This document provides information about meat balls, including their ingredients, production process, packaging, storage, and quality control. Key points include:
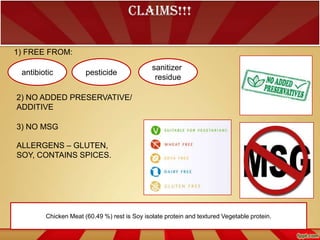
- Meat balls are made by emulsifying ground or minced meat with starches, eggs, breadcrumbs, and herbs. Common additives include salt, nitrites, phosphates, and MSG.
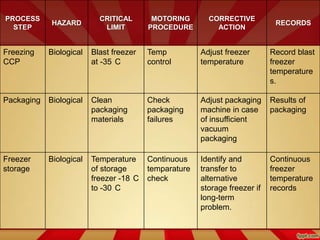
- Production involves grinding meat, mixing in ingredients, molding into balls, freezing, packaging, and storing at frozen temperatures.
- Quality is ensured through following GMP and implementing HACCP plans which identify hazards at each process step and establish critical limits and corrective actions.
- Packaging aims to control moisture and prevent spoilage through use of materials like PET