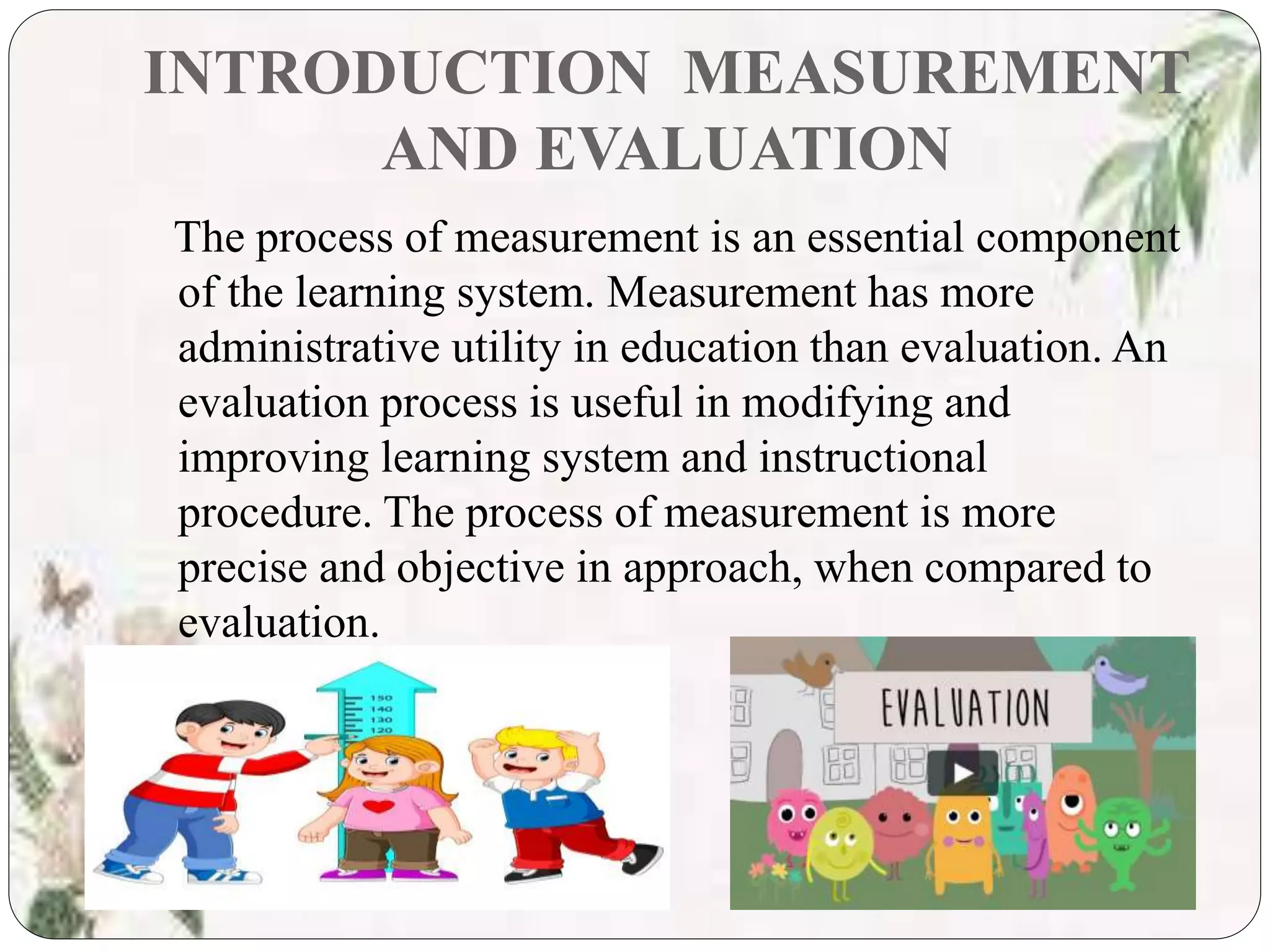
The document focuses on the concepts of measurement and evaluation in education, highlighting their definitions, characteristics, functions, and types. It emphasizes that measurement is more objective and precise, while evaluation is essential for improving learning processes. Key aspects include the importance of various evaluation techniques and the role of measurement in guiding educational practices.