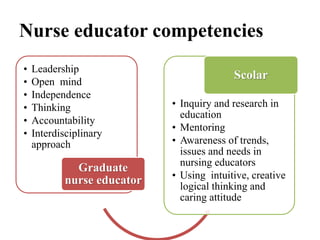
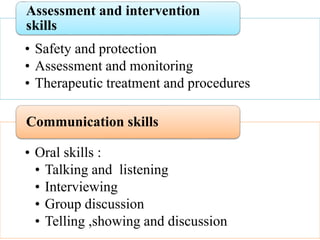
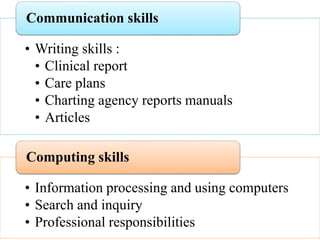
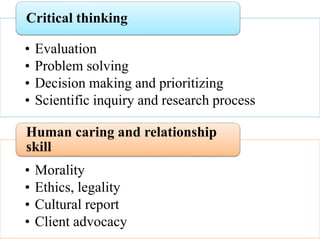
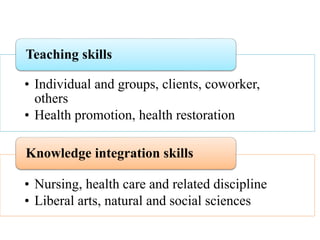
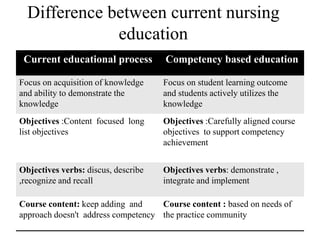
Competency based education focuses on outcomes and linking education to workforce needs. It is defined as an instructional system using performance based learning to meet standards of practice. The document discusses the meaning of competency, competence, and performance. It outlines the principles, purposes, needs, and levels of competencies in competency based education. Characteristics include acquiring skills through authentic assessments using adult learning principles. The document discusses developing competence in students through guided practice and in educators through reflective practice. Core competencies for nursing include basic skills, thinking skills, personal qualities, and fundamental competencies like communication. Nurse educator competencies encompass teacher, scholar and collaborator roles.