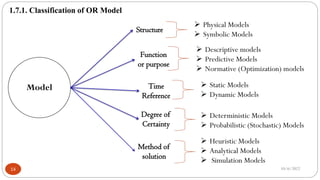
This chapter introduces operations research as a quantitative approach to decision making. It discusses the history of operations research emerging during World War II to help manage scarce resources. Operations research is defined as applying scientific methods to complex problems involving systems of people, machines, materials and money. The chapter outlines the nature, features, and significance of operations research in decision making. It also introduces modeling as used in operations research to analyze systems through representations that maintain essential elements.