
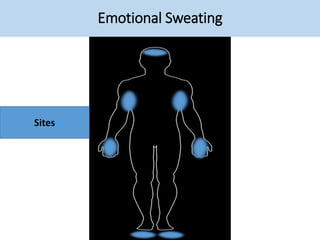
• Sweating induced by thermal stimuli mostly affects the upper
trunk and face but may involve the whole body
Thermoregulatory Sweating](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sweatgland-180102174533/85/Sweat-gland-anatomy-and-function-53-320.jpg)



![LACTATE
• @ low sweat rate- 30-40 m mol
• @ high sweat rate- 10 to 15 m mol
• Concentration higher than plasma (<2 mM) indicating that sweat lactate is derived
mainly from the sweat gland as an end product of glycolysis.
UREA
• Same as, or slightly higher than that of plasma
AMMONIA
• 0.5 to 8 mM.
• It is 20 to 50 times higher than the plasma ammonia concentration. [Diffusion
entrapment mechanism].
• Sweat ammonia levels are inversely proportional to the sweat rate and sweat pH.
PROTEINS
• 20 mg/dl,
• The majority are small molecular weight proteins less than 10 kDa.
• The concentration of high Mw proteins (>10kDa) increases with increase in sweat rate.
GLUCOSE
• 0.2-1.5mg/dl,
• Increase in uncontrolled diabetics, favors bacterial growth on skin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sweatgland-180102174533/85/Sweat-gland-anatomy-and-function-71-320.jpg)








![• Peripheral sweat rate was significantly (P less than 0.05) greater in
trained men [6.9 +/ 0.6 (SE) g.m2.min1] and women (6.1 +/ 0.7)
compared with sedentary men (3.1 +/ 0.5) and women (2.5 +/ 0.4)
• Physical training improves the secretory activity of the human
sweat gland](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sweatgland-180102174533/85/Sweat-gland-anatomy-and-function-82-320.jpg)