1. The document provides instructional objectives and content on physics concepts including work, kinetic energy, potential energy, and conservation and conversion of energy.
2. Key formulas are introduced such as work (W=F×d), kinetic energy (KE=1/2mv^2), and gravitational potential energy (GPE=mgh).
3. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating work, kinetic energy, potential energy, and how energy is conserved but can be converted between forms such as kinetic and potential energy for a falling object.






![8
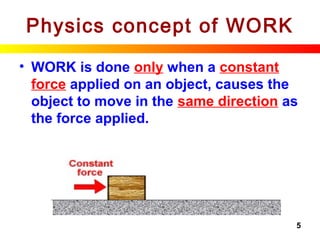
Physics concept of WORK
WORK can be calculated by:
Work done = Constant x Distance moved
force (N) in the direction
of force (m)
W = F x s
Units: [J] [N] [m]
SI Unit for Work is JOULE (J)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/energyandwork-140325063925-phpapp02/85/Energyandwork-8-320.jpg)






![15
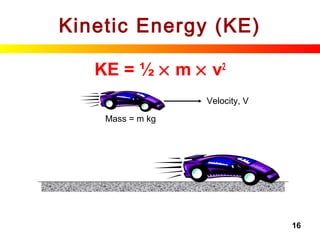
Kinetic Energy (KE)
• Formula:
• SI Unit: Joule [ J ] … same as Work Done
Kinetic Energy = x Mass x (Velocity)2
KE = x m x v2
Units: [ J ] [kg] [ms-1
]2
2
1
2
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/energyandwork-140325063925-phpapp02/85/Energyandwork-15-320.jpg)







![25
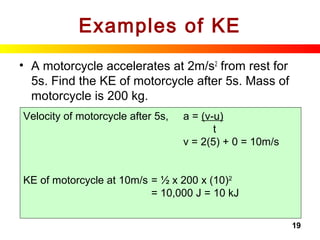
Gravitational PE
• Can be calculated with:
GPE = mass × gravitational × height above
acceleration ground level
= m × g × h
Units:
[J] [kg] [m/s2
] [m]
SI Units of GPE : Joule [J]
Ground,
0 GPE
Distance from
ground, h
Object on top of
building, of mass, mg
earth](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/energyandwork-140325063925-phpapp02/85/Energyandwork-25-320.jpg)