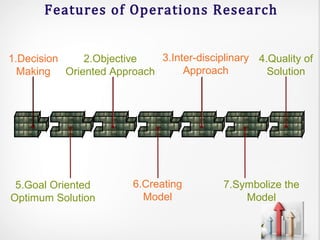
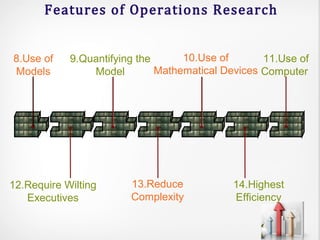
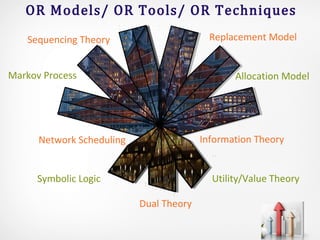
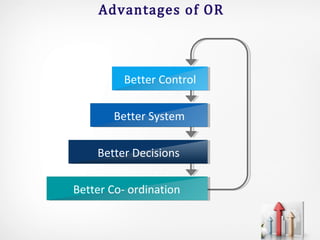
Operations research (OR) is an interdisciplinary field that uses advanced analytical methods to help make better decisions. It originated during World War II to help with military operations and has since expanded to business applications. OR takes a scientific approach to decision-making by building mathematical models, collecting data, and using techniques like linear programming, simulation, and queuing theory to optimize resources and minimize costs. While it provides improved decision-making, OR has limitations such as computational requirements, accounting for non-quantitative factors, and implementation challenges.