The document contains information about the Operations Research course module for Punjab College of Technical Education, Ludhiana. It includes the syllabus, internal and external assessment details, instructions for paper setters and candidates, and important guidelines for students taking the course. The syllabus covers topics such as linear programming, transportation problems, decision making, integer programming, and dynamic programming. References for the course are also provided.
![PUNJAB COLLEGE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION,
LUDHIANA
COURSE MODULE
OPERATIONS RESEARCH
[ BC- 504(N2) ]
Max. Marks 100 Internal
Assessment - 40
External Assessment -
60
Instruction for paper setter
The question paper will consist of two sections A and B.
Sections B will have Six questions and will carry 10 marks
each. Section A will have 10 short answer type questions,
which will cover the entire syllabus uniformly and will carry
20 marks in all.
Instructions for Candidates
Candidates are required to attempt four questions from
section B and the entire section A.
Use of non-programmable scientific calculator is allowed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bc-504-kp-100821005734-phpapp01/75/BC-504-Operation-Research-1-2048.jpg)


![Important Guidelines
1. ATTENDANCE CRITERIA – 75% (NO COMPROMISES!!)
2. YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE IN CLASS ON/BEFORE SCHEDULED
TIME. AFTER THAT YOU CAN ATTEND THE CLASS BUT WOULD
NOT BE AWARDED ATTENDANCE. NO EXCUSES FOR BEING LATE
WILL BE ENTERTAINED.
3. MAKE SURE YOU ARE NOT ABSENT ON PRESENTATION DAY OR
ACTIVITY DAY OR TESTS. ZERO MARKS WOULD BE AWARDED TO
ABSENTEES. YOU’LL BE INFORMED WELL IN ADVANCE ABOUT
THE IMPORTANT DEADLINES.
4. DO NOT COPY ASSIGNMENTS. ALL THE COPIED ASSIGNMENTS
AND MASTER ASSIGNMENT WOULD BE STRAIGHT AWAY
CANCELLED & AWARDED ZERO MARKS.
Following are the parameters along with weight-age for the final calculation of
Internal.
Internal Evaluation Breakup
Marks Parameters
15 MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION [MSE]
5 PRESENTATION
10 TESTS [First Hourly, Second Hourly]
10 ASSIGNMENTS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bc-504-kp-100821005734-phpapp01/85/BC-504-Operation-Research-4-320.jpg)
![Course Breakup
Class: BCA-III-D Lectures: 47
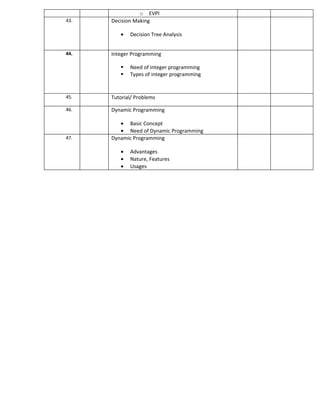
Subject: Operations Research No. of Tests: 3
Code: BC- 504(N2) Assignments: 3
Teacher: Kapil Prashar [KP]
Lecture Date Contents of Lecture
Tests Assignment
No.
1. Introduction to Operation Research:
Origin & Development of O. R.
Meaning & Definitions of O.R.
Nature and Characteristics of O. R.
2. Introduction to O.R.
Various Models of O. R.
Methodology of O.R.
3. Introduction to Operation Research:
O. R. And Decision making
Applications of O. R.
Uses and Limitations of O.R.
4. Assignment Problems
♦ Meaning of Assignment Problems
♦ Formulation of Assignment Matrix
• Hungarian Method
5. • Application of Hungarian Method. ASSG 1
6. • Maximization and Unbalanced case in
Assignment Problems
7. • Air crew Assignment Problems
8. Assignment Problem
• Travelling Salesman Problem
9. • Tutorial/ Problems
10. Introduction to Transportation Model
• Feasible solution
• Basic feasible solution
• Optimal solution
• Balanced & Unbalanced Transportation
Model](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bc-504-kp-100821005734-phpapp01/85/BC-504-Operation-Research-5-320.jpg)